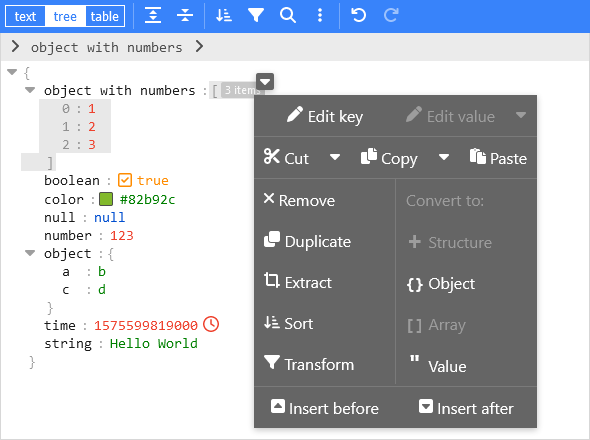
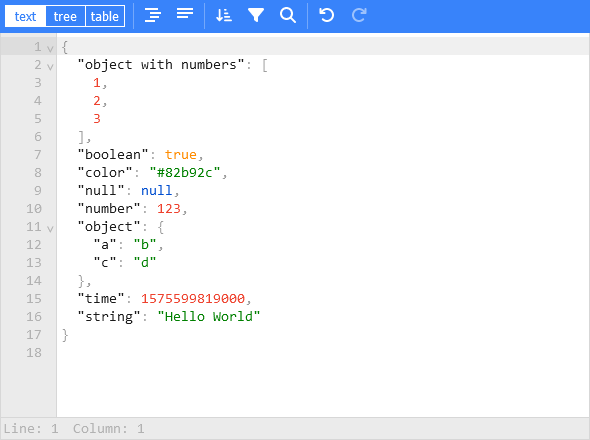
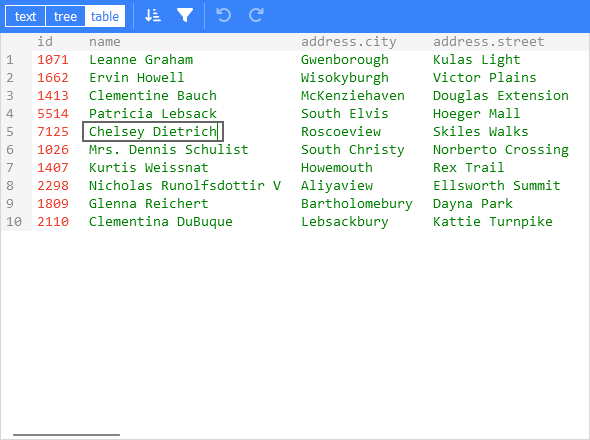
A web-based tool to view, edit, format, transform, and validate JSON.
Try it out: https://jsoneditoronline.org
The library is written with Svelte, but can be used in plain JavaScript too and in any framework (SolidJS, React, Vue, Angular, etc).
- View and edit JSON
- Has a low level text editor and high level tree view and table view
- Format (beautify) and compact JSON
- Sort, query, filter, and transform JSON
- Repair JSON
- JSON schema validation and pluggable custom validation
- Color highlighting, undo/redo, search and replace
- Utilities like a color picker and timestamp tag
- Handles large JSON documents up to 512 MB
For usage in a Svelte project:
npm install svelte-jsoneditor
For usage in vanilla JavaScript or frameworks like SolidJS, React, Vue, Angular, etc:
npm install vanilla-jsoneditor
- Svelte:
- Playground: https://www.sveltelab.dev/q1l38ztdys4at87
- Examples: /src/routes/examples
- Plain JavaScript examples:
- Try it out: https://jsbin.com/gatibux/edit?html,output
- Examples: /examples/browser
- React example: https://codesandbox.io/s/svelte-jsoneditor-react-59wxz
- Vue example: https://codesandbox.io/s/svelte-jsoneditor-vue-toln3w
Create a JSONEditor with two-way binding bind:json:
<script>
import { JSONEditor } from 'svelte-jsoneditor'
let content = {
text: undefined, // can be used to pass a stringified JSON document instead
json: {
array: [1, 2, 3],
boolean: true,
color: '#82b92c',
null: null,
number: 123,
object: { a: 'b', c: 'd' },
string: 'Hello World'
}
}
</script>
<div>
<JSONEditor bind:content />
</div>Or one-way binding:
<script>
import { JSONEditor } from 'svelte-jsoneditor'
let content = {
text: undefined, // can be used to pass a stringified JSON document instead
json: {
greeting: 'Hello World'
}
}
function handleChange(updatedContent, previousContent, { contentErrors, patchResult }) {
// content is an object { json: JSONValue } | { text: string }
console.log('onChange: ', { updatedContent, previousContent, contentErrors, patchResult })
content = updatedContent
}
</script>
<div>
<JSONEditor {content} onChange="{handleChange}" />
</div>The library provides a standalone bundle of the editor via the npm library vanilla-jsoneditor (instead of svelte-jsoneditor) which can be used in any browser environment and framework. In a framework like React, Vue, or Angular, you'll need to write some wrapper code around the class interface.
Browser example loading the ES module:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>JSONEditor</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="jsoneditor"></div>
<script type="module">
import { JSONEditor } from 'vanilla-jsoneditor'
// Or use it through a CDN (not recommended for use in production):
// import { JSONEditor } from 'https://unpkg.com/vanilla-jsoneditor/index.js'
// import { JSONEditor } from 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vanilla-jsoneditor/index.js'
let content = {
text: undefined,
json: {
greeting: 'Hello World'
}
}
const editor = new JSONEditor({
target: document.getElementById('jsoneditor'),
props: {
content,
onChange: (updatedContent, previousContent, { contentErrors, patchResult }) => {
// content is an object { json: JSONValue } | { text: string }
console.log('onChange', { updatedContent, previousContent, contentErrors, patchResult })
content = updatedContent
}
}
})
// use methods get, set, update, and onChange to get data in or out of the editor.
// Use updateProps to update properties.
</script>
</body>
</html>To make it easier to use the library in your framework of choice, you can use a wrapper library:
Svelte component:
<script>
import { JSONEditor } from 'svelte-jsoneditor'
let content = { text: '[1,2,3]' }
</script>
<div>
<JSONEditor {content} />
</div>JavasScript class:
import { JSONEditor } from 'vanilla-jsoneditor'
const content = { text: '[1,2,3]' }
const editor = new JSONEditor({
target: document.getElementById('jsoneditor'),
props: {
content,
onChange: (updatedContent, previousContent, { contentErrors, patchResult }) => {
// content is an object { json: JSONValue } | { text: string }
console.log('onChange', { updatedContent, previousContent, contentErrors, patchResult })
}
}
})-
content: ContentPass the JSON contents to be rendered in the JSONEditor.Contentis an object containing a propertyjson(a parsed JSON document) ortext(a stringified JSON document). Only one of the two properties must be defined. You can pass both content types to the editor independent of in what mode it is. -
mode: 'tree' | 'text' | 'table'. Open the editor in'tree'mode (default),'table'mode, or'text'mode (formerly:codemode). -
mainMenuBar: booleanShow the main menu bar. Default value istrue. -
navigationBar: booleanShow the navigation bar with, where you can see the selected path and navigate through your document from there. Default value istrue. -
statusBar: booleanShow a status bar at the bottom of the'text'editor, showing information about the cursor location and selected contents. Default value istrue. -
askToFormat: booleanWhentrue(default), the user will be asked whether he/she wants to format the JSON document when a compact document is loaded or pasted in'text'mode. Only applicable to'text'mode. -
readOnly: booleanOpen the editor in read-only mode: no changes can be made, non-relevant buttons are hidden from the menu, and the context menu is not enabled. Default value isfalse. -
indentation: number | stringNumber of spaces use for indentation when stringifying JSON, or a string to be used as indentation like'\t'to use a tab as indentation, or' 'to use 4 spaces (which is equivalent to configuringindentation: 4). See also propertytabSize. -
tabSize: numberWhen indentation is configured as a tab character (indentation: '\t'),tabSizeconfigures how large a tab character is rendered. Default value is4. Only applicable totextmode. -
escapeControlCharacters: boolean. False by default. Whentrue, control characters like newline and tab are rendered as escaped characters\nand\t. Only applicable for'tree'mode, in'text'mode control characters are always escaped. -
escapeUnicodeCharacters: boolean. False by default. Whentrue, unicode characters like ☎ and 😀 are rendered escaped like\u260eand\ud83d\ude00. -
flattenColumns: boolean. True by default. Only applicable to'table'mode. Whentrue, nested object properties will be displayed each in their own column, with the nested path as column name. Whenfalse, nested objects will be rendered inline, and double-clicking them will open them in a popup. -
validator: function (json: JSONValue): ValidationError[]. Validate the JSON document. For example use the built-in JSON Schema validator powered by Ajv:import { createAjvValidator } from 'svelte-jsoneditor' const validator = createAjvValidator({ schema, schemaDefinitions })
-
parser: JSON = JSON. Configure a custom JSON parser, likelossless-json. By default, the nativeJSONparser of JavaScript is used. TheJSONinterface is an object with aparseandstringifyfunction. For example:<script> import { JSONEditor } from 'svelte-jsoneditor' import { parse, stringify } from 'lossless-json' const LosslessJSONParser = { parse, stringify } let content = { text: '[1,2,3]' } </script> <div> <JSONEditor {content} parser="{LosslessJSONParser}" /> </div>
-
validationParser: JSONParser = JSON. Only applicable when avalidatoris provided. This is the same asparser, except that this parser is used to parse the data before sending it to the validator. Configure a custom JSON parser that is used to parse JSON before passing it to thevalidator. By default, the built-inJSONparser is used. When passing a customvalidationParser, make sure the output of the parser is supported by the configuredvalidator. So, when thevalidationParsercan outputbigintnumbers or other numeric types, thevalidatormust also support that. In tree mode, whenparseris not equal tovalidationParser, the JSON document will be converted before it is passed to thevalidatorviavalidationParser.parse(parser.stringify(json)). -
pathParser: JSONPathParser. An optional object with a parse and stringify method to parse and stringify aJSONPath, which is an array with property names. ThepathParseris used in the path editor in the navigation bar, which is opened by clicking the edit button on the right side of the navigation bar. ThepathParser.parsefunction is allowed to throw an Error when the input is invalid. By default, a JSON Path notation is used, which looks like$.data[2].nested.property. Alternatively, it is possible to use for example a JSON Pointer notation like/data/2/nested/propertyor something custom-made. Related helper functions:parseJSONPathandstringifyJSONPath,parseJSONPointerandcompileJSONPointer. -
onError(err: Error). Callback fired when an error occurs. Default implementation is to log an error in the console and show a simple alert message to the user. -
onChange(content: Content, previousContent: Content, changeStatus: { contentErrors: ContentErrors | null, patchResult: JSONPatchResult | null }). The callback which is invoked on every change of the contents, both changes made by a user and programmatic changes made via methods like.set(),.update(), or.patch(). The returnedcontentis sometimes of type{ json }, and sometimes of type{ text }. Which of the two is returned depends on the mode of the editor, the change that is applied, and the state of the document (valid, invalid, empty). Please be aware that{ text }can contain invalid JSON: whilst typing intextmode, a JSON document will be temporarily invalid, like when the user is typing a new string. The parameterpatchResultis only returned on changes that can be represented as a JSON Patch document, and for example not when freely typing intextmode. -
onChangeMode(mode: 'tree' | 'text' | 'table'). Invoked when the mode is changed. -
onClassName(path: Path, value: any): string | undefined. Add a custom class name to specific nodes, based on their path and/or value. Note that in the custom class, you can override CSS variables like--jse-contents-background-colorto change the styling of a node, like the background color. Relevant variables are:--jse-contents-background-color --jse-selection-background-color --jse-selection-background-inactive-color --jse-hover-background-color --jse-context-menu-pointer-hover-background --jse-context-menu-pointer-background --jse-context-menu-pointer-background-highlight --jse-collapsed-items-background-color --jse-collapsed-items-selected-background-color
To adjust the text color of keys or values, the color of the classes
.jse-keyand.jse-valuecan be overwritten. -
onRenderValue(props: RenderValueProps) : RenderValueComponentDescription[]EXPERIMENTAL! This API will most likely change in future versions.
Customize rendering of the values. By default,
renderValueis used, which renders a value as an editable div and depending on the value can also render a boolean toggle, a color picker, and a timestamp tag. Multiple components can be rendered alongside each other, like the boolean toggle and color picker being rendered left from the editable div. Built in value renderer components:EditableValue,ReadonlyValue,BooleanToggle,ColorPicker,TimestampTag,EnumValue.For JSON Schema enums, there is a value renderer
renderJSONSchemaEnumwhich renders enums using theEnumValuecomponent. This can be used like:import { renderJSONSchemaEnum, renderValue } from 'svelte-jsoneditor' function onRenderValue(props) { // use the enum renderer, and fallback on the default renderer return renderJSONSchemaEnum(props, schema, schemaDefinitions) || renderValue(props) }
-
onRenderMenu(items: MenuItem[], context: { mode: 'tree' | 'text' | 'table', modal: boolean }) : MenuItem[] | undefined. Callback which can be used to make changes to the menu items. New items can be added, or existing items can be removed or reorganized. When the function returnsundefined, the originalitemswill be applied. Using the context valuesmodeandmodal, different actions can be taken depending on the mode of the editor and whether the editor is rendered inside a modal or not.A menu item
MenuItemcan be one of the following types:-
Button:
interface MenuButtonItem { onClick: () => void icon?: IconDefinition text?: string title?: string className?: string disabled?: boolean }
-
Separator (gray vertical line between a group of items):
interface MenuSeparatorItem { separator: true }
-
Space (fills up empty space):
interface MenuSpaceItem { space: true }
-
-
queryLanguages: QueryLanguage[].
Configure one or multiple query language that can be used in the Transform modal. The library comes with three languages:import { jmespathQueryLanguage, lodashQueryLanguage, javascriptQueryLanguage } from 'svelte-jsoneditor' const allQueryLanguages = [jmespathQueryLanguage, lodashQueryLanguage, javascriptQueryLanguage]
By default, only
javascriptQueryLanguageis loaded. -
queryLanguageId. Theidof the currently selected query language. -
onChangeQueryLanguage: (queryLanguageId: string) => void. Callback function invoked when the user changes the selected query language in the TransformModal via the configuration button top right. -
onFocus()callback fired when the editor got focus. -
onBlur()callback fired when the editor lost focus.
Note that most methods are asynchronous and will resolve after the editor is re-rendered (on the next tick).
-
get(): ContentGet the current JSON document. -
set(content: Content): Promise<void>Replace the current content. Will reset the state of the editor. See also methodupdate(content). -
update(content: Content): Promise<void>Update the loaded content, keeping the state of the editor (like expanded objects). You can also calleditor.updateProps({ content }). See also methodset(content). -
patch(operations: JSONPatchDocument) : Promise<JSONPatchResult>Apply a JSON patch document to update the contents of the JSON document. A JSON patch document is a list with JSON Patch operations. -
updateProps(props: Object): Promise<void>update some or all of the properties. Updatedcontentcan be passed too; this is equivalent to callingupdate(content). Example:editor.updateProps({ readOnly: true })
-
expand([callback: (path: Path) => boolean]): Promise<void>Expand or collapse paths in the editor. Thecallbackdetermines which paths will be expanded. If nocallbackis provided, all paths will be expanded. It is only possible to expand a path when all of its parent paths are expanded too. Examples:editor.expand(path => true)expand alleditor.expand(path => false)collapse alleditor.expand(path => path.length < 2)expand all paths up to 2 levels deep
-
transform({ id?: string, rootPath?: [], onTransform: ({ operations: JSONPatchDocument, json: JSONValue, transformedJson: JSONValue }) => void, onClose: () => void })programmatically trigger clicking of the transform button in the main menu, opening the transform model. If a callbackonTransformis provided, it will replace the build-in logic to apply a transform, allowing you to process the transform operations in an alternative way. If provided,onClosecallback will trigger when the transform modal closes, both after the user clicked apply or cancel. If anidis provided, the transform modal will load the previous status of thisidinstead of the status of the editors transform modal. -
scrollTo(path: Path): Promise<void>Scroll the editor vertically such that the specified path comes into view. Only applicable to modestreeandtable. The path will be expanded when needed. The returned Promise is resolved after scrolling is finished. -
findElement(path: Path)Find the DOM element of a given path. Returnsnullwhen not found. -
acceptAutoRepair(): Promise<Content>In tree mode, invalid JSON is automatically repaired when loaded. When the repair was successful, the repaired contents are rendered but not yet applied to the document itself until the user clicks "Ok" or starts editing the data. Instead of accepting the repair, the user can also click "Repair manually instead". Invoking.acceptAutoRepair()will programmatically accept the repair. This will trigger an update, and the method itself also returns the updated contents. In case oftextmode or when the editor is not in an "accept auto repair" status, nothing will happen, and the contents will be returned as is. -
refresh(): Promise<void>. Refresh rendering of the contents, for example after changing the font size. This is only available intextmode. -
validate() : ContentErrors | null. Get all current parse errors and validation errors. -
focus(): Promise<void>. Give the editor focus. -
destroy(): Promise<void>. Destroy the editor, remove it from the DOM.
- Rendering of values:
renderValuerenderJSONSchemaEnum- Components:
BooleanToggleColorPickerEditableValueEnumValueReadonlyValueTimestampTag
- Validation:
createAjvValidator
- Query languages:
lodashQueryLanguagejavascriptQueryLanguagejmespathQueryLanguage
- Content:
isContentisTextContentisJSONContentisLargeContenttoTextContenttoJSONContentestimateSerializedSize
- Selection:
isValueSelectionisKeySelectionisInsideSelectionisAfterSelectionisMultiSelection,isEditingSelectioncreateValueSelectioncreateKeySelectioncreateInsideSelection,createAfterSelectioncreateMultiSelection
- Parser:
isEqualParser
- Path:
parseJSONPathstringifyJSONPath
- Actions:
resizeObserveronEscape
- Typeguards:
isContentParseErrorisContentValidationErrors
- Functions from
immutable-json-patch:immutableJSONPatchrevertJSONPatchparseJSONPointerparsePathparseFromcompileJSONPointercompileJSONPointerPropgetInsetInupdateIninsertAtexistsIndeleteIn
type JSONValue = { [key: string]: JSONValue } | JSONValue[] | string | number | boolean | null
type TextContent = { text: string }
type JSONContent = { json: JSONValue }
type Content = JSONContent | TextContent
type JSONParser = JSON
interface JSONPathParser {
parse: (pathStr) => JSONPath
stringify: (path: JSONPath) => string
}
type JSONPatchDocument = JSONPatchOperation[]
type JSONPatchOperation = {
op: 'add' | 'remove' | 'replace' | 'copy' | 'move' | 'test'
path: string
from?: string
value?: JSONValue
}
type JSONPatchResult = {
json: JSONValue
previousJson: JSONValue
undo: JSONPatchDocument
redo: JSONPatchDocument
}
interface ParseError {
position: number | null
line: number | null
column: number | null
message: string
}
interface ValidationError {
path: JSONPath
message: string
severity: ValidationSeverity
}
interface ContentParseError {
parseError: ParseError
isRepairable: boolean
}
interface ContentValidationErrors {
validationErrors: ValidationError[]
}
type ContentErrors = ContentParseError | ContentValidationErrors
interface QueryLanguage {
id: string
name: string
description: string
createQuery: (json: JSONValue, queryOptions: QueryLanguageOptions) => string
executeQuery: (json: JSONValue, query: string, parser: JSONParser) => JSONValue
}
interface QueryLanguageOptions {
filter?: {
path?: string[]
relation?: '==' | '!=' | '<' | '<=' | '>' | '>='
value?: string
}
sort?: {
path?: string[]
direction?: 'asc' | 'desc'
}
projection?: {
paths?: string[][]
}
}
interface RenderValuePropsOptional {
path?: Path
value?: JSONValue
readOnly?: boolean
enforceString?: boolean
selection?: Selection
searchResultItems?: SearchResultItem[]
isSelected?: boolean
isEditing?: boolean
normalization?: ValueNormalization
onPatch?: TreeModeContext['onPatch']
onPasteJson?: (pastedJson: { path: Path; contents: JSONValue }) => void
onSelect?: (selection: Selection) => void
onFind?: (findAndReplace: boolean) => void
focus?: () => void
}
interface RenderValueProps extends RenderValuePropsOptional {
path: Path
value: JSONValue
readOnly: boolean
enforceString: boolean | undefined
selection: Selection | undefined
searchResultItems: SearchResultItem[] | undefined
isSelected: boolean
isEditing: boolean
normalization: ValueNormalization
onPatch: (patch: JSONPatchDocument, afterPatch?: AfterPatchCallback) => JSONPatchResult
onPasteJson: (pastedJson: { path: Path; contents: JSONValue }) => void
onSelect: (selection: Selection) => void
onFind: (findAndReplace: boolean) => void
focus: () => void
}
type ValueNormalization = {
escapeValue: (any) => string
unescapeValue: (string) => string
}
type SearchResultItem = {
path: Path
field: Symbol
fieldIndex: number
start: number
end: number
}
interface RenderValueComponentDescription {
component: SvelteComponent
props: RenderValuePropsOptional
}The editor can be styled using the available CSS variables. A full list with all variables can be found here:
https://github.com/josdejong/svelte-jsoneditor/blob/main/src/lib/themes/jse-theme-default.css
For example, to change the default blue theme color to anthracite:
<script>
import { JSONEditor } from 'svelte-jsoneditor'
let content = {
text: undefined, // can be used to pass a stringified JSON document instead
json: {
string: 'Hello custom theme color :)'
}
}
</script>
<div class="my-json-editor">
<JSONEditor bind:content />
</div>
<style>
.my-json-editor {
/* define a custom theme color */
--jse-theme-color: #383e42;
--jse-theme-color-highlight: #687177;
}
</style>The editor comes with a built-in dark theme. To use this theme:
- Load the css file of the dark theme:
themes/jse-theme-dark.css - Add the class name
jse-theme-darkof the dark theme to the HTML container element where the editor is loaded.
It is possible to load styling of multiple themes, and toggle them by changing the class name (like jse-theme-dark) attached to the HTML container element.
Full Svelte example:
<script>
import { JSONEditor } from 'svelte-jsoneditor'
let content = {
text: undefined, // can be used to pass a stringified JSON document instead
json: {
string: 'Hello dark theme :)'
}
}
</script>
<!-- use a theme by adding its name to the container class -->
<div class="my-json-editor jse-theme-dark">
<JSONEditor bind:content />
</div>
<style>
/* load one or multiple themes */
@import 'svelte-jsoneditor/themes/jse-theme-dark.css';
</style>When updating CSS variables dynamically, it is necessary to refresh the via editorRef.refresh() to update the font-size of the line numbers in the gutter and update the colors of the indentation markers in text mode:
<script>
let editorRef
function refresh() {
editorRef?.refresh()
}
</script>
<JSONEditor bind:this="{editorRef}" ... />This library josdejong/svelte-jsoneditor is the successor of josdejong/jsoneditor. The main differences are:
josdejong/jsoneditor |
josdejong/svelte-jsoneditor |
|
|---|---|---|
| Creation | Original (first published in 2011) | Successor (first published in 2021) |
| Framework | Implemented in plain JavaScript, using low level DOM operations | Uses Svelte |
| Tree mode | A tree view having context menu buttons on the left of every line. The keys and values are always in editable state. | A tree view utilizing right-click to open the context menu, and double-click to start editing a key or value (more similar to a Spreadsheet or text editor). It supports copy/paste from and to the system clipboard. |
| Text mode | Powered by Ace editor | Powered by Code Mirror |
| Preview mode | Used to preview large documents | Not needed, both tree and text mode can handle large documents |
The main reasons to create a new library instead of extending the existing one are:
- The codebase had become hard to maintain, the architecture needed a big overhaul. The codebase uses plain JavaScript to create and update the DOM based on changes in the state of the application. This is complex. Letting a framework like Svelte do this for you makes the code base much simpler.
- Performance limitations in the old editor.
- Tree mode: the classic tree mode of
josdejong/jsoneditoris simple and straightforward, but also limited. The new tree mode ofjosdejong/svelte-jsoneditorallows for much more streamlined editing and interaction. It works quite similar to a Spreadsheet or text editor. Navigate and select using the Arrow and Shift+Arrow keys or by dragging with the mouse. Double-click (or press Enter) to start editing a key or value. Open the context menu by right-clicking on the item or selection you want to operate on. Use cut/copy/paste to move parts of the JSON around and interoperate with other applications. - Code or text mode: the Ace editor library is using an outdated module system (AMD) and the way it is bundled and published is hard to integrate in modern JavaScript projects. Code Mirror 6 is very straightforward to integrate, has much better performance, and is very extensible (paving the way for future features).
When the library gives compile errors in your Svelte setup, it could be related to Vite having trouble importing ESM/CommonJS libraries the right way. The error could look like:
SyntaxError: The requested module '/node_modules/json-source-map/index.js?v=fda884be' does not provide an export named 'default' (at jsonUtils.js?v=fda884be:2:8)
A workaround is to add the following to your vite.config.js file (read more):
// ...
/** @type {import('vite').UserConfig} */
const config = {
// ...
optimizeDeps: {
include: [
'ajv-dist',
'immutable-json-patch',
'lodash-es',
'@fortawesome/free-regular-svg-icons',
'jmespath'
]
}
}
// ...Clone the git repository
Install dependencies (once):
npm install
Start the demo project (at http://localhost:5173):
npm run dev
Build the library:
npm run build
Run unit tests (in watch mode):
npm test
Run unit tests and exit:
npm run test-ci
Run linter:
npm run lint
Run coverage (coverage results will be generated in the folder ./coverage):
npm run coverage
Automatically fix linting issues:
npm run format
Publish to npm (will increase version number and publish to npm):
npm run release
Note that it will publish two npm packages: svelte-jsoneditor and vanilla-jsoneditor. You'll need to enter an npm one-time password twice.
To try a build and see the change list, run:
npm run release-dry-run
svelte-jsoneditor is released as open source under the permissive the ISC license.
If you are using svelte-jsoneditor commercially, there is a social (but no legal) expectation that you help fund its maintenance. Start here.