A machine type specifies a particular collection of virtualized hardware resources available to a virtual machine (VM) instance, including the memory size, virtual CPU count, and maximum persistent disk capability.
Machine types are classified into two categories:
- Predefined machine types: Machines that are managed by Google Compute Engine and have a fixed collection of resources.
- Custom machine types: Machines with custom virtualized hardware settings. You can create an instance with a custom number of vCPUs and amount of memory.
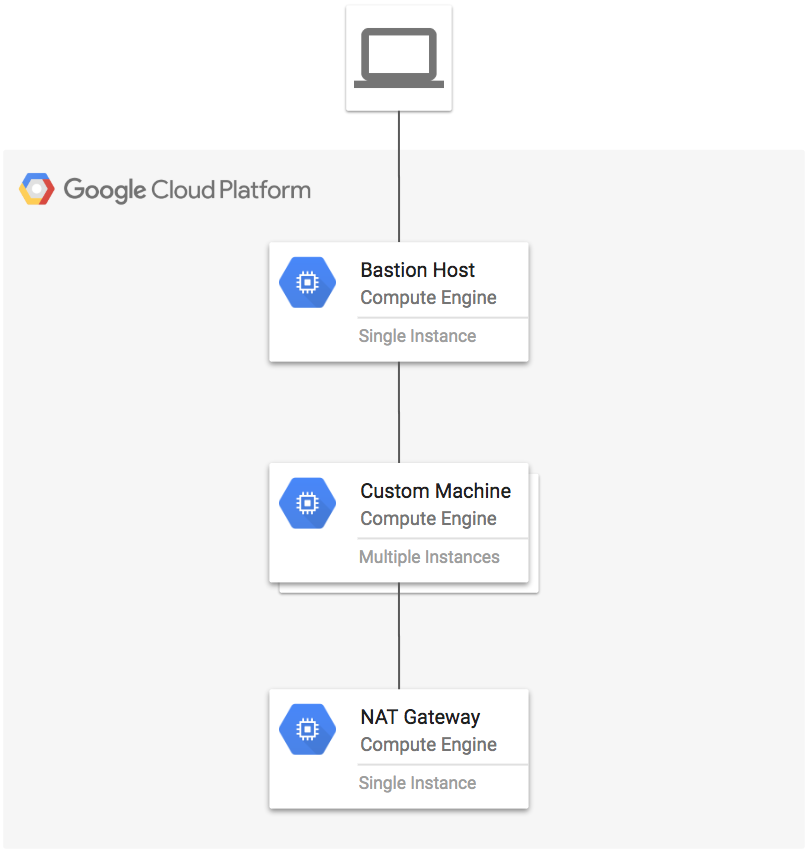
We are going to create an instance with a custom machine type (6 vCPU i.e. 6 cores and 64 GB memory with attached GPU), a bastion host, and a NAT gateway using Terraform.
Google Compute Engine provides graphics processing units (GPUs) that you can add to your virtual machine instances. You can use these GPUs to accelerate specific workloads on your instances such as machine learning and data processing. In this lab you are going to attach a GPU to the instance with a custom machine type.
The ''terraform init'' command is used to initialize a working directory containing Terraform configuration files. This is the first command that should be run after writing a new Terraform configuration or cloning an existing one from version control. It is safe to run this command multiple times.
The ''terraform plan'' command is used to create an execution plan. This command is a convenient way to check whether the execution plan for a set of changes matches your expectations without making any changes to real resources or to the state. For example, ''terraform plan'' might be run before committing a change to version control, to create confidence that it will behave as expected.
The ''terraform apply'' command is used to apply the changes required to reach the desired state of the configuration. By default it scans the current directory for the configuration and applies the changes accordingly.