en_cl_fix is a multi-language fixed-point math library for FPGA and ASIC development.
It provides fixed-point functionality in both HDL (currently VHDL) and software languages (currently Python and MATLAB). This allows fixed-point algorithms to be designed, modelled and evaluated in software, before committing to the HDL implementation. Similarly, HDL implementations can be easily verified in simulation and/or hardware by comparing the simulation/hardware output with the bit-true software model's output.
This library provides only low-level fixed-point functionality such as basic arithmetic (addition, multiplication, etc) and number format conversions (with rounding and saturation).
This library supports arbitrary precision, but software executes faster for bit-widths ≤ 53 bits.
This library is free and open-source.
It is published under the PSI HDL Library License, which is LGPL plus some additional exceptions to clarify the LGPL terms in the context of firmware development.
This library is maintained by Enclustra GmbH.
See Changelog.
- Python
- numpy
- vunit-hdl
It is recommended to watch Enclustra's Fixed-Point Python Co-simulation webinar before working with en_cl_fix. It covers important background information on fixed-point number representation.
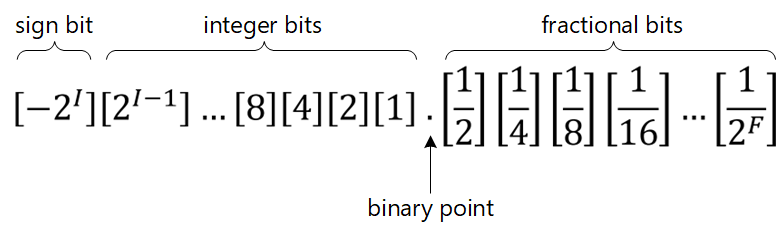
The fixed point number format used in this library is defined as follows:
[S, I, F]
where:
S= Number of sign bits (0 or 1).I= Number of integer bits.F= Number of fractional bits.
Therefore, the total bit-width is simply S+I+F.
The contributions of the integer bits and fractional bits in a fixed-point binary number depend on their position relative to the binary point (I bits left, F bits right). This is the same concept as for an ordinary decimal number (with a decimal point), except with powers of 2 instead of powers of 10. For signed numbers, the (two's complement) sign bit carries a weight of -2I.
Some examples are given below:
| Fixed-Point Format | Range | Bit Pattern | Example (in Decimal) | Example (in Binary) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1,2,1] | -4 ... +3.5 | sii.f | -2.5 | 101.1 |
| [1,2,2] | -4 ... +3.75 | sii.ff | -2.5 | 101.10 |
| [0,4,0] | 0 ... 15 | iiii. | 5 | 0101. |
| [0,4,2] | 0 ... 15.75 | iiii.ff | 5.25 | 0101.01 |
| [1,4,-2] | -16 ... 12 | sii--. | -8 | 110--. |
| [1,-2,4] | -0.25 ... +0.1875 | .-sff | 0.125 | .-010 |
Rounding behavior is relevant when the number of fractional bits F is decreased. This is the same concept as rounding decimal numbers, but in base 2.
Several widely-used rounding modes are implemented in en_cl_fix. They are summarized below:
| Rounding Mode | Description | Example values, rounded to [1,2,0] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.2 | 2.7 | -1.5 | -0.5 | 0.5 | 1.5 | ||
| Trunc_s | Truncate (discard LSBs) | 2 | 2 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| NonSymPos_s | Non-symmetric round to +infinity | 2 | 3 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| NonSymNeg_s | Non-symmetric round to -infinity | 2 | 3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| SymInf_s | Symmetric round "outwards" to +/- infinity | 2 | 3 | -2 | -1 | 1 | 2 |
| SymZero_s | Symmetric round "inwards" to zero | 2 | 3 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| ConvEven_s | Convergent rounding to even | 2 | 3 | -2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| ConvOdd_s | Convergent rounding to odd | 2 | 3 | -1 | -1 | 1 | 1 |
Trunc_s is the most resource-efficient mode, but introduces the largest rounding error. Its integer equivalent is floor(x).
NonSymPos_s is the most common general-purpose rounding mode. It is fairly resource-efficient, but introduces error bias because all ties are rounded towards +infinity. Its integer equivalent is floor(x + 0.5).
All the other rounding modes differ from NonSymPos_s only with respect to how ties are handled (see table above).
Saturation behavior is relevant when the number of integer bits I is decreased and/or the number of sign bits S is decreased (signed to unsigned).
If saturation is not enabled, then MSBs are simply discarded, causing any out-of-range values to "wrap".
If warnings are enabled, then the HDL simulator or software environment will issue a warning when an out-of-range value is detected.
| Saturation Mode | Saturate? | Warn? |
|---|---|---|
| None_s | No | No |
| Warn_s | No | Yes |
| Sat_s | Yes | No |
| SatWarn_s | Yes | Yes |
- Python tests can be found in bittrue/tests/python/.
- MATLAB tests can be found in bittrue/tests/matlab/.
- VHDL testbenches can be found in tb/.
- Important: These testbenches require the Enclustra testbench library, en_tb. As of February 2024, this library has not yet been open-sourced, so the VHDL testbenches cannot be run. We are working to resolve this issue.