This repository contains solution for level 1-5 Google foo.bar challenge by Muhammad Ikhsan using Java programming language. The Google foo.bar challenge itself contains several problems related to computer science and its principles in solving real world cases. For more detail about this challenge can be found in this link.
The problems consists of 5 different levels that are increasing in difficulty. The details of the challenge elaborated below:
-
Problem 1 (level 1)
array accessingad-hocindexing:
The easiest problems. The tasks is to convert text into braille code. -
Problem 2 (level 2)
mathad-hoc:
Math problems (about configuration of pegs) related to linear equations but it can be simplified intoO(1)algorithm. -
Problem 3 (level 2)
greedybig numberspecial cases:
Greedy approach problem that must be solved with big number library or specialized library for big number computation> 64 bit integer. I used Java programming language, therefore it is more easy because Java offersjava.math.BigIntegerlibrary that can handle big number computations. For the basic idea, this library treat number like sequences of number, therefore it is array-like data structure that can contain many numbers. It also consists of specialized cases (corner cases) which have to be considered separately. -
Problem 4 (level 2)
combinatoricscounting techniquesdynamic programming:
This problem is about counting the combinations using recursive algorithm. In order to speed up the algorithm in terms of time complexity, we have to add cache (memoization) about the state that already visited. -
Problem 5 (level 3)
big numberad-hoc:
The tasks related to ad-hoc problem that must be solved with big number computation library or algorithm. -
Problem 6 (level 3)
dynamic programmingmatrix adjacencymatrix traversalcounting techniques:
The problems related to counting combinations in a map (similar to raster data type), which has 4 direction neighborhood adjacency (top, right, left, down), similar to rook adjacency from picture below: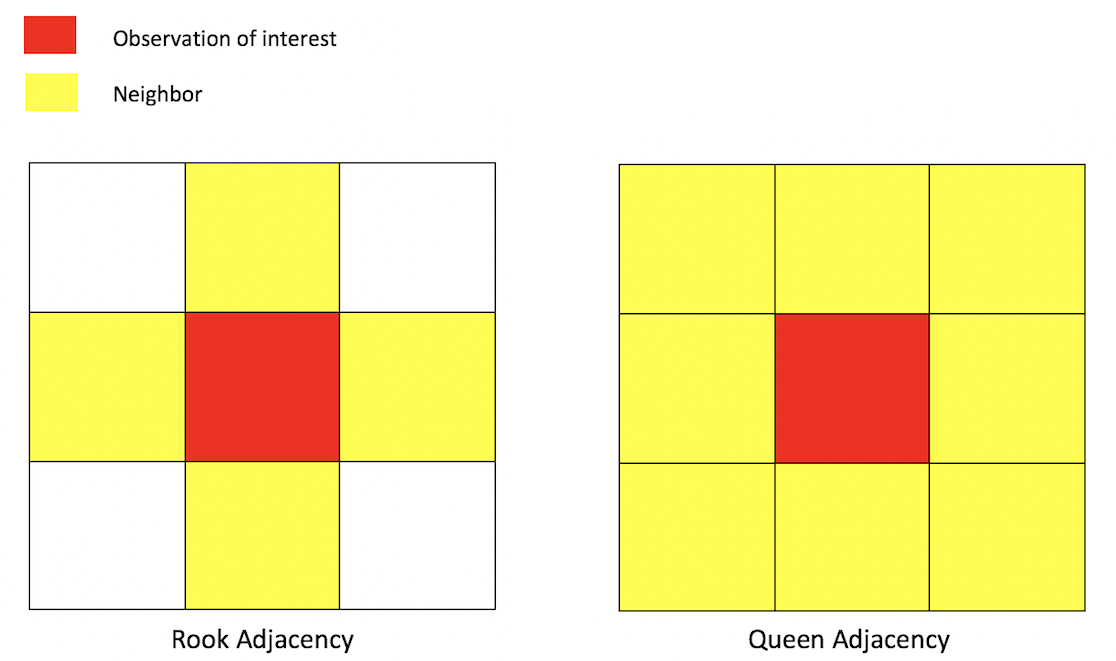
4 dir and 8 dir adjacency
In order to solve the problem we have to implement dynamic programming, I use bottom-up approach in this problem unlike the problem 4 which use top-down approach (Actually for most of problems both of approach could be used interchangeably). -
Problem 7 (level 4)
greedygraph adjacencyunion set:
It is related to maximization problem using greedy approach that also use graph adjacency and checking if set is disjoint or not. -
Problem 8 (level 4)
dynamic programmingqueuegraph traversalmaximization:
Dynamic programming using top down approach where the order of the state are stored in queue using FIFO scheme. Actually maximization problems usually using priority queue, but it is not applicable in this model because it can contain infinite steps and negative weight. Therefore the most appropriate is using basic queue with no variable that is prioritized in the order. -
Problem 9 (level 5)
dynamic programmingbitmaskscounting techniques:
The problem is related to counting all possible combinations of prior state (time = now -1) of 2D matrix, given certain rules that translate timestep t-1 to t. It can be solved with dynamic programming using bitmasks state, because there is relations between previous column to the possible value in current column and the input size is sufficient to be represented as bitmasks state. The value that must be computed is all possible combinations of 2D matrix state at time = t-1 given the 2D matrix in time t. The 2D matrix represents some chemicals that are dissolved in the atmosphere.
It is said that Google foo.bar is part of Google hiring recruitment, but unfortunately since 2020, it is not used anymore. This is the screenshot of final state of the challenge:
Finished state of the challenge