Python library for building and rendering latex tables in an easy way.
pip install etabsCode:
from etabs import RuleType, TexTable
# Example values
values = [
[60, 20, 20],
[50, 40, 10],
[30, 10, 60],
[5, 90, 5],
]
row_labels = ["A", "B", "C", "D"]
col_labels = ["C1", "C2", "C3"]
# TexTabel is the main structure for creating tables
table = TexTable(centered=True, caption="Example table")
# Add rows
table.add_row(None, *col_labels) # First value empty, rest are column labels
for label, row in zip(row_labels, values):
table.add_row(label, *row)
# You can optionally add rules at specific rows
table.add_rule(0, RuleType.TOP)
table.add_rule(1) # By default, the rule is a midrule
# If no row is specified, it will be added at the end
table.add_rule(rule_type=RuleType.BOTTOM)
# Finally to get the latex code use the render method
print(table.render())Output:
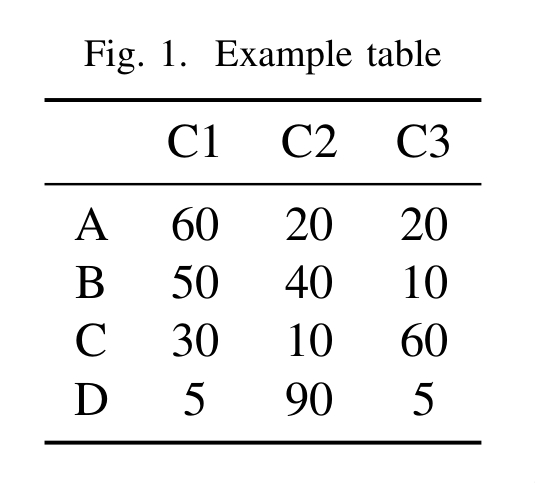
\begin{figure}[h!]
\centering
\caption{Example table}
\vspace{0.5em}
\begin{tabular}{cccc}
\toprule
& C1 & C2 & C3 \\
\midrule
A & 60 & 20 & 20 \\
B & 50 & 40 & 10 \\
C & 30 & 10 & 60 \\
D & 5 & 90 & 5 \\
\bottomrule
\end{tabular}
\end{figure}Result:
from etabs import RuleType, TexTable
# Example values
values = [
[60, 20, 20],
[50, 40, 10],
[30, 10, 60],
[5, 90, 5],
]
col_labels = ["C1", "C2", "C3"]
table = TexTable(centered=True, caption="Example table")
# Add values
table.add_row(*col_labels, start=2) # Colum 0 and 1 are empty
for row in values:
# Preprocess each value to show as percentage
table.add_row(*row, prep=lambda x: f"{x} \\%", start=2)
# Add a vertical separator before column 2
table.seps[2] = "|"
# Assign values directly
table[1, 1] = table[3, 1] = "A1"
table[2, 1] = table[4, 1] = "B2"
# Merge cells using slices
table[0, 0:2] = "Types"
table[1:3, 0] = "Typa A"
table[3:, 0] = "Typa B"
# Add some style using slices too
table[0, :].set_bold(True)
table[:, 0:2].set_bold(True)
table[1:, 0:2].set_italic(True)
# Add rules
table.add_rule(0, RuleType.TOP)
table.add_rule(1)
table.add_rule(rule_type=RuleType.BOTTOM)
print(table.render())Output:
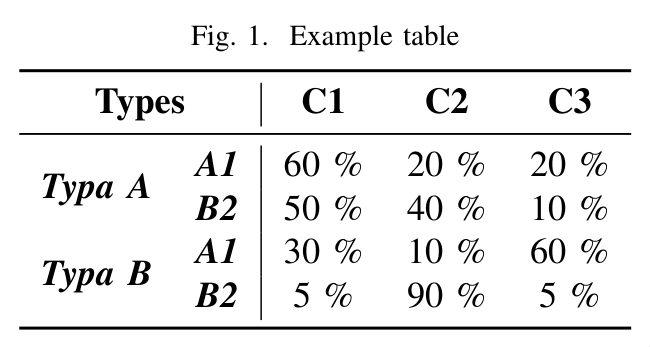
\begin{figure}[h!]
\centering
\caption{Example table}
\vspace{0.5em}
\begin{tabular}{cc|ccc}
\toprule
\multicolumn{2}{c|}{\textbf{Types}} & \textbf{C1} & \textbf{C2} & \textbf{C3} \\
\midrule
\multirow{2}{*}{\textit{\textbf{Typa A}}} & \textit{\textbf{A1}} & 60 \% & 20 \% & 20 \% \\
& \textit{\textbf{B2}} & 50 \% & 40 \% & 10 \% \\
\multirow{2}{*}{\textit{\textbf{Typa B}}} & \textit{\textbf{A1}} & 30 \% & 10 \% & 60 \% \\
& \textit{\textbf{B2}} & 5 \% & 90 \% & 5 \% \\
\bottomrule
\end{tabular}
\end{figure}Result:
According the commands you use, some packages may need to be added to the document for the correct rendering of the table.
To see the dependencies for a given table you can use de render_deps method:
# following the example from the last section
print(table.render_deps())Output:
\usepackage{multirow}
\usepackage{booktabs}