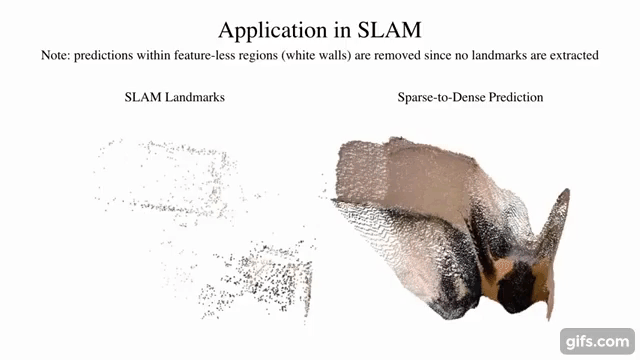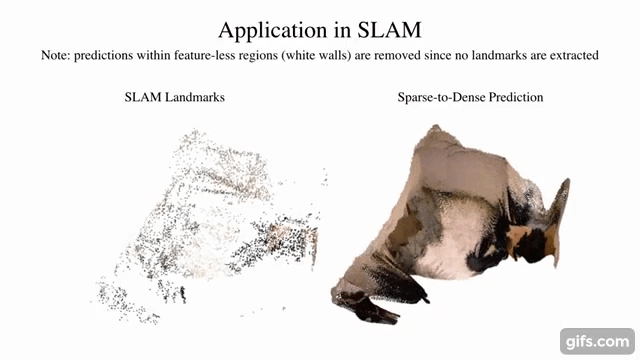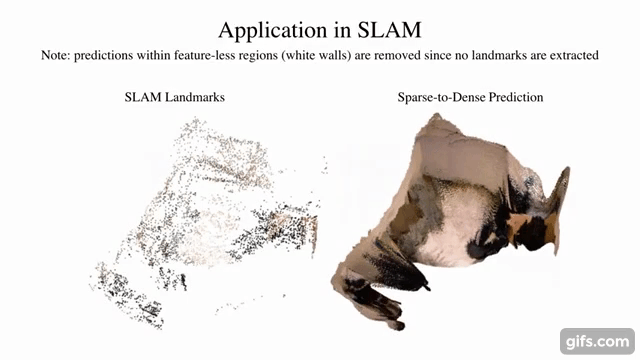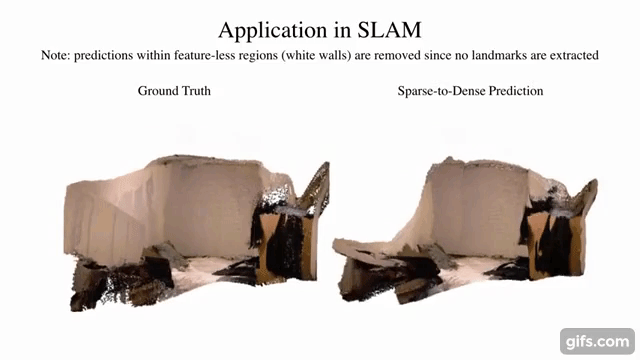
sparse-to-dense.pytorch
This repo implements the training and testing of deep regression neural networks for "Sparse-to-Dense: Depth Prediction from Sparse Depth Samples and a Single Image" by Fangchang Ma and Sertac Karaman at MIT. A video demonstration is available on YouTube.
This repo can be used for training and testing of
- RGB (or grayscale image) based depth prediction
- sparse depth based depth prediction
- RGBd (i.e., both RGB and sparse depth) based depth prediction
The original Torch implementation of the paper can be found here.
Contents
Requirements
This code was tested with Python 3.6 and PyTorch 1.2.0
- Install PyTorch on a machine with CUDA GPU.
- Install the HDF5 and other dependencies (files in our pre-processed datasets are in HDF5 formats).
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y libhdf5-serial-dev hdf5-tools pip3 install h5py matplotlib imageio scipy==1.2.2 scikit-image==0.15.0 opencv-python
- Download the preprocessed NYU Depth V2 and/or KITTI Odometry dataset in HDF5 formats, and place them under the
datafolder. The downloading process might take an hour or so. The NYU dataset requires 32G of storage space, and KITTI requires 81G.mkdir data; cd data wget http://datasets.lids.mit.edu/sparse-to-dense/data/nyudepthv2.tar.gz tar -xvf nyudepthv2.tar.gz && rm -f nyudepthv2.tar.gz wget http://datasets.lids.mit.edu/sparse-to-dense/data/kitti.tar.gz tar -xvf kitti.tar.gz && rm -f kitti.tar.gz cd ..
Training
The training scripts come with several options, which can be listed with the --help flag.
python3 main.py --helpFor instance, run the following command to train a network with ResNet50 as the encoder, deconvolutions of kernel size 3 as the decoder, and both RGB and 100 random sparse depth samples as the input to the network.
python3 main.py -a resnet50 -d deconv3 -m rgbd -s 100 --data nyudepthv2Training results will be saved under the results folder. To resume a previous training, run
python3 main.py --resume [path_to_previous_model]Testing
To test the performance of a trained model without training, simply run main.py with the -e option. For instance,
python3 main.py --evaluate [path_to_trained_model]Trained Models
A number of trained models is available here.
Benchmark
The following numbers are from the original Torch repo.
-
Error metrics on NYU Depth v2:
RGB rms rel delta1 delta2 delta3 Roy & Todorovic (CVPR 2016) 0.744 0.187 - - - Eigen & Fergus (ICCV 2015) 0.641 0.158 76.9 95.0 98.8 Laina et al (3DV 2016) 0.573 0.127 81.1 95.3 98.8 Ours-RGB 0.514 0.143 81.0 95.9 98.9 RGBd-#samples rms rel delta1 delta2 delta3 Liao et al (ICRA 2017)-225 0.442 0.104 87.8 96.4 98.9 Ours-20 0.351 0.078 92.8 98.4 99.6 Ours-50 0.281 0.059 95.5 99.0 99.7 Ours-200 0.230 0.044 97.1 99.4 99.8 -
Error metrics on KITTI dataset:
RGB rms rel delta1 delta2 delta3 Make3D 8.734 0.280 60.1 82.0 92.6 Mancini et al (IROS 2016) 7.508 - 31.8 61.7 81.3 Eigen et al (NIPS 2014) 7.156 0.190 69.2 89.9 96.7 Ours-RGB 6.266 0.208 59.1 90.0 96.2 RGBd-#samples rms rel delta1 delta2 delta3 Cadena et al (RSS 2016)-650 7.14 0.179 70.9 88.8 95.6 Ours-50 4.884 0.109 87.1 95.2 97.9 Liao et al (ICRA 2017)-225 4.50 0.113 87.4 96.0 98.4 Ours-100 4.303 0.095 90.0 96.3 98.3 Ours-200 3.851 0.083 91.9 97.0 98.6 Ours-500 3.378 0.073 93.5 97.6 98.9 Note: our networks are trained on the KITTI odometry dataset, using only sparse labels from laser measurements.
Citation
If you use our code or method in your work, please consider citing the following:
@article{Ma2017SparseToDense,
title={Sparse-to-Dense: Depth Prediction from Sparse Depth Samples and a Single Image},
author={Ma, Fangchang and Karaman, Sertac},
booktitle={ICRA},
year={2018}
}
@article{ma2018self,
title={Self-supervised Sparse-to-Dense: Self-supervised Depth Completion from LiDAR and Monocular Camera},
author={Ma, Fangchang and Cavalheiro, Guilherme Venturelli and Karaman, Sertac},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.00275},
year={2018}
}
Please create a new issue for code-related questions. Pull requests are welcome.