In a word: BIOS is a new form of low-intrusive, high-adaptation, and fast output to enable digital transformation of enterprises.
|
Tip
|
For the Chinese description see: http://www.idealworld.group/2021/06/09/bios/ |
|
Tip
|
For a performance version of the service framework see: https://github.com/ideal-world/tardis |
|
Tip
|
For a generic version of the service framework see: https://github.com/gudaoxuri/dew/ |
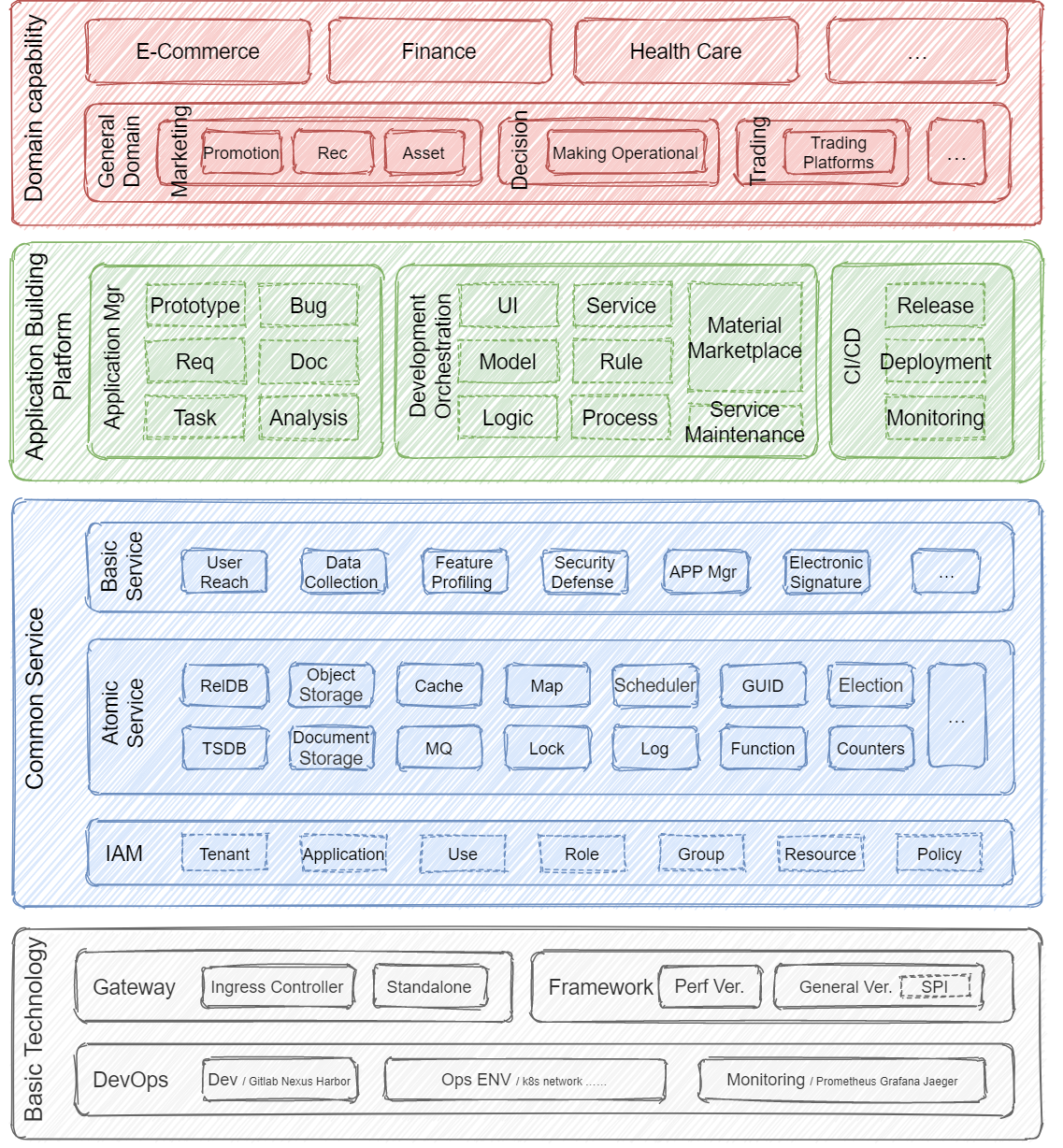
BIOS can serve the digital transformation of enterprises independently or be integrated with the mainstream middle platform. As the core capability of the middle platform, it can realize higher-level R&D collaboration and capability reuse by pulling through the organizational structure of the middle platform.
In the form of BIOS, enterprises can deploy it on different (public or private) cloud platforms with low cost (software and hardware). BIOS itself provides basic functions such as user rights, user reach, process decision, and more reusable functions in the material market, providing rich service support for our product development. At the same time, the low-code build capability also provides a strong guarantee for the rapid build and secondary development of the product. Enterprises only need to focus on business implementation, and the complexity of software development is absorbed by BIOS itself. And all of this is scalable and can be integrated with existing enterprise systems and can be integrated by the middle platform.
The core requirements of Bios from a technical perspective are:
-
Security and reliability: As the core platform, security and reliability must be the most basic requirements. Technically, we focus on using memory/type-safe language, avoiding reflection, reducing three-party dependency, using stateless services, and improving testing, etc. -
High performance: performance is the eternal pursuit, core interface TPS more than 1w/per node, technical attention to the introduction of Reactive model, the use of distributed architecture, reasonable cache architecture, reduce or avoid GC, etc. -
Low cost: reduce the cost of deployment and use, verification environment resources control within 8C32G, technically concerned about Docker deployment, reduce the use of heavy frameworks such as Spring, services can be split and combined. -
Scalable: support secondary development and integration, technically concerned about the design of functional extension points, model abstraction, etc.