R-tree is a tree data structure used for storing spatial data indexes in an efficient manner. R-trees are highly useful for spatial data queries and storage. Some of the real life applications are mentioned below:
- Indexing multi-dimensional information.
- Handling geospatial coordinates.
- Implementation of virtual maps.
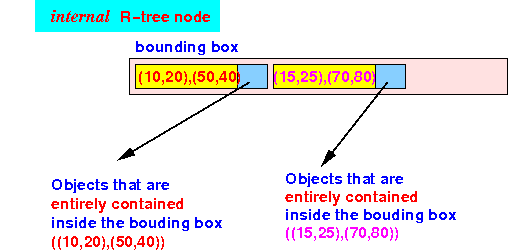
- Consists of a single root, internals nodes and leaf nodes.
- Root contains the pointer to the largest region in the spatial domain.
- Parent nodes contains pointers to their child nodes where region of child nodes completely overlaps the regions of parent nodes.
- Leaf nodes contains data about the MBR to the current objects.
- MBR-Minimum bounding region refers to the minimal bounding box parameter surrounding the region/object under consideration.
- Code implemented in C++.
- main.cpp file contain code for this.
- Run that file on any c++ compiler.
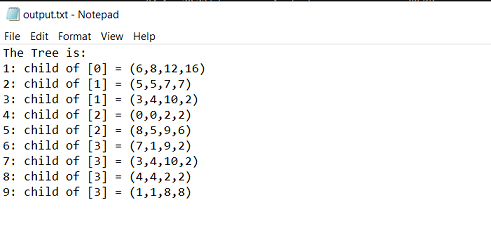
- Rect(0, 0, 2, 2), // xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (for 2 dimensional RTree)
- Rect(5, 5, 7, 7),
- Rect(8, 5, 9, 6),
- Rect(7, 1, 9, 2),
- Rect(3, 4, 10, 2),
- Rect(4, 4, 2, 2),
- Rect(6, 8, 12, 16),
- Rect(1, 1, 8, 8),
- Linear split
- Quadrratic split complexity
- Exponential Split, checking every possible partition, complexity
Here, we have applied Linear split which is more effcient for runtime. But, Exponential split is more efficient in terms of splitted node area covered.
For complete descussion: