yum/dnf install http://people.redhat.com/rsawhill/rpms/latest-rsawaroha-release.rpm
yum/dnf install Rebooty-inspector
Usage: Rebooty-inspector [-l|-a|-e #] [-q|-v|-n #] [-o OS] [-f LOG] [-gx] [ROOTDIR]
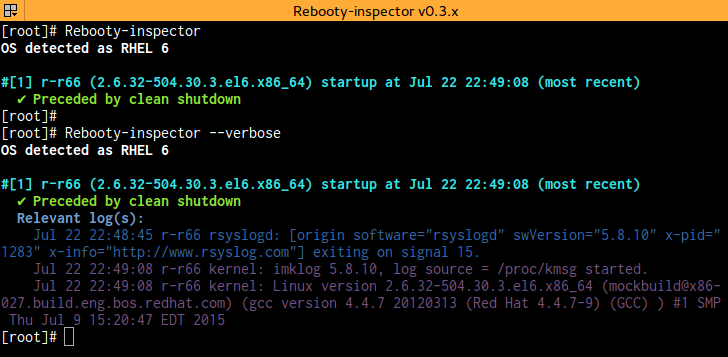
Inspect recent startup events to see if they were preceded by clean shutdowns
By default, only most recent boot is inspected and explanation is printed
If it followed a graceful shutdown, exit with success; else exit w/ code 9
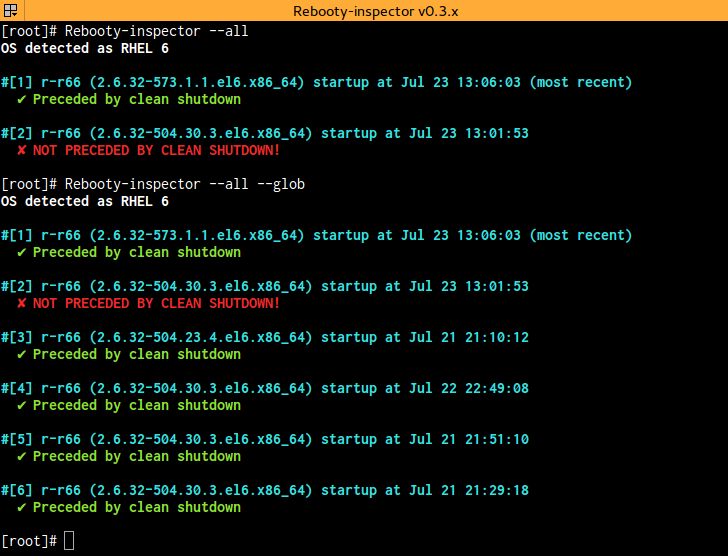
This behavior can be changed by using the --all or --event= options
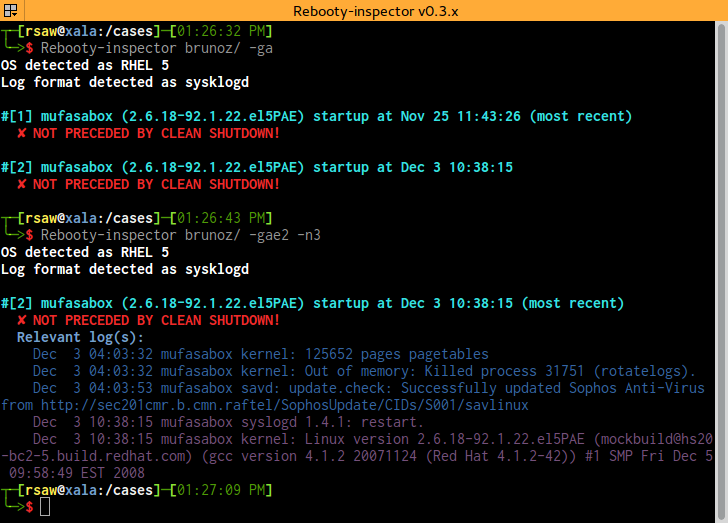
If a directory is passed as ROOTDIR, then that will be used instead of '/'
This is useful to parse sosreports
OPTIONS
-l, --logit Log result via logger cmd
See NOTES below on this option
-a, --all Expand search to all startup events
Disables exit on first match; can't be used with --logit
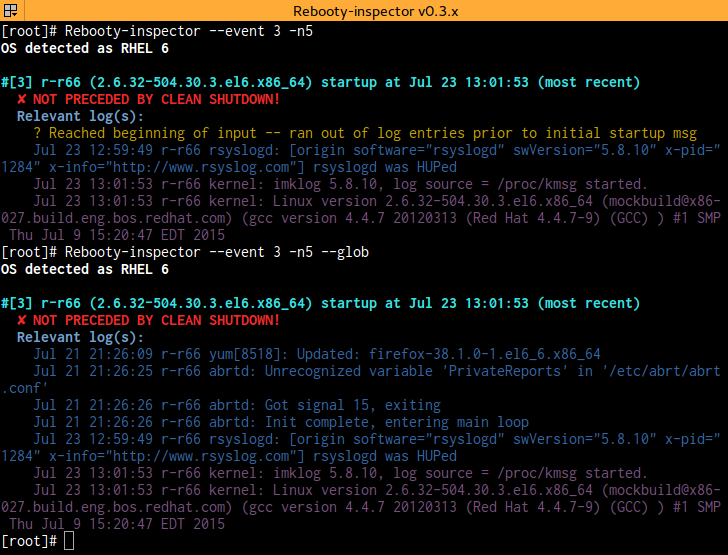
-e, --event=# Inspect specific event number (as reported by --all)
Implies --all --lines=40
-q, --quiet Don't print any messages to stdout (useful with --logit)
-v, --verbose Include relevant log entries in output
-n, --lines=# Print # number of lines prior to startup event; implies -v
-o, --os=OS Specify OS to determine what to search for in log
Default: auto-detects based on /etc/redhat-release
Does NOT auto-detect by reading LOG file
Choices: 5, 5-rsyslog3, 5-rsyslog5, 6, and 7
(All referring to RHEL)
-f, --file=LOG Specify non-default log file, e.g., one from another system
Default: '/var/log/messages'
-g, --glob Add '*' character to LOG, i.e., multiple logs will be parsed
Useful if system uptime is so great that main log has no
record of last startup (or if you want to see all events)
-x, --nocolor Disable terminal color-escapes
NOTES
This tool expects standard syslog/rsyslog log file formats.
It cannot handle customized rsyslog templates or use of non-standard loggers
like syslog-ng. Consolidated logs [from multiple hosts] could cause trouble.
Many things that aren't configurable with options can be tweaked with
environment variables (including log messages sent with --logit).
Reference variables names declared at the start of the script.
Version info: Rebooty-inspector v0.3.0 last mod 2015/07/23
Contact rsaw@redhat.com or <github.com/ryran/Rebooty-inspector>