RxState a predictable state container for Swift apps. It's a tiny library built on top of RxSwift and inspired by Redux that facilitates building Unidirectional Data Flow architecture.
- Helps you manage state in a consistent and unified way that guaranty it’s always predictable (After all, state is the source of all evil and you wanna keep that evil in check).
- Limits the way app state can be mutated, which makes your app easier to understand.
- Makes your code easy to test.
- Enables faster debugging.
- It’s is entirely platform independent - you can easily use the same business logic and share it between apps for multiple platforms (iOS, tvOS, etc.).
-
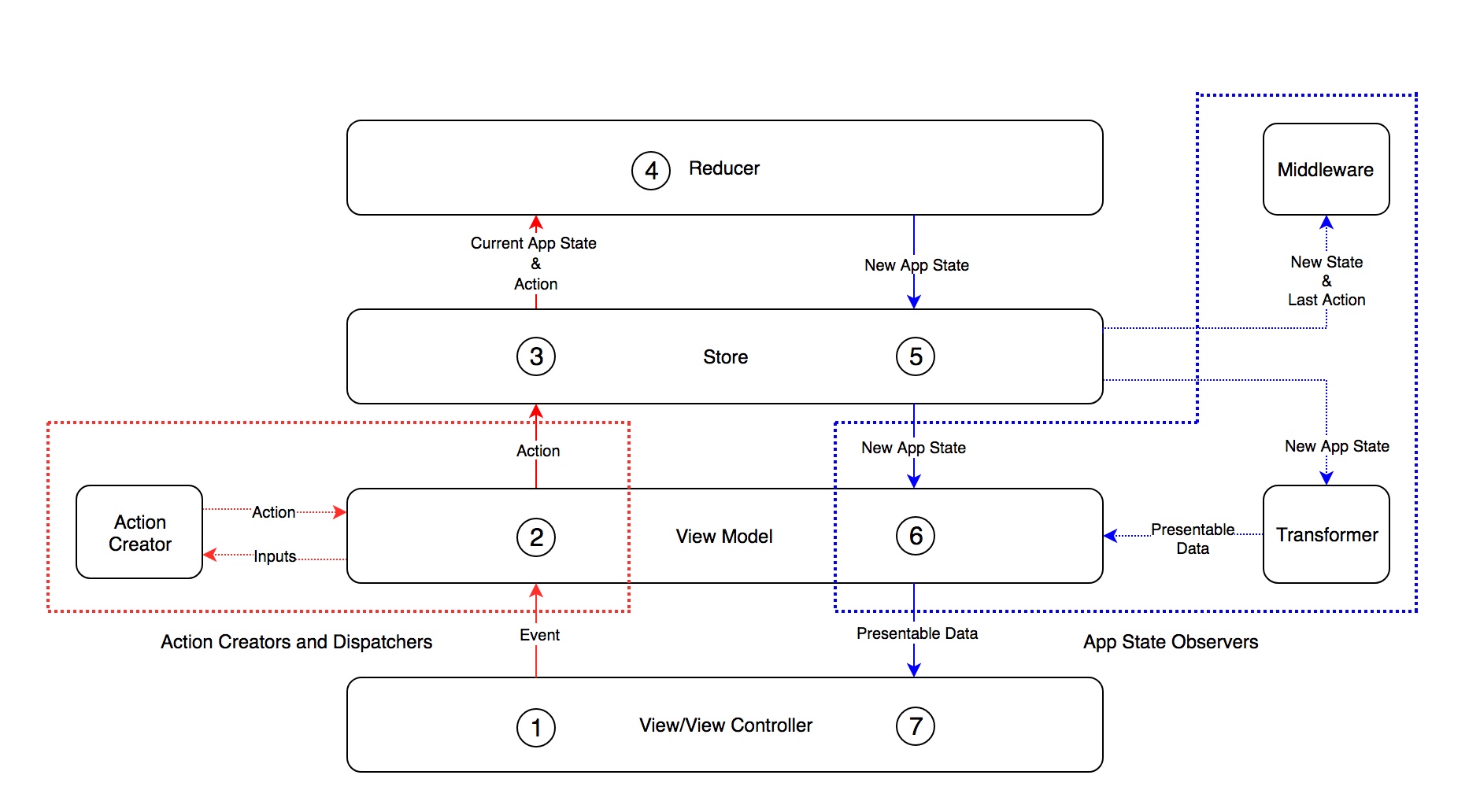
App State: A single immutable data structure. It includes the UI state, the navigation state and the state of your model layer.
-
Store:Contains the app state and notifies the
App State Observersof theApp Stateupdates. -
Reducer: A pure function that takes the current app state and an
Actionas input, creates a newApp Statethat reflects the changes described by theAction, and returns the newApp State. -
Action: Actions describe a state change. The only way to modified the
App Stateis by dispatchingActionsto theStore. -
Action Creators and Dispatchers: Creates
Actions and dispatch them to the store. -
App State Observers: Observers the
App Statein theStoreto transform it to presentable data, write logs, etc. -
View: Presents the presentable data that was deriver from the
App Stateand delivers the user's interactions to theAction Creators and Dispatchers.
-
The
View/View Controllersends events (TheView Model's inputs) to theView Model. -
The
View Modelcreates anActionfrom the received inputs and dispatch them to theStore.
- The
View Modelcan use a dedicatedAction Creators to createActions.Action Creators do can async work and, based on the results it gets, returns differentActions to theView Modelto dispatch.
-
The
Storesends theApp Stateand the receivedActionto theReducer. -
The
Reducerreceives the currentApp Stateand the dispatchedAction, computes and returns newApp State. -
The
Storesends the newApp Stateto the subscribers.
- One of the subscribers could be a
Middlewarethat logs theApp Stateresulted from dispatching anAction.
- The
View Modelreceives the newApp State, transform it presentable data, and send it to theView/View Controller.
- The
View Modelcan useTransformers to transform theApp Stateto presentable data. This helps you reuse the transformation code in differentView Models.
- The
View/View Controllerrender the UI to show the presentable data to the user.
RxState defines the main component for you:
-
Store: Contains theApp Statein the form ofDriver<[SubstateType]>. -
SubstateType: A protocol that tags structs representing a substate. Ex.
struct TasksState: SubstateType {
var tasks: [Task]
var addingTask: Bool
}You can add a Substates to the App State by dispatching StoreAction.add(states: [SubstateType]).
let tasksState = TasksState()
let action = StoreAction.add(states: [tasksState])
store.dispatch(action: action)ActionType: A protocol that tags anAction. TheStorehas the followingActions:
public enum StoreAction: ActionType {
/// Adds substates to the application state.
case add(states: [SubstateType])
/// Removes all substates in the application state.
case reset
}MainReducer: A reducer used by theStore's dispatch function to call the respective reducer based on the Action type.
let mainReducer: MainReducer = { (state: [SubstateType], action: ActionType) -> [SubstateType] in
// Copy the `App State`
var state: [SubstateType] = state
// Cast to a specific `Action`.
switch action {
case let action as TasksAction:
// Extract the `Substate`.
guard var (tasksStateIndex, tasksState) = state
.enumerated()
.first(where: { (_, substate: SubstateType) -> Bool in
return substate is Store.TasksState}
) as? (Int, Store.TasksState)
else {
fatalError("You need to register `TasksState` first")
}
// Reduce the `Substate` to get a new `Substate`.
tasksState = Store.reduce(state: tasksState, action: action)
// Replace the `Substate` in the `App State` with the new `Substate`.
state[tasksStateIndex] = tasksState as SubstateType
default:
fatalError("Unknown action type")
}
// Return the new `App State`
return state
}MiddlewareType: A protocol defining an object that can observe theApp Stateand the last dispatchedActionand does something with it like logging:
protocol LoggingMiddlewareType: Middleware, HasDisposeBag {}
final class LoggingMiddleware: LoggingMiddlewareType {
var disposeBag = DisposeBag()
func observe(currentStateLastAction: Driver<CurrentStateLastAction>) {
currentStateLastAction
.drive(
onNext: { (currentState: [SubstateType], lastAction: ActionType?) in
print(currentState)
print(lastAction)
}, onCompleted: nil, onDisposed: nil)
.disposed(by: disposeBag)
}
}
}- Swift 5
- Using CocoaPods:
pod 'RxState'- Using Swift Package Manager:
Create a Package.Swift file in your project's root folder.
Add following content into the Package.swift file
// swift-tools-version:5.0
import PackageDescription
let package = Package(
name: "YourProjectName",
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/RxSwiftCommunity/RxState.git", from: "0.6.0")
],
targets: [
.target(name: "YourProjectTarget", dependencies: ["RxState"])
]
)I have tried to make the demo app as comprehensive as possible. It currently runs on iOS and macOS. Notice how, because of the architecture, only the View/ View Controller layer needed to change in order to port the app from iOS to macOS.
We would love to see you involved! Feedback and contribution are greatly appreciated :) Checkout the Contributing Guide and the Code of Conduct.
Nazih Shoura, shoura.nazeeh@gmail.com
This library belongs to RxSwiftCommunity.
RxState is available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.