The SAS code and macros in this project are designed to make common tasks easier when using SAS to access Microsoft 365 content. This includes OneDrive and SharePoint Online (including content in Microsoft Teams).
To use SAS or any scripting language with Microsoft 365, you must first register a client app, authenticate with your identity to grant it permissions, and obtain an authorization code. With the auth code in hand, you can then use the code routines in this project to get an access token and invoke API methods to accomplish tasks such as:
- List available drives in OneDrive
- List folders and files within OneDrive and SharePoint folders (include files within Microsoft Teams)
- Download files from OneDrive or SharePoint into your SAS session
- Upload files from SAS to a folder on OneDrive or SharePoint
For more guidance about how to register a client app for use with the Microsoft Graph API, see Using SAS with Microsoft 365.
These macros use a file named config.json to reference your client app details, including the app ID and your Azure tenant ID. The file has this format:
{
"tenant_id": "your-azure-tenant",
"client_id": "your-app-client-id",
"redirect_uri": "https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/nativeclient",
"resource" : "https://graph.microsoft.com"
}
Designate a secure location for this file and for your token.json file (to be created in a later step). The information within these files is sensitive and specific to you and should be protected. See How to protect your REST API credentials in SAS programs for guidance.
This repository contains a SAS program (named ms-graph-macros.sas) with all of the macro routines you need for the remaining tasks. Download this file to a local folder and use %INCLUDE to submit in SAS.
%let src=<my-local-project>\sas-microsoft-graph-api;
%include "&src./ms-graph-macros.sas";
You can also include directly from GitHub:
/* Run just once in your session */
options dlcreatedir;
%let repopath=%sysfunc(getoption(WORK))/sas-microsoft-graph-api;
libname repo "&repopath.";
data _null_;
rc = git_clone(
"https://github.com/sascommunities/sas-microsoft-graph-api",
"&repoPath."
);
put 'Git repo cloned ' rc=;
run;
%include "&repopath./ms-graph-macros.sas";
The macro routines need to know where your config.json and token.json file are located. The initConfig macro initializes this.
/* This path must contain your config.json, and will also */
/* be the location of your token.json */
%initConfig(configPath=/u/yourId/Projects/ms365);
The code in this project uses PROC HTTP without proxy options. If your organization requires a proxy gateway to access the internet, specify the proxy value in the special PROCHTTP_PROXY macro variable:
%let PROCHTTP_PROXY=proxyhost.company.com:889;
Add this line before calling any other actions.
Note: you need this step only if you haven't already generated an auth code and stored in token.json. See Step 2 in this article.
This helper macro will generate the URL you can use to generate an auth code.
%generateAuthUrl();
The SAS log will contain a URL that you should copy and paste into your browser. After authenticating to Microsoft 365 and granting permissions, the URL address bar will change to include a code= value that you need for the next step. Copy only the code= value, not any other values that follow in the URL. (Again, this is covered in Step 2 of this article -- reference for the specific steps to follow!)
If you just generated your auth code for the first time or needed to get a new one because the old one was revoked or expired, then you need to use the auth code to get an initial access token.
/* Note: this code can be quite long -- 700+ characters. */
%let auth_code=PASTE-YOUR-AUTH-CODE-HERE;
/*
Now that we have an authorization code we can get the access token
This step will write the token.json file that we can use in our
production programs.
*/
%get_access_token(&auth_code.);
When successful, token.json will be created/updated in the config directory you specified.
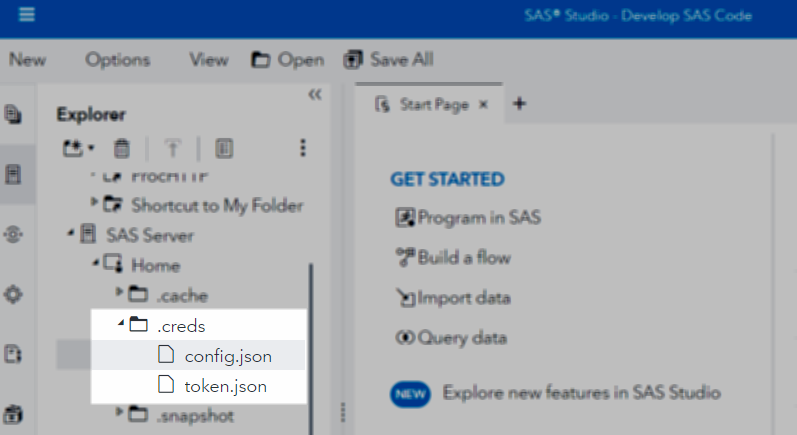
You should now have both config.json and token.json in your designated config folder. This screenshot shows an example of these files in a hidden folder named "~/.creds".
Use the %initSessionMS365 macro routine to exchange the refresh-token stored in token.json for an active non-expired access token.
%initSessionMS365;
With a valid access token to connect to Microsoft 365, we can now use various methods to discover and list content within OneDrive and SharePoint (including Teams), and also copy files from these sources into your SAS session, and copy files from SAS into Microsoft 365.
The flow for file discovery is iterative. Each method creates an output data set that can be queried/filtered to a selection of interest, and that will result in an identifier for a folder or file that feeds into the next method.
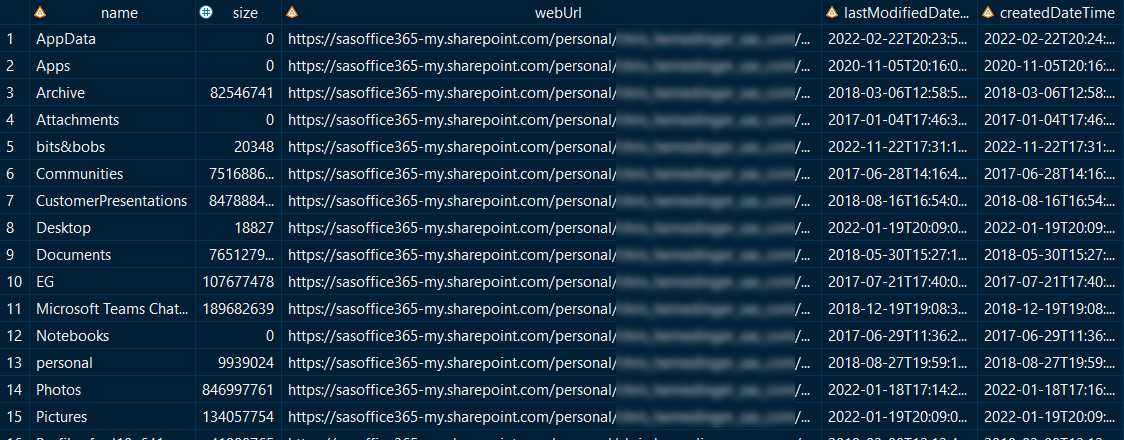
This sequence lists your OneDrive "root" drives (you may have more than one), and then lists the contents of the "Documents" drive.
%listMyDrives(out=work.drives);
/* store the ID value for the drive in a macro variable, where "Documents" is at root */
proc sql noprint;
select id into: driveId from work.drives where driveDisplayName="Documents";
quit;
%listFolderItems(driveId=&driveId, folderId=root, out=work.folderItems);
Example output:
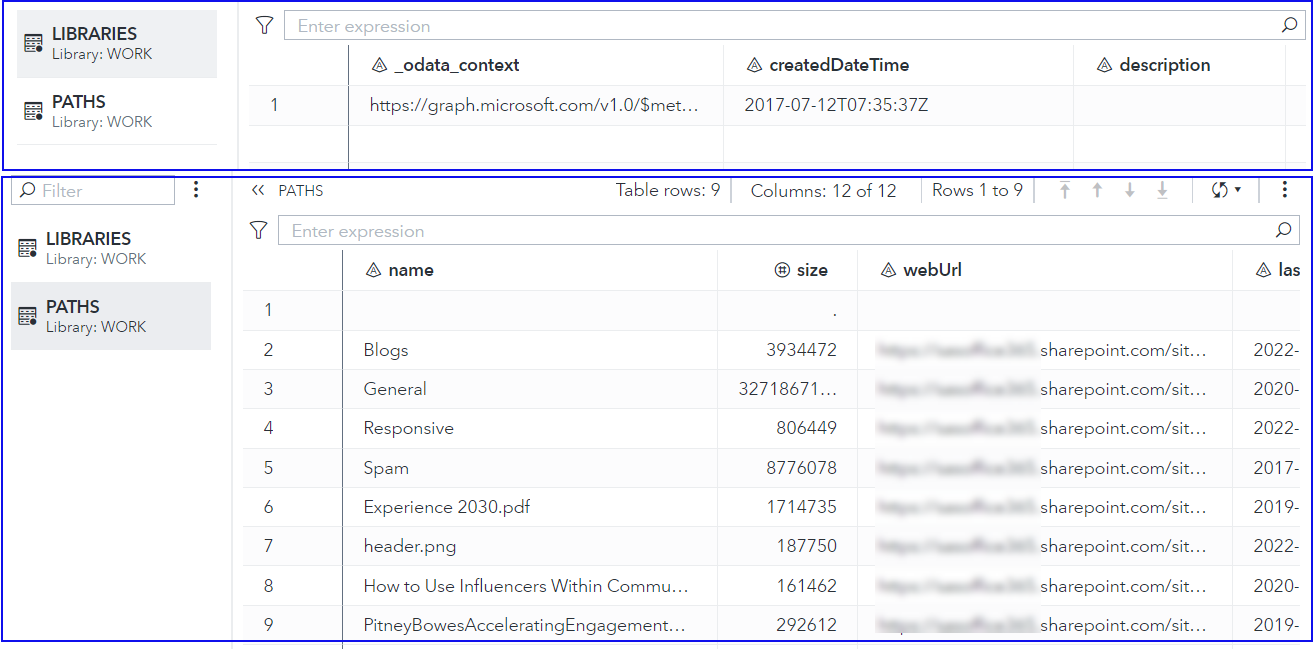
Here's an example code flow:
/* this macro fetches the root IDs for document libraries in your site */
%listSiteLibraries(
siteHost=mysite.sharepoint.com,
sitePath=/sites/Department,
out=libraries);
/* store the ID value for the library in a macro variable, where "Documents" is at root */
proc sql noprint;
select id into: libraryId from libraries where name="Documents";
quit;
/* LIST TOP LEVEL FOLDERS/FILES */
/* special macro to pull ALL items from root folder */
%listFolderItems(driveId=&libraryId., folderId=root, out=work.paths);
Example output:
/* LIST ITEMS IN A SPECIFIC FOLDER */
/*
At this point, if you want to act on any of the items, you just replace "root"
with the ID of the item. So to list the items in the "General" folder I have:
- find the ID for that folder
- list the items within using %listFolderItems and passing that folder ID
*/
/* Find the ID of the folder I want */
proc sql noprint;
select id into: folder from paths
where name="General";
quit;
/* Pull ALL items from a folder */
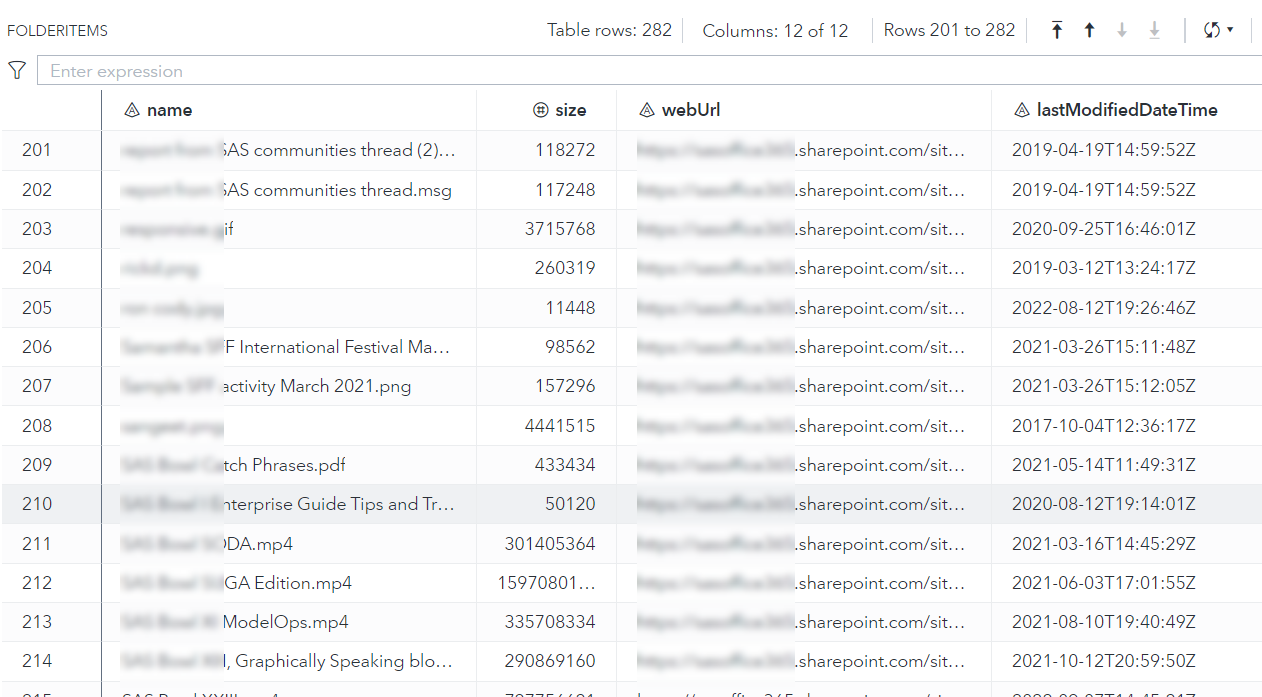
%listFolderItems(driveId=&libraryId., folderId=&folder., out=work.folderItems);
Example output (data set):
/*
With a valid source folderId and knowledge of the items in this folder,
we can download any file of interest.
This example downloads a file named "ScoreCard2022.xlx" from a known
folder on SharePoint (obtained in previous steps) and places it in a
file location on the SAS session.
*/
%downloadFile(driveId=&driveId.,
folderId=&folder.,
sourceFilename=ScoreCard2022.xlsx,
destinationPath=/tmp);
/* Downloaded an Excel file into SAS? Now we can PROC IMPORT if we want */
proc import file="/tmp/ScoreCard2022.xlsx"
out=xldata
dbms=xlsx replace;
run;
/* Create a sample file to upload */
%let targetFile=iris.xlsx;
filename tosave "%sysfunc(getoption(WORK))/&targetFile.";
ods excel(id=upload) file=tosave;
proc print data=sashelp.iris;
run;
ods excel(id=upload) close;
/* Upload to the "General" folder, the folder ID from previous step */
%uploadFile(driveId=&libraryId.,
folderId=&folder.,
sourcePath=%sysfunc(getoption(WORK)),
sourceFilename=&targetFile.);
Notes:
-
The "list" methods (such as
listFolderItems) have special handling to use multiple API calls to gather a complete list of results. The Microsoft Graph API methods return a max of 200 items in a response with an indicator if there are more. These SAS macros will follow through and gather the complete list. -
The
uploadFilemethod uses the special "large file upload" handling to create an upload session that can accommodate files larger than the 4MB size that is the default size limit.
With the authenticated session established, you can use PROC HTTP to execute any API endpoint that your app permissions allow. For example, with User.Read (most apps have this), you can download your own account profile photo:
filename img "c:/temp/profile.jpg";
proc http url="&msgraphApiBase./me/photo/$value"
method='GET'
oauth_bearer="&access_token"
out = img;
run;
The msgraphApiBase and access_token macro variables are set during %initSessionMS365 macro routine.
This example shows how to retrieve the SharePoint Lists that are defined at the site root. The /sites/root/lists endpoint requires Sites.Read.All permission.
filename resp temp;
proc http url="&msgraphApiBase./sites/root/lists"
method='GET'
oauth_bearer="&access_token"
out = resp;
run;
libname lists JSON fileref=resp;
proc sql;
create table work.list_names as
select t1.name,
t1.displayname,
t1.weburl,
t2.template
from lists.value t1
inner join lists.value_list t2 on
(t1.ordinal_value = t2.ordinal_list);
quit;
All APIs are documented in the Microsoft Graph API reference.