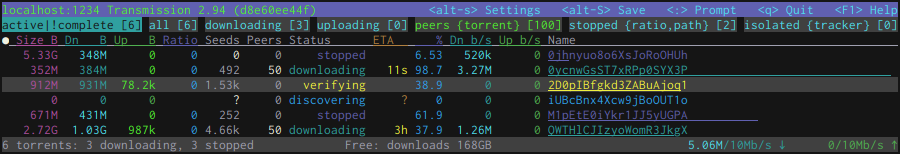
stig is a TUI (text user interface) and CLI (command line interface) client for the BitTorrent client Transmission.
stig is in maintenance mode. The code needs to be split it into multiple projects and the current client doesn’t really support more clients besides Transmission. Please don’t make any feature PRs. The more time I invest in reviewing and testing code that is going to be dead, the less time I have for future-proofing stig.
- Filters are used to select torrents for listing, starting/stopping, deleting, etc
- Tabs allow you to open and switch between multiple lists (torrents, peers, files, etc)
- Commands do almost everything, and they can be invoked
- through single- or multi-key (think emacs) keybindings,
- by entering them in a command prompt in the TUI (think vi) with tab completion,
- by providing them as CLI arguments when invoking stig (think git),
- or by listing them in an rc file which is automatically loaded.
- Color themes support 16 and 256 colors
- Complete built-in documentation with
helpcommand or--helpargument - Full API abstraction layer makes it possible to add support for other BitTorrent clients with RPC interfaces (contributors are welcome)
Add two torrents, one by file and one by hash, and exit
$ stig add /path/to/some.torrent d4d6b73851fe3288e40389a8e1fb98124a9b9ba5Connect to non-default host and present the TUI
$ stig set connect.host torrents.localPrint all uploading and/or downloading torrents on localhost:9092 and exit
$ stig set connect.port 9092 \; ls activeList torrents with more than 50 seeds, then remove them
$ stig ls 'seeds>50'
$ stig rm 'seeds>50'Stop down/uploading torrents with /foo/ in their download path and a ratio
above 10
$ stig stop 'path~/foo/&ratio>10'Open two tabs with different torrent lists:
- slowly uploading torrents with
/foo/in their download path - small or well-seeded torrents, sorted by size (ascending) and number of seeds (descending)
$ stig tab ls 'path~/foo/&rate-up<10k' \; tab ls 'size<500M|seeds>=1k' --sort 'size,!seeds'All configuration is done in an rc file, which is just a script containing a
list of commands (think vim and .vimrc) that are executed during startup.
The default rc file is $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/stig/rc. XDG_CONFIG_HOME
defaults to $HOME/.config if not set. Because a default rc file is empty,
it is not created automatically to avoid clutter.
See stig help cfgman for more information.
# Host that runs Transmission daemon set connect.host example.org set connect.port 123 # Update torrent/peer/file/etc lists every 10 seconds set tui.poll 10 # Default columns in torrent lists set columns.torrents name ratio rate-up rate-down # Open a few tabs on startup tab ls active --sort !%downloaded,path,!rate tab ls paused --sort !%downloaded --columns name,%downloaded,ratio,size tab ls isolated --sort tracker --columns name,path
Run different rc files either with stig -c path/to/file or with the rc
command. You can even turn them into executables with the shebang
#!/path/to/stig -Tc (-T disables the TUI, -c specifies the rc file).
#!/path/to/stig -Tc rm path=/path/to/torrents/trash pause seeds>100 start seeds<20&size>10G|seeds<50&size>20G
The latest release is always on PyPI.
Pipx installs applications in self-contained virtual environments in
$HOME/.local/pipx/ that include all dependencies. Executables are
sym-linked to $HOME/.local/bin/.
$ pipx install stig
$ pipx upgrade stig
$ pipx uninstall stigpip installs applications with their dependencies in the system-wide
(/usr/local) or user-wide ($HOME/.local) environment.
$ pip3 install stig # Installs in /usr/local/
$ pip3 install --user stig # Installs in $HOME/.local/To update, add the --upgrade or -U option.
The following extras are available to enable optional features:
setproctitle- Strip arguments from process title when running in tmux
session (this requires Python headers; e.g.
apt-get install libpython3-dev) proxy- Tunnel the connection to the Transmission daemon through a SOCKS5, SOCKS4 or HTTP proxy
To install stig with dependencies for an extra:
$ pipx install 'stig[setproctitle,proxy]' # For pipx version>=0.15.0.0
$ pipx install stig --spec 'stig[setproctitle,proxy]' # For pipx version<0.15.0.0To install the latest development version of stig with pipx:
$ pipx install 'git+https://github.com/rndusr/stig.git#egg=stig' # For pipx version>=0.15.0.0
$ pipx install stig --spec 'git+https://github.com/rndusr/stig.git#egg=stig' # For pipx version<0.15.0.0To make your code changes effective immediately, you can either run
python3 -m stig <ARGUMENTS> in the project directory or use pip3’s
--editable option.
To run the tests with the Python version that is installed on your system,
simply run make test in the project directory. This creates a virtual
environment in ./venv, installs stig and its dependencies in there and
runs all tests.
If you want to only run tests for a specific module or package:
- Create a virtual environment with all dependencies:
make venv - Activate the virtual environment:
source venv/bin/activate - Pass any path in the
testsdirectory to pytest:pytest tests/settings_test
- Install and set up pyenv.
- With pyenv, install the supported Python versions listed in
.setup.py. - In stig’s project directory, create a virtual environment with all
dependencies:
make venv - Activate the virtual environment:
source venv/bin/activate - Run the tests for each supported Python version:
tox - Pass arguments to pytest:
tox -- --exitfirst tests/settings_test
- Python >=3.6
- urwid >=1.3.0
- urwidtrees >=1.0.3dev0
- aiohttp
- async_timeout
- pyxdg
- blinker
- natsort
- setproctitle (optional; prettifies the process name)
- asynctest (only needed to run tests)
Pull requests, bug reports, features requests, ideas for improvement and all other constructive contributions are welcome.
If you want to contribute code and get stuck, don’t know where to even begin, or just to make sure you’re not duplicating someone else’s efforts, open an issue.
Please submit your custom themes if you would like them to be included in stig.
stig is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.