Templated module generator is tool for generating multiple files from template. It allows to create connected files that are part of some "module" like MVC classes. It allows to create structure of new "module" without typing a lot of code.
- Allows to create module based on workspace structure or paste some "module" into specified location
- Allows to use input variables to generate code with required names
- Allows to use calculated variables using JavaScript and another variables
- Allows to add special registration code
- Json schema for config
To use this extension you need to create file with name '.templateGenerator.json' in the workspace directory. This this describes what templates you want to use. Below there is example of such file
[
{
"name": "Module",
"type": "workspace",
"path": "templates/module",
"variables": [
{
"name": "nameOfModule",
"prompt": "Input name of module"
},
{
"name": "nameOfModuleCamel",
"input": false,
"expression": "camelCase(nameOfModule)"
},
{
"name": "curDate",
"input": false,
"expression": "new Date().toString()"
}
],
"actions": [
{
"type": "insertTemplateToFile",
"fileName": "{{workspace_directory}}/index.js",
"snippet": "// end list of modules init",
"template": "init{{nameOfModule}}Module(modelsFacade),",
"position": "before"
},
{
"type": "insertTemplateToFile",
"fileName": "{{workspace_directory}}/index.js",
"snippet": "// end import modules",
"template": "import { init{{nameOfModule}}Module } from './src/Modules/{{nameOfModule}}/{{nameOfModule}}Module';",
"position": "before"
}
]
},
]
Also you can move template description into separate file and link it into '.templateGenerator.json' using import statment
{ "import": "../templates/application.json" }
Where value of import property is path to json file with template description.
Config file contains array of descriptions of templates. Each template has
- name of template
- type of template (workspace or local)
- path to templates directory
- descriptions of variables
- descriptions of post generation actions
"Workspace" template means that template that is defined with structure of whole workspace. E.g. if workspace has structure
src
app
module1
module2
test
module1
module2
then files in the template directory must follow structure like this
src
app
{{templatedMoudle}}
test
{{testOftemplatedModule}}
If template type is "local" then all templates files with structure will be generated in the place where you click to generate code. E.g. You template module has structure
{{templateModule}}
{{file1}}
{{file2}}
test
{{testFile1}}
{{testFile2}}
Workspace structure is following
src
app
modules
module1
module2
When you click in context menu of modules directory "Generate templated module" you will generate new module inside of modules directory.
So you workspace will be
src
app
modules
module1
module2
newModule
newModuleFile1
newModuleFile2
test
newModuleTestFile1
newModuleTestFile2
Templates are files with code with placeholders for variables. Placeholders are set using double braces. e.g. {{myVariable}}. Spaces in braces are not allowed.
Example of templated file
// generated at {{curDate}}
import { {{nameOfModule}}DataAccess } from './{{nameOfModule}}DataAccess';
import { ModelsFacade } from '../../models/ModelsFacade';
import { {{nameOfModule}}Service } from './{{nameOfModule}}Service';
import { set{{nameOfModule}}Service } from './{{nameOfModuleCamel}}Controller.socket';
export const init{{nameOfModule}}Module = async (modelsFacade: ModelsFacade) => {
const dataAccess = new {{nameOfModule}}DataAccess(modelsFacade);
const {{nameOfModuleCamel}}Service = new {{nameOfModule}}Service(dataAccess);
set{{nameOfModule}}Service({{nameOfModuleCamel}}Service);
};
You can use any number of variables in templates.
You can setup multiple templates so when you choose to generate module you will see selection of templates to generate
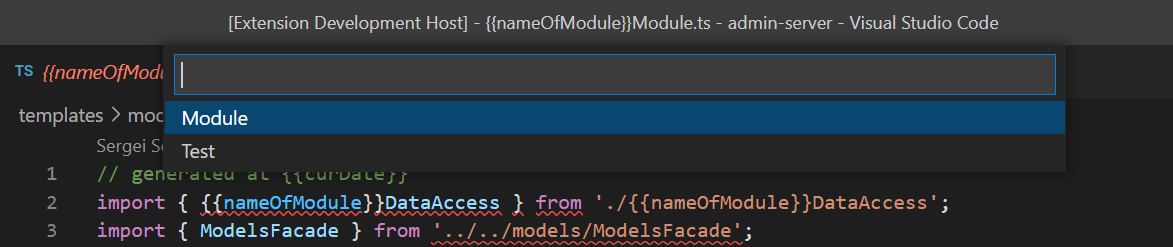
Variables are part of templates that is inputed or calculated. By default all variables are inputed until theres is no field "input": false.
So you need to input variables by hand.
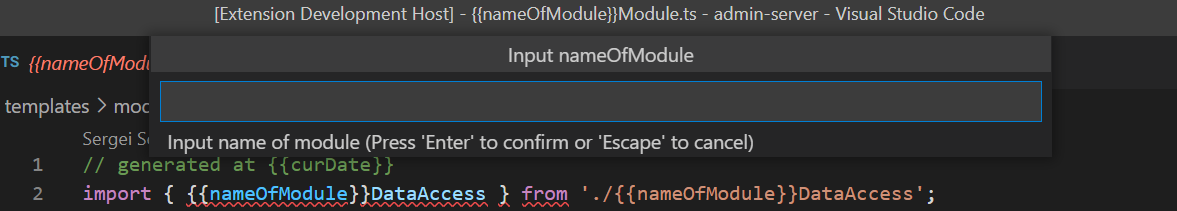 When variable must be input then you can set prompt to describe meaning of the variable. If variable is not inputed you must set field
When variable must be input then you can set prompt to describe meaning of the variable. If variable is not inputed you must set field "expression": "some expression". Expressions are javascript code with additional build-in functions:
- camelCase
- pascalCase
- snakeCase
- dashCase
- fileContent
- workspaceToAbsolutePath
- absoluteToWorkspacePath
- pathJoin
There are also 2 build-in variables workspace_directory and context_directory. Variable context_directory is set only for templates with type "local".
E.g. it is possible to calculate varibale nextId with expression
(parseInt(fileContent(pathJoin(workspace_directory, 'build.number'))) + 1).toString)
There is not possibility to use external libraries in calculations.
You can use variables in name of files of the templates. I.e. your file can be file{{module}}Name.js and name will be generated for variable module=foo -> filefooName.js.
After successfl generation code it is possible to run some actin to configure this code.
Currently there are following generation actions: insertTemplateToFile, runCommand, npmInstall. All of actions have property type
type- type of action. Can be onlyinsertTemplateToFile,runCommand,npmInstall
It inserts some pattern into file after or before specified line. Description of this action.
{
"type": "insertTemplateToFile",
"fileName": "{{workspace_directory}}/index.js",
"snippet": "// end list of modules init",
"template": "init{{nameOfModule}}Module(modelsFacade),",
"position": "before"
},
fileName- file where to addtemplate. Can contains variablessnippet- pattern to search in thefileName. It is place to inserttemlatetemplate- what to insert.templatecan contains variablesposition- can be one of "before" and "after". Before means insert in the previous line ofsnippet. After means on next line ofsnippet
It runs command in terminal
{
"type": "runCommand",
"cmd": "run my command"
},
cmd- command string to execute in terminal
It installs npm package
{
"type": "npmInstall",
"packages": "eslint",
"dev": "false"
},
packages- Name of packages to install with version if neededdev- Optional. True to install dev dependency
Just call from context menu for the directory you want to apply new template.
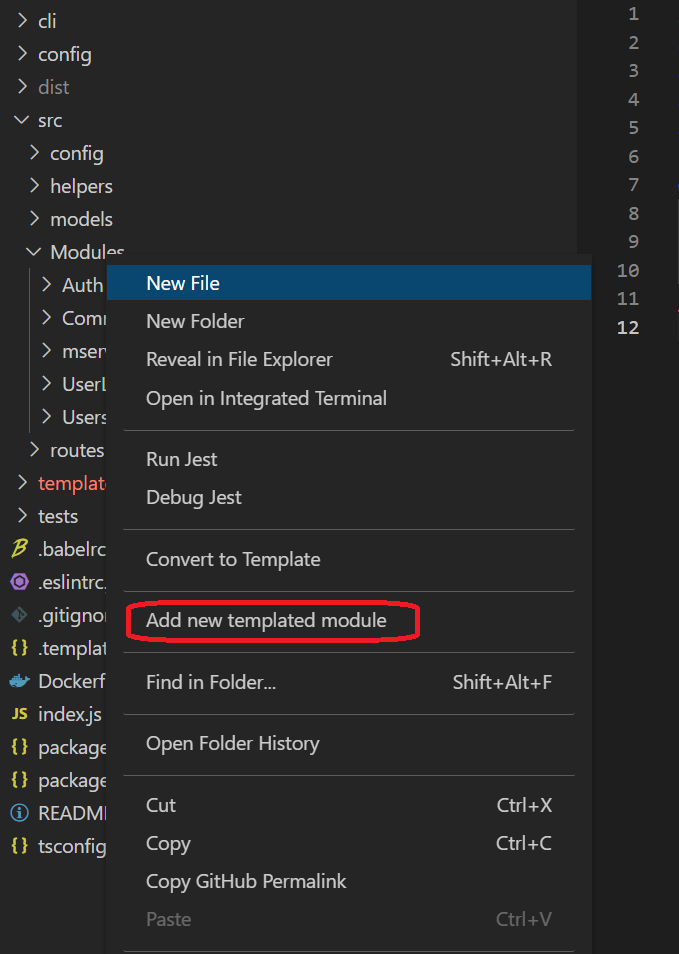
You can set key binding in settings for command salos.module.generator.
If you have any requirements or dependencies, add a section describing those and how to install and configure them.