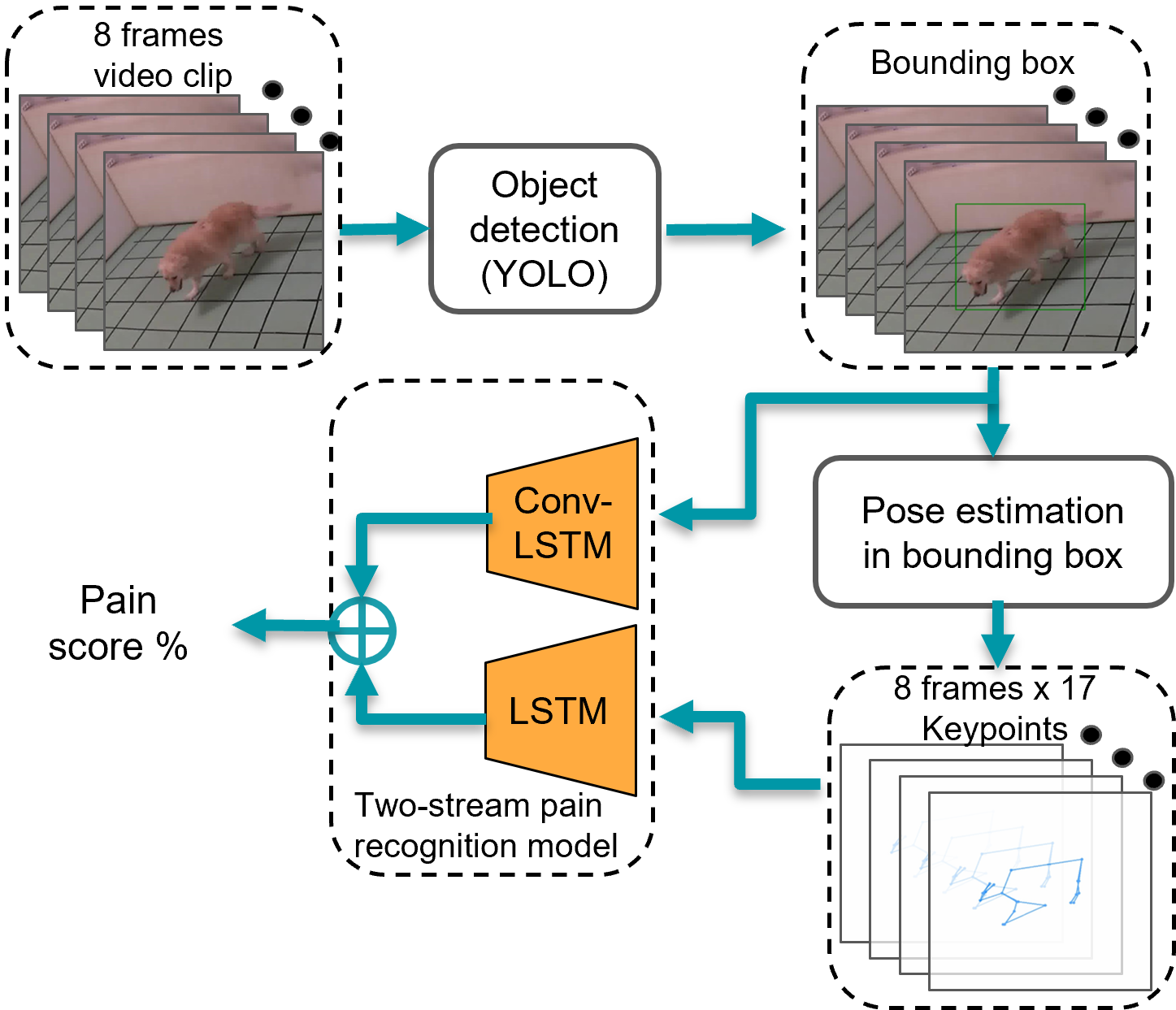
This is a video-based dog's pain behavior recognition algorithm .We implement a hierarchical method that can localize the position of the dog within the image frames, extract the pose information, treat missing data problems and normalize the keypoint coordinates. A two-stream ConvLSTM and LSTM model is applied to detect dogs' pain action from the RGB video frames and corresponding keypoints sequence. This repository includes implementations of the following methods:
- Two-stream (RGB+keypoints) model for dog pain behavior recognition
- Auxiliary learning to boost model's generalization ability
- Three fusion methods: late fusion, concatenation, bilinear fusion.
Video frames --> croped images (bbox_keypoints.py)
- We extract video frames from our own OFT dog pain video dataset. Applying pretrained YOLOv5 algorithm to get bounding box of dogs, and crop the image frame according to the bbox, make sure the dogs' body take a majority of area in the image. All the images are re-scaled to (112X112X3).
Croped images --> body keypoints (kp_process.py)
- We apply pretrained HRNet algorithm to extract 17 keypoints within the bbox.
- Applying our own missing data treatment algorihtm to filter and complement the keypoints graph.
- ConvLSTM is used to extract spatial information from the RGB video frame. Input data of the ConvLSTM is a video clip consist of a stack of RGN frames. The input shape is (N, 112, 112,3), N is length of video clip
- LSTM with attention mechenism is applied to process the keypoints graph. Input data of the LSTM is a stack of keypoints 2-D coordinates. The input shape is (N, 2X17), N is length of video clip, is the number of keypoints.
All code details can be found in ./tool/train.py. See all the configs file in ./configs
-
Videos frames are sampled in 2FPS. We select the video clips with two frames overlapping. The model would ouptut the confident score of a video clip contain the dog in pain state. Both stream apply the same data augmentation technique such as horizontal flipping, random rotation and shift.
-
Auxiliary learning would train a extra classifier head alongside the primary task (confidence score of pain) to classify the video clip into contains the dog has "orthopedic pain," "neurological pain", or "not in pain" state.
python test.py --cfg configs/two_stream.yaml \
KEYPOINT_FILE path to_your_keypoint_file \
TRAIN_TEST_SPLIT path_to_your_label_file \
CROP_IMAGE path_to_your_image_file \
CHECKPOINTS_FOLD filename_of_checkpoint_file\
ENABLE_TRAIN True
All code details can be found in ./tool/test.py.
video clips are sampled without overlapping. Enable output model prediction result by setting SAVE_PREDS = True.
python test.py --cfg configs/two_stream.yaml \
KEYPOINT_FILE path to_your_keypoint_file \
TRAIN_TEST_SPLIT path_to_your_label_file \
CROP_IMAGE path_to_your_image_file \
TEST_INITIAL_WEIGHT path_to_your_checkpoint_file\
CHECKPOINTS_FOLD filename_of_checkpoint_folder\
ENABLE_TEST True
- Clone this repository
https://github.com/s04240051/pain_detection.git
- Install PyTorch>=1.6 and torchvision>=0.7 from the PyTorch official website
pip install -r requirements.txt