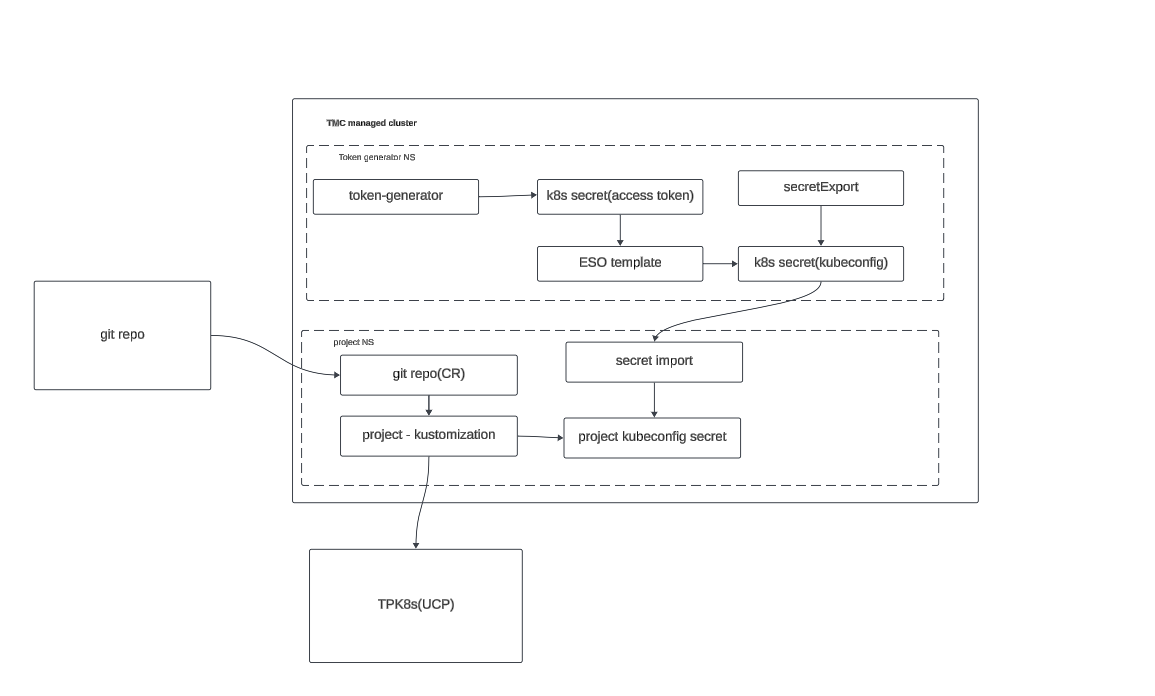
Flux has the ability to specify a kubeconfig in a kustomization. The Tanzu platform kubeconfigs use the exec function to get a token since this token expires often the command it runs will generate a new one when needed. To use this with flux two things are needed to be done.
- enable the flux kustomize controller argument that allow
execto be run.--insecure-kubeconfig-exec. - build a custom image for flux that has the cli tools you need to execute.
There is a security risk with enabling the exec functionality in flux. This also requires that you have full control over the flux install.
If you have a managed provider that installs your flux controllers like Tanzu platform then you won't want to deal with hacking the above to work. This solutions uses the OOTB flux controllers and some extra tools to handle connecting to the tanzu platform. It also does not require the --insecure-kubeconfig-exec flag. There are multiple ways this could be implemented , this was was chosen in order to reduce custom work and re-use as much existing tooling as possible.
The token-generator deployment will handle creating a access token from the CSP token as well as continously renewing it before expiration. This token is placed into a secret and the ESO templating capability is used to then create a valid kubeconfig for the project in UCP. Then a secret export is used to make this available to other namespaces. a standard flux kustomization is created that then uses the imported kubeconfig secret to target the UCP api.
This example is not meant to show how to do gitops with flux. This is setup in a very minimal so it can be easily understood.
Pre-reqs:
- TMC
- TMC managed flux
- external-secrets
This could easily be done by flux but for simplicity we are just deploying this via the command line.
- create the secret needed for the controller. this should be your CSP token.
cat <<'EOF' >deploy/token-generator-deploy/generator.env
CSP_TOKEN=<your-token>
EOF- deploy the controller into the cluster you plan to use for gitops with flux. Ideally this is a cluster managed by TMC with flux enabled.
kubectl apply -k deploy/token-generator-deploy We will be using external secrets operator to handle the kubeconfig creation and also secretgen controller to handle the distribution of the kubeconfigs to the correct namespaces. This could also easily be managed via flux but for simplicity we are just using the command line. Thsi example just sets up the project context but this could be done for space or cluster group the same way.
- get the server url from the current context on the cli. this is used for our in cluster kubecofnig secret
#get the context url from your local cli
tanzu project use AMER-West
export KUBECONFIG=~/.config/tanzu/kube/config
kubectl config view --minify -o json | jq -r '.clusters[0].cluster.server'-
Update the
deploy/secret-templates/project-context.ymlto use your server url. -
create the secret store, secret export, and templated secret.
kubectl apply -f deploy/secret-templatesSince the purpose of this is to deploy objects to UCP using gitops for this one we will be using flux for the deployment.
- create the flux kustomization and git repo to point to the sample repo and directory. This also imports the secret
k apply -f deploy/flux-resourcesat this point you should see a kustomization that is successfull and a new space created in your project.
this isn't necessary unless you are doing dev.
tanzu build config --containerapp-registry ghcr.io/{contact.team}/{name}
cd token-generator
tanzu build -r container-image