This is an implementation of two machine learning algorithms, Contrastive Divergence and Back-propagation. Contrastive Divergence is used to pre-train each layer of the Neural Network as a Restricted Boltzmann Machine. After the RBM training the weights should approximate the problem space represented by the dataset. Back-propagation is then used to classify the data.
This library is intended to serve as an example implementation of the algorithms using the Repa vector library.
Haddock documentation can be found here.
Implements the back-propagation algorithm for multi-layer perceptron networks
Implements the Contrastive Divergence learning algorithm for a single layer RBM. The layers can easily be composed together as done in Data.DNN.Trainer.
Implements a stateful monad for live training and monitoring the RBM and MLP. You can write simple scripts to control and monitor the training.
-- see Examples/Mnist.hs
trainCD :: T.Trainer IO ()
trainCD = forever $ do
T.setLearnRate 0.001 -- set the learning rate
let batchids = [0..468::Int]
forM_ batchids $ \ ix -> do
big <- liftIO $ readBatch ix -- read the batch data
small <- mapM M.d2u $ M.splitRows 5 big -- split the data into mini-batches
forM_ small $ \ batch -> do
T.contraDiv batch -- train each mini-batch
cnt <- T.getCount
when (0 == cnt `mod` 1000) $ do -- animate the weight matrix updates
nns <- T.getDNN
ww <- M.cast1 <$> M.transpose (last nns)
liftIO $ I.appendGIF "rbm.gif" ww -- animate the last layer of the dnn
when (cnt >= 100000) $ T.finish_ -- terminate after 100k
trainBP :: T.Trainer IO ()
trainBP = forever $ do
T.setLearnRate 0.001
let batchids = [0..468::Int]
forM_ batchids $ \ ix -> do
bbatch <- liftIO $ readBatch ix -- data
blabel <- liftIO $ readLabel ix -- labels for the data
sbatch <- mapM M.d2u $ M.splitRows rowCount bbatch -- split into mini-batches
slabel <- mapM M.d2u $ M.splitRows rowCount blabel
forM_ (zip sbatch slabel) $ \ (batch,label) -> do
T.backProp batch label -- train the backprop
cnt <- T.getCount
when (0 == cnt `mod` 10000) $ do -- draw a digit with the network
gen <- T.backward (Matrix $ toLabelM [0..9]) -- for each digit run the network backward
liftIO $ I.appendGIF "bp.gif" gen -- animate the result
when (cnt >= 100000) $ T.finish_ -- terminate after 100k
A class that wraps the Repa APIs to compile check the matrix operations used by the algorithms. For example:
-- symbolic types for the weight matrix and input data shapes
data I -- input nodes
data H -- hidden nodes
data B -- number of batches
type RBM = Matrix U I H
-- We can constrain the weight and input matrix types
-- such the compiler will make sure that all the matrix operations
-- correctly match up to what we expect.
hiddenPs :: (Monad m) => RBM -> Matrix U B I -> m (Matrix U B H)
hiddenPs ixh bxi = do
-- mmult :: Monad m => (Matrix U a b) -> (Matrix U b c) -> m (Matrix U a c)
-- the compiler will verify the shape of the input and output matrixes.
-- !bxh <- ixh `M.mmult` bxi would cause an error
!bxh <- bxi `M.mmult` ixh
let update _ _ 0 = 1
update v _ _ = sigmoid v
-- preserves the type of bxh since the shape doesn't change
M.d2u $ M.traverse update bxhImplements bmp and gif generation utilities for monitoring the weights. Only supports square input node sizes.
Implements the MNIST training example.
run make mnist_data to generate the test data
run make mnist to test the mnist training.
After backprop there is very strong correlation between the output and the labels
- 25k minibatches of 5 at 0.01 learning rate
| label | correlation |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.96931061006877 |
| 1 | 0.97586250662331 |
| 2 | 0.92920411708058 |
| 3 | 0.93181485208514 |
| 4 | 0.92997917370580 |
| 5 | 0.86159049963061 |
| 6 | 0.95335043333702 |
| 7 | 0.94365052624500 |
| 8 | 0.91446780721296 |
| 9 | 0.86919757980633 |
- 250k minibatches of 5 at 0.01 learning rate
| label | correlation |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.99341336376690 |
| 1 | 0.99060696767070 |
| 2 | 0.98038157977265 |
| 3 | 0.98314542811599 |
| 4 | 0.97051993597869 |
| 5 | 0.97578985146789 |
| 6 | 0.98018183041991 |
| 7 | 0.97570483598546 |
| 8 | 0.96970036917824 |
| 9 | 0.97368923077333 |
After 250k minibatches there is a significant improvement in digit recognition.
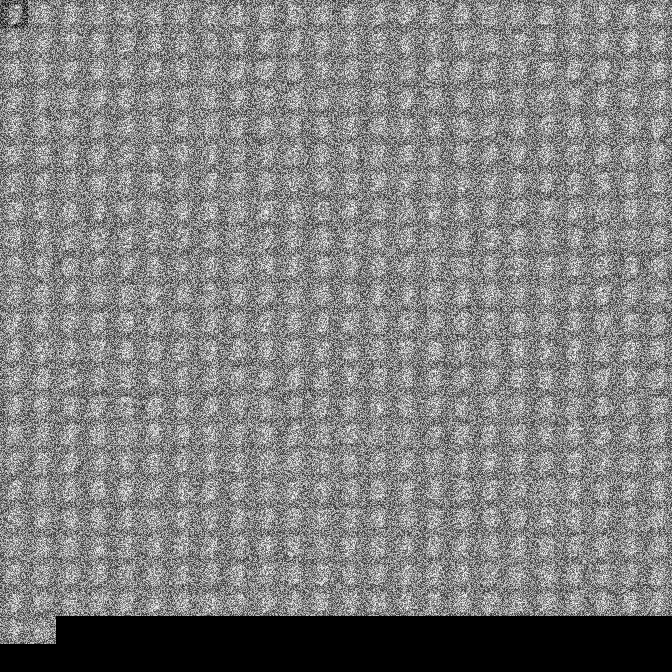
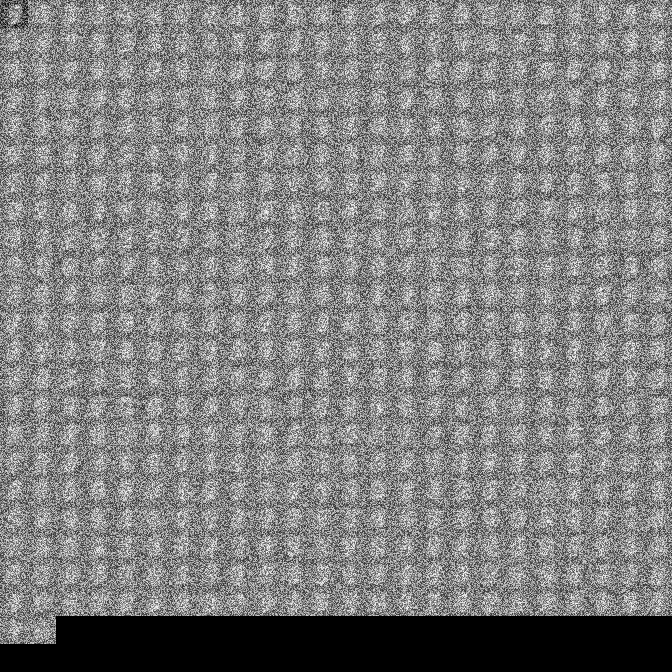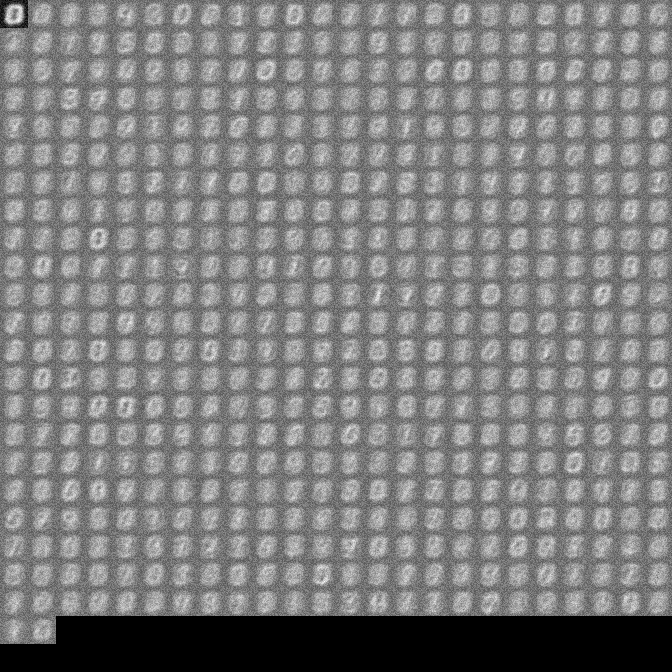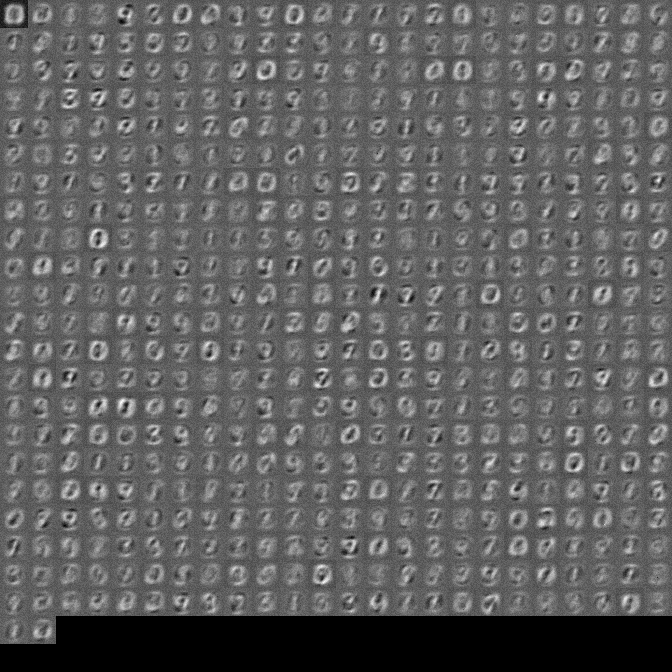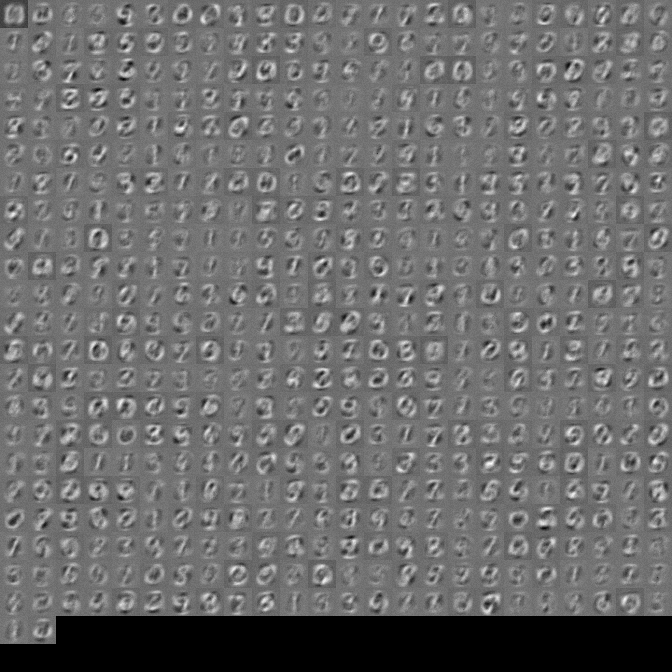
First layer of weights should approximate the input we are training on.
- output after 1k mini-batches
- final output
- animation (it's a large gif, so it takes a few seconds to load)
For monitoring back-propagation the script generated the output of the neural network run backwards after each batch of backprop training. The animated gif represents about 250k mini-batches of 5 images at 0.01 learning rate. The initial output shows the generic digit image that the network learned after the RBM training step for each class. With back-propagation the network slowly converges on what looks like the numbers it's trying to classify as they are separately activated.
- initial output
- final output
- animation
The Repa library targets multi-core CPUs, and the program effectively scales with +RTS -N. The mini-batch size thats used for training has a fairly significant impact on performance, the larger the mini-batch size you can get away with the better performance you get.
I haven't put any effort in optimizing this algorithm to utilize all of the system's memory. My naive attempt seemed to have caused too many page faults and the running time became really slow.
- [Anatoly Yakovenko] (http://aeyakovenko.github.io)
- [mhwombat] (https://github.com/mhwombat) for MNIST file format parsing.
- [The DPH Team] (https://hackage.haskell.org/package/repa) for the awesome Repa package.
- [Geoffrey Hinton] (http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/) for the numerious RBM papers.
- [Raul Rojas] (http://page.mi.fu-berlin.de/rojas/neural/) for the amazing book on Neural Networks.
- The haskell community that provided all the great libraries.
- dropouts
- activation functions besides sigmoid
- non square image generation
- use faster image loading APIs from repa when reading input data