GitVote is a GitHub application that allows holding a vote on issues and pull requests.
The first step is to install the GitVote application in the organization or repositories you'd like.
Once the application has been installed we can proceed with its configuration.
To create votes, you'll first need to add a .gitvote.yml configuration file. GitVote will look for it in the following locations (in order of precedence):
- At the root of the repository where the vote was created
- At the root of the
.githubrepository, for organization wide configuration
Please note that the configuration file is required and no commands will be processed if it cannot be found. Once a vote is created, the configuration it will use during its lifetime will be the one present at the vote creation time.
For more information about the configuration file format please see the reference documentation.
Votes can be created by calling the /vote command on an issue or pull request. This can be done by:
- adding the /vote command to the issue or pull request body at creation time
- adding a new comment to an existing issue or pull request with the /vote command in it
The command must be on a line by itself. Please note that GitVote only detects commands in issues or pull requests bodies when they are opened, or when comments are created, not when any of them are edited.
Alternatively, if you have setup multiple configuration profiles, you can also start votes using any of them with the command /vote-PROFILE.
Only repositories collaborators can create votes. For organization-owned repositories, the list of collaborators includes outside collaborators, organization members that are direct collaborators, organization members with access through team memberships, organization members with access through default organization permissions, and organization owners.
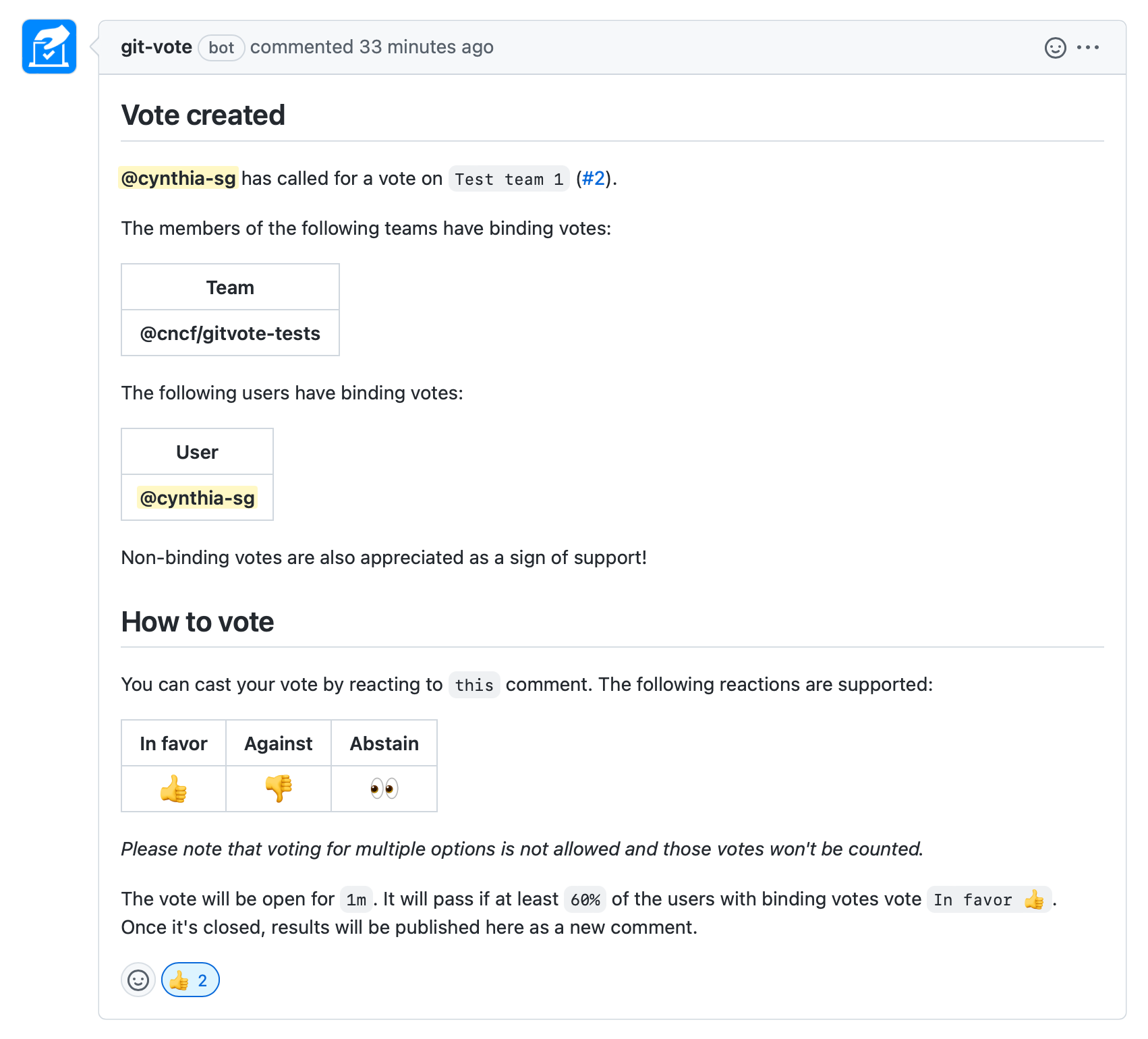
Shortly after the comment with the /vote command is posted, the vote will be created and the bot will post a new comment to the corresponding issue or pull request with the vote instructions.
GitVote allows votes to be created automatically on pull requests when any of the files affected matches certain predefined patterns. For more information about how to set it up, please see the automation section in the reference documentation.
Users can cast their votes by reacting to the git-vote bot comment where the vote was created (screenshot above).
It is possible to vote in favor, against or to abstain, and each of these options can be selected with the following reactions:
| In favor | Against | Abstain |
|---|---|---|
| 👍 | 👎 | 👀 |
Only votes from users with a binding vote as defined in the configuration file will be counted.
Please note that voting multiple options is not allowed and those votes won't be counted.
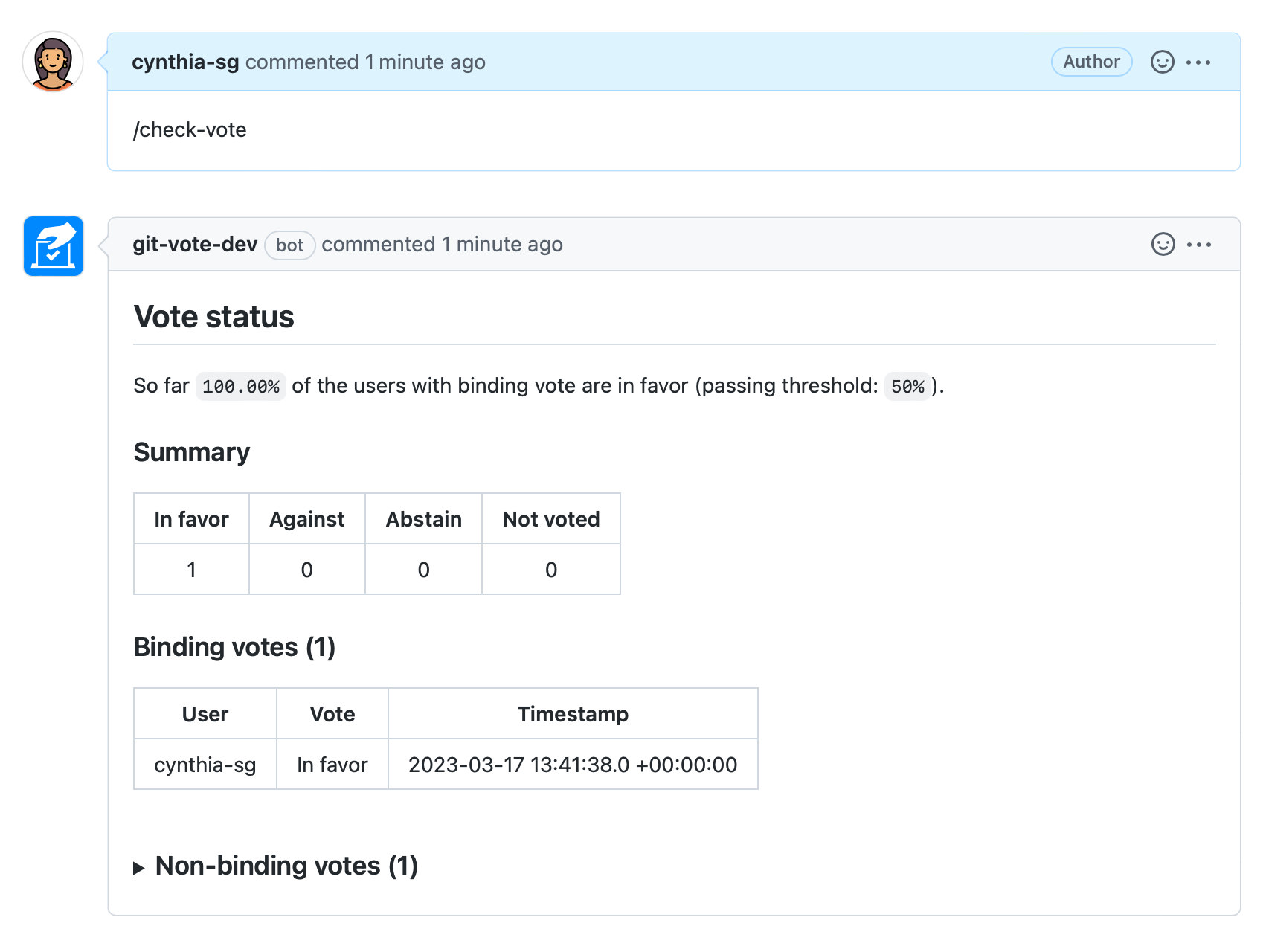
It is possible to check the status of a vote in progress by calling the /check-vote command:
Please note that this command can only be called once a day per vote (additional calls will be ignored).
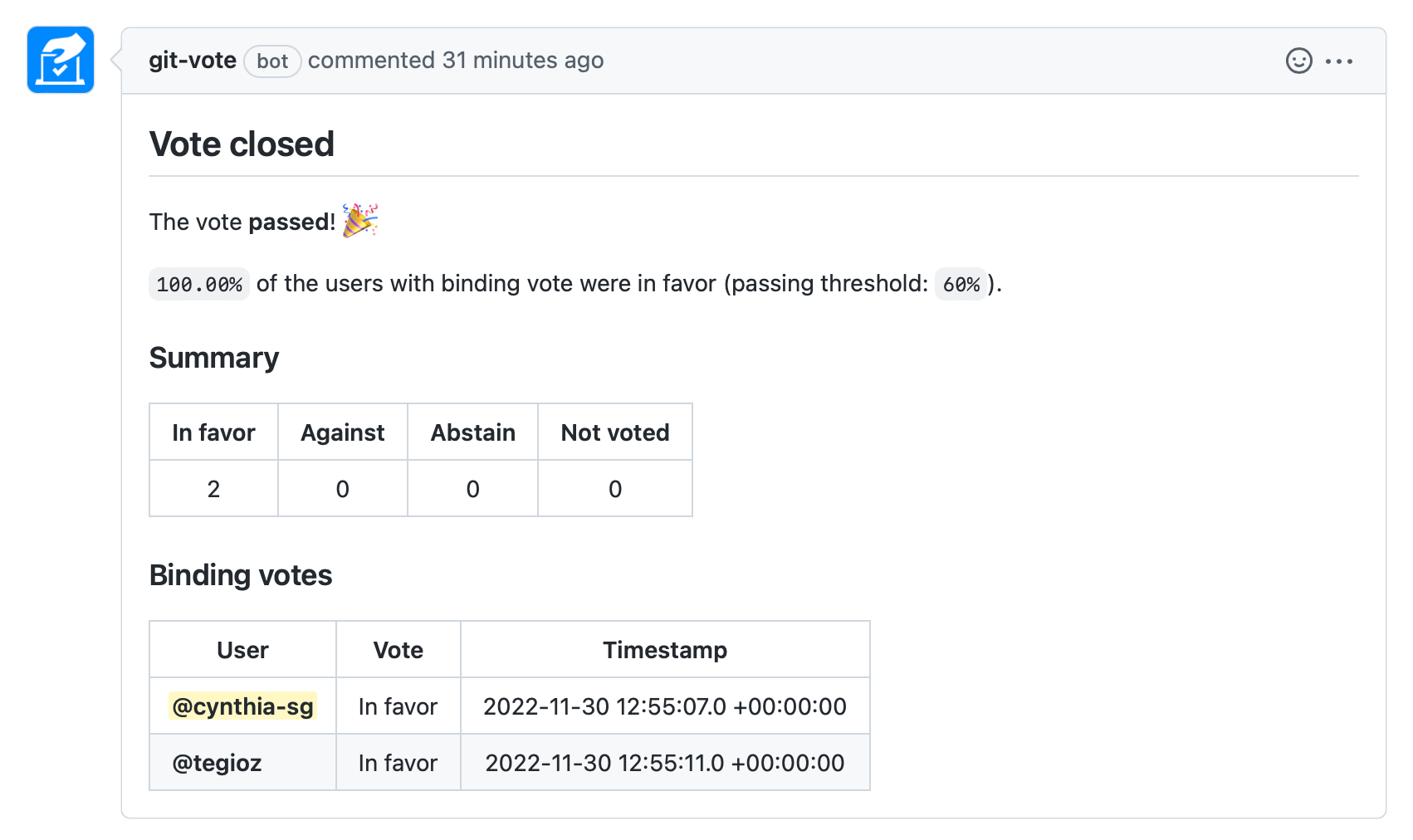
Once the vote time is up, the vote will be automatically closed and the results will be published in a new comment.
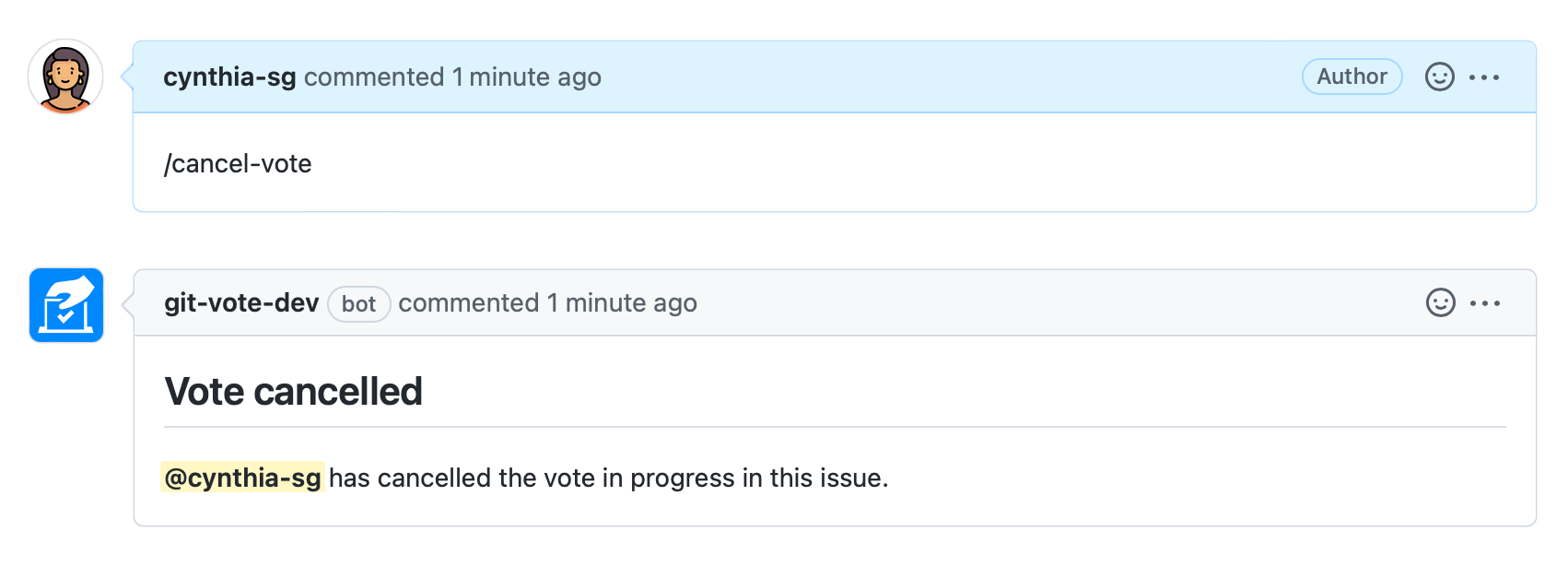
It is possible to cancel a vote in progress by calling the /cancel-vote command:
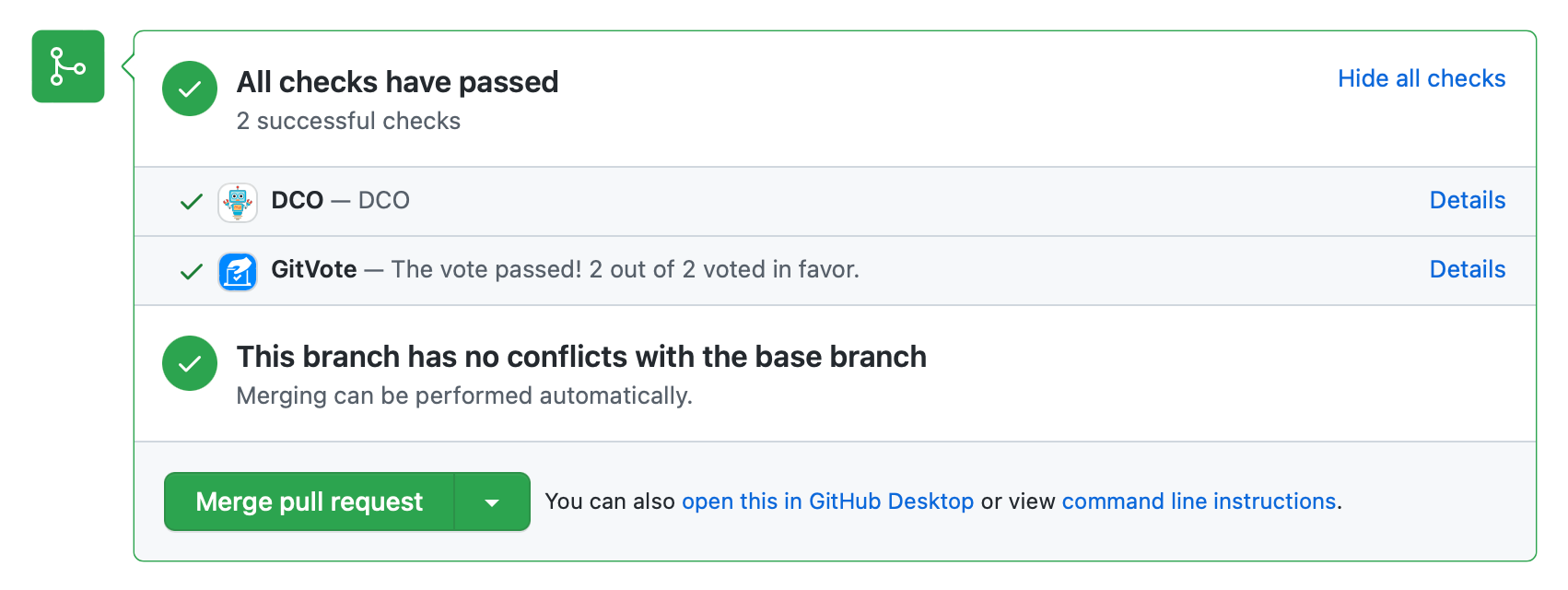
When a vote on a pull request is closed, GitVote will add a check to the head commit with its result. If the vote passes, the result of the check will be success, whereas if it doesn't pass, it'll be failure. When used in combination with protected branch, this feature can be used to require a vote in favor before a pull request can be merged.
At the moment this feature is always enabled but we'll make it configurable so that votes creators can opt-out per configuration profile.
Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for more details.
This project follows the CNCF Code of Conduct.
GitVote is an Open Source project licensed under the Apache License 2.0.