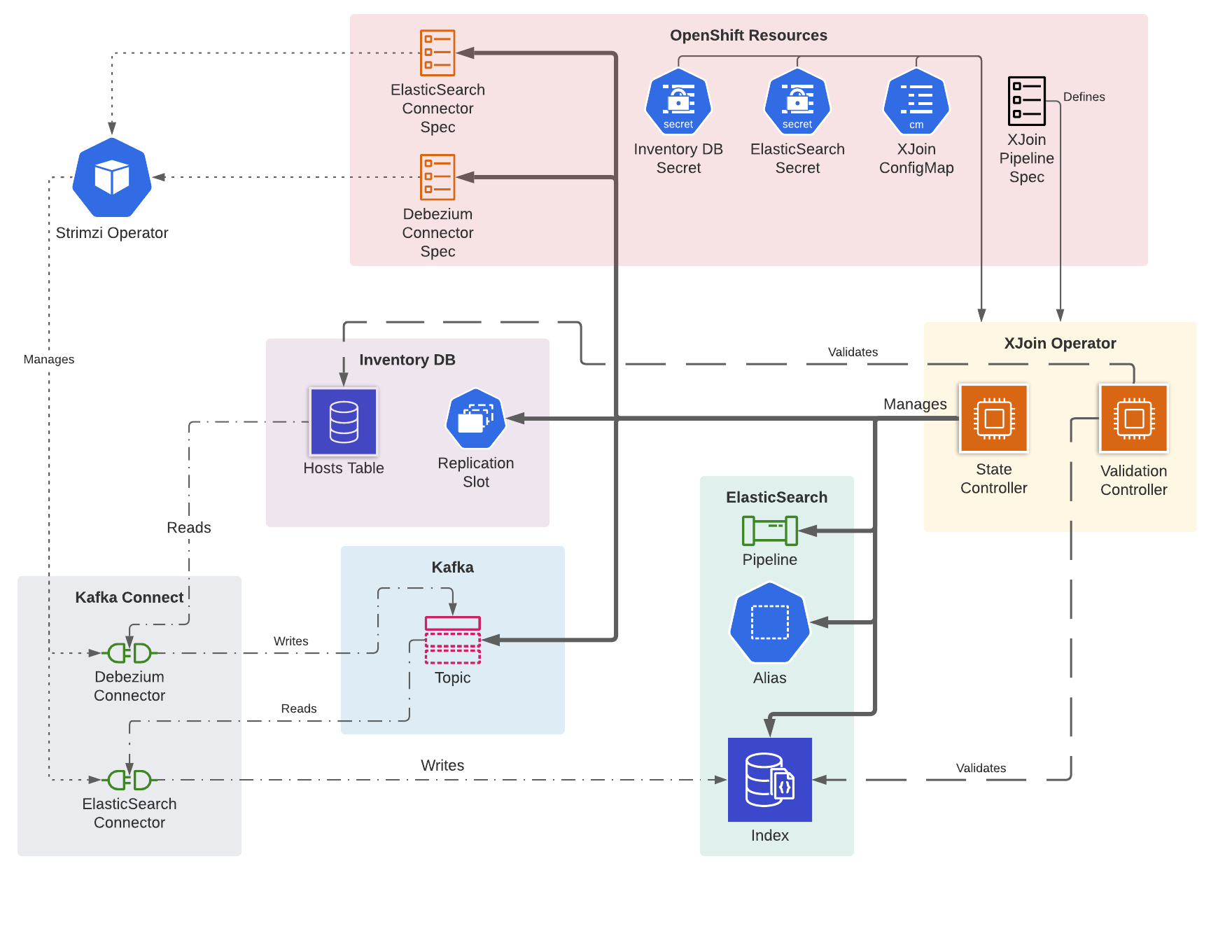
Openshift operator that manages the XJoin pipeline. It currently manages the M2 version of XJoin, i.e. it maintains the replication pipeline between HBI and ElasticSearch. Modifications will be necessary to support M3 (joining data between applications).
A XJoin pipeline is defined by the XJoinPipeline custom resource. It indexes the hosts table of the HBI database into an ElasticSearch index. A Debezium Kafka Connector is used to read from the HBI database's replication slot. An ElasticSearch connector is used to index the hosts. Kafka Connect transformations are performed on the ElasticSearch connector to prepare the host records to be indexed. An ElasticSearch pipeline is used to transform the JSON fields on a host prior to being indexed.
The operator is responsible for:
- management of an ElasticSearch index, alias, and pipeline
- management of Debezium (source) and ElasticSearch (sink) connectors in a Kafka Connect cluster (using Strimzi)
- management of a Kafka Topic in a Kafka cluster (using Strimzi)
- management of the HBI replication slot. The Debezium connector should manage this. The operator ensures there are no orphaned replication slots.
- periodic validation of the indexed data
- automated recovery (e.g. when the data becomes out-of sync)
The operator defines two controllers that reconcile a XJoinPipeline
- PipelineController which manages all the resources (connectors, elasticsearch resources, topic, replication slots) and handles recovery
- ValidationController which periodically compares the data in the ElasticSearch index with what is stored in HBI to determine whether the pipeline is valid
-
Set up a local Kubernetes environment. Known to work with the following:
-
Configure Kubernetes to use at least 16G of memory and 6 cpus. This is known to work although you can try with less.
./crc config set memory 16384 ./crc config set cpus 6minikube config set cpus 6 minikube config set memory 16384 -
Start Kubernetes
./crc startminikube start -
If using CRC
- When prompted for a pull secret paste it (you obtained pull secret on step 1 when downloading CRC)
- Log in to the cluster as kubeadmin (oc login -u kubeadmin -p ...) You'll find the exact command to use in the CRC startup log
-
Login to https://quay.io and https://registry.redhat.io
docker login -u=<quay-username> -p="password" quay.iodocker login https://registry.redhat.io
-
Append the following line into
/etc/hosts127.0.0.1 inventory-db xjoin-elasticsearch-es-default.test.svc connect-connect-api.test.svc xjoin-elasticsearch-es-http -
./dev/setup-clowder.sh
The Openshift environment can be deleted with this script:
dev/teardown.sh
Afterwards, the environment can be setup again without restarting Kubernetes via dev/setup.sh.
With the cluster set up it is now possible to install manifests and run the operator locally.
-
Install CRDs
make install -
Run the operator
make run ENABLE_WEBHOOKS=false -
Finally, create a new pipeline
kubectl apply -f ../config/samples/xjoin_v1alpha1_xjoinpipeline.yaml
There is also make delve to debug the operator. After starting the Delve server process, connect to it with a Delve debugger.
This is useful when testing deployment related changes. It's a little cumbersome for everyday development because an image needs to be built by app-interface and pushed to the cluster for each change.
- To deploy the operator via locally OLM run
./dev/install.operator.locally.sh- To uninstall the OLM deployed operator run
./dev/uninstall.operator.locally.shThis is more convenient than using the app-interface build because the build is done locally then pushed to quay.io. More info
docker login -u=$QUAY_USERNAME -p $QUAY_PASSWORD
./dev/install.operator.with.operator.sdk.sh./dev/uninstall.operator.with.operator.sdk.sh to uninstall.
- The tests require an initialized Kubernetes environment. See Setting up the development environment.
- They can be executed via
make test. - There is also
make delve-testto run the tests in debug mode. Thendelvecan be used to connect to the test run. - The tests take a while to run. To whitelist one or a few tests, prepend
Itwith an F. e.g. changeIt("Creates a connector...toFIt("Creates a connector...) { - Sometimes when the test execution fails unexpectedly it will leave orphaned projects in kubernetes. Use
dev/cleanup.projects.shto remove them.