A Scala.js project that makes it easy to convert to and from Json and native JavaScript.
import scala.scalajs.js
import org.getshaka.nativeconverter.NativeConverter
case class User(name: String, isAdmin: Boolean, age: Int) derives NativeConverter
val u = User("John Smith", true, 42)
// serialize
val json: String = u.toJson
val nativeJsObject: js.Any = u.toNative
// deserialize
val parsedUser = NativeConverter[User].fromJson(json)
val parsedUser1 = NativeConverter[User].fromNative(nativeJsObject)The primary goals are:
- Easy conversion from case classes and enums to Json Strings.
- Make interop with native JavaScript libraries easier.
- High performance and no dependencies.
Contents
- Installing
- ScalaDoc
- Built-In NativeConverters
- Typeclass Derivation
- Cross Building
- Performance
- Thanks
- License
Installing
This library requires Scala 3. After setting up a Scala.js project with SBT,
In /project/plugins.sbt add the latest sbt-dotty and Scala.js plugin:
addSbtPlugin("org.scala-js" % "sbt-scalajs" % "1.6.0")Then in /build.sbt, set the scala version and add the native-converter dependency:
scalaVersion := "3.0.1",
libraryDependencies ++= Seq(
"org.getshaka" %%% "native-converter" % "0.5.1"
)ScalaDoc
Built-In NativeConverters
Many built-in NativeConverters are already included.
Primitive Types
You can summon built-in NativeConverters for all the primitive types:
val i: Int = NativeConverter[Int].fromNative(JSON.parse("100"))
val nativeByte: js.Any = NativeConverter[Byte].toNative(127.toByte)
val s: String = NativeConverter[String]
.fromJson(""" "hello world" """)Char, Long, and Overriding the Defaults
Char and Long are always converted to String, since they cannot be represented directly in JavaScript:
// native String
val nativeLong = NativeConverter[Long].toNative(Long.MaxValue)
val parsedLong = NativeConverter[Long]
.fromJson(s""" "${Long.MaxValue}" """)
If you want to change this behavior for Long, implement a given instance of NativeConverter[Long]. The example below uses String for conversion only when the Long is bigger than Int.
given NativeConverter[Long] with
extension (t: Long) def toNative: js.Any =
if t > Int.MaxValue || t < Int.MinValue then t.toString
else t.toInt.asInstanceOf[js.Any]
def fromNative(nativeJs: js.Any): Long =
try nativeJs.asInstanceOf[Int]
catch case _ => nativeJs.asInstanceOf[String].toLong
// "123"
val smallLong: String = NativeConverter[Long].toJson(123L)
// """ "9223372036854775807" """.trim
val bigLong: String = NativeConverter[Long].toJson(Long.MaxValue)Functions
Functions can be converted between Scala.js and Native:
val helloWorld = (name: String) => "hello, " + name
val nativeFunc = NativeConverter[String => String].toNative(helloWorld)
// returns "hello, Ray"
nativeFunc.asInstanceOf[js.Dynamic]("Ray")But remember, Javascript functions are not valid Json and will be not included in toJson output.
IArrays, Arrays, Iterables, Seqs, Sets, and Lists
These collections are serialized using JavaScript Arrays:
import scala.collection.{Seq, Set}
val seq = Seq(1, 2, 3)
val set = Set(1, 2, 3)
// "[1,2,3]"
val seqJson = NativeConverter[Seq[Int]].toJson(seq)
// "[1,2,3]"
val setJson = NativeConverter[Set[Int]].toJson(set)Maps and EsConverters
Maps become JavaScript objects:
import scala.collection.Map
import scala.collection.mutable.HashMap
val map = HashMap("a" -> 1, "b" -> 2)
// """ {"a":1,"b":2} """.trim
val mapJson = NativeConverter[Map[String, Int]].toJson(map)Only String keys are supported, since JSON requires String keys. If you'd rather convert to an ES 2016 Map, do the following:
import org.getshaka.nativeconverter.EsConverters.esMapConv
val map = HashMap(1 -> 2, 3 -> 4)
val nativeMap = NativeConverter[Map[Int, Int]].toNative(map)
// returns 4
nativeMap.asInstanceOf[js.Dynamic].get(3)Converters are not yet implemented for many native ES types, please file an issue or PR if we're missing one you'd like.
Option
Option is serialized with null if None, and the converted value if Some.
val nc = NativeConverter[Option[Array[Int]]]
val some = Some(Array(1,2,3))
// "[1,2,3]"
val someJson = nc.toJson(some)
// None
val none = nc.fromJson("null")Typeclass Derivation
Any Product or Sum type can derive a NativeConverter. Product types are serialized into objects with the parameter names as keys. Simple Sum types (ie, non-parameterized enums and sealed hierarchies) are serialized using their (short) type name. Other Sum types are serialized and deserialized using a @type property that equals the (short) type name.
This behavior closely matches Jackson and other popular libraries, in order to maximize compatibility.
You can for example redefine Option as a Scala 3 enum:
enum Opt[+T] derives NativeConverter:
case Sm(x: T)
case Nn
// """ {"@type":"Nn"} """.trim
val nnJson = Opt.Nn.toJson
// Opt.Sm(123L)
val sm = NativeConverter[Opt[Long]].fromJson(""" {"x":123,"@type":"Sm"} """)And of course, you can nest to any depth you wish:
// recommended but not required for X to derive NativeConverter
case class X(a: List[String])
case class Y(b: Option[X]) derives NativeConverter
val y = Y(Some(X(List())))
val yStr = """ {"b":{"a":[]}} """.trim
assertEquals(yStr, y.toJson)
assertEquals(y, NativeConverter[Y].fromJson(yStr))Cross Building
If Cross Building your Scala project you can use one language for both frontend and backend development. Sub-project /jvm will have your JVM sources, /js your JavaScript, and in /shared you can define all of your validations and request/response DTOs once. In the /shared project you do not want to depend on NativeConverter, since that would introduce a dependency on Scala.js in your /jvm project. So instead of writing derives NativeConverter on your case classes, create an object in /client that holds the derived converters:
// in shared project
case class User(name: String, isAdmin: Boolean, age: Int)
// in js project
object DtoConverters:
given NativeConverter[User] = NativeConverter.derived
object App:
import DtoConverters.given
@main def launchApp: Unit =
println(User("John", false, 21).toJson)Here is a sample cross-project you can clone: https://github.com/AugustNagro/native-converter-crossproject
Performance
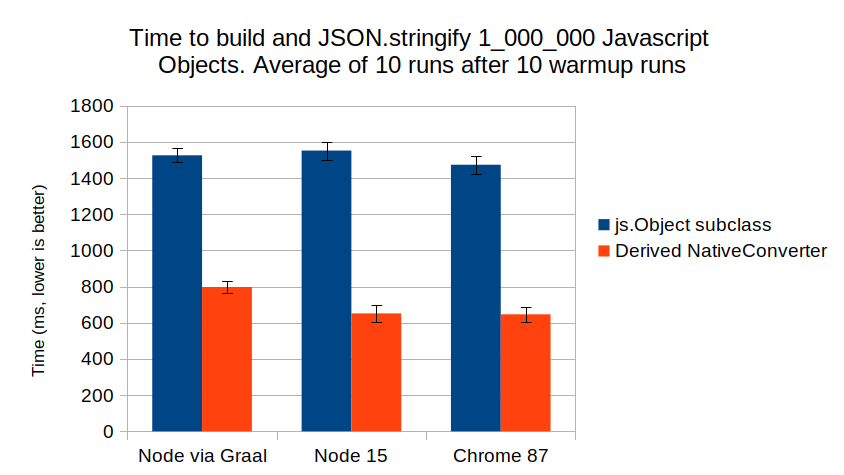
But what about performance, surely making your own js.Object subclasses is faster?
Nope, derived NativeDecoders are 2x faster, even for simple cases like User("John Smith", true, 42):
The generated JavaScript code is very clean. This is all possible because of Scala 3's inline keyword, and powerful type-level programming capabilities. That's right.. no Macros used whatsoever! The derives keyword on type T causes the NativeConverter Typeclass to be auto-generated in T's companion object. Only once, and when first requested.
Thanks
It is safe to say that Scala 3 is very impressive. And a big thank you to Sébastien Doeraene and Tobias Schlatter, who are first-rate maintainers of Scala.js, as well as Jamie Thompson who provided advice on the conversion of Sum types.