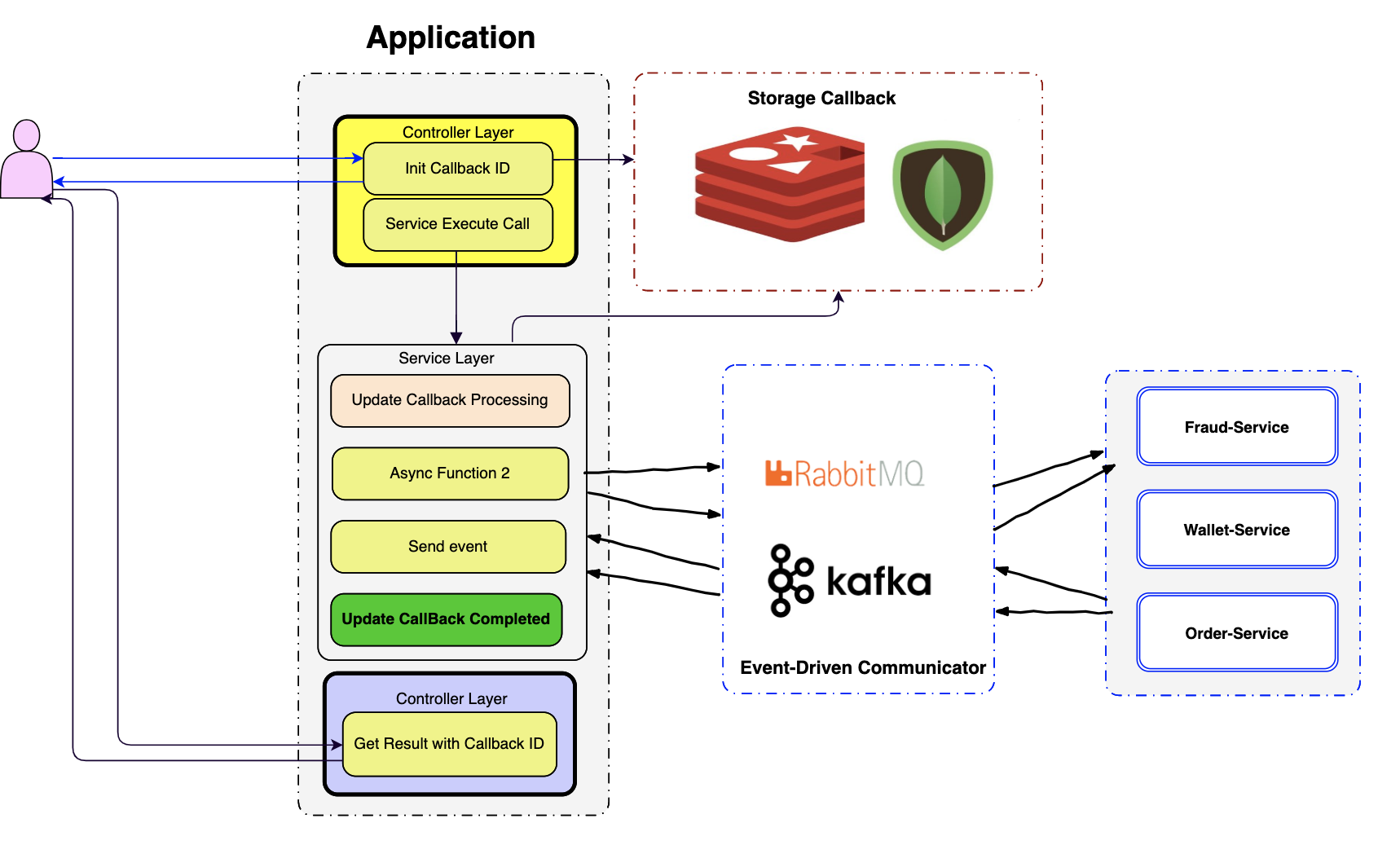
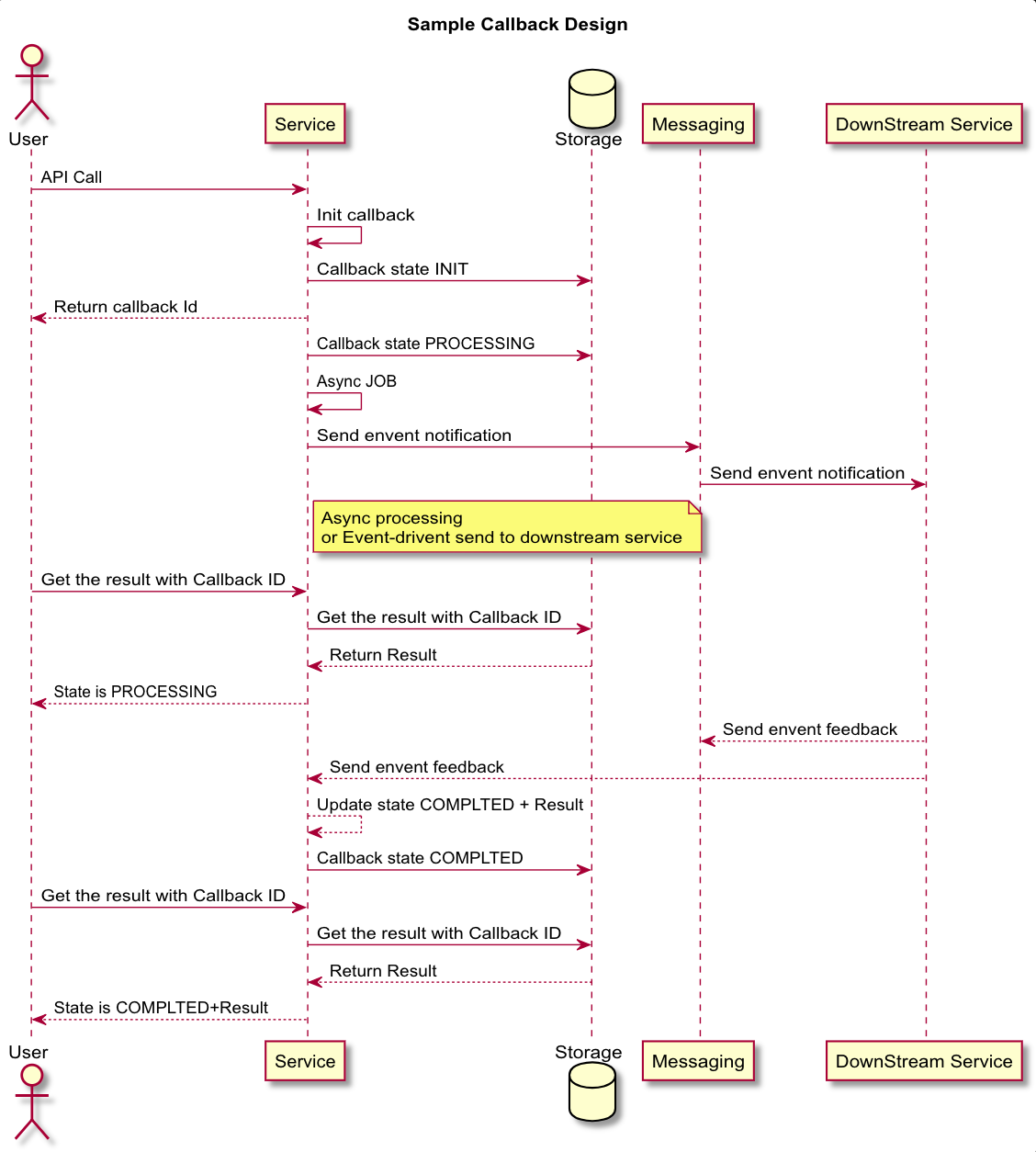
Build the API for scale and reliable might need a lot of things required such as Deployment Process that be able to scale, failover, Non-Blocking I/O framework, Messaging, Event-driven architecture etc.
Sometime you need to increase amount of CPU/RAM to enable scale or deploy copy of replicas if you are using containerization. However if you build your API using Blocking IO, when the clients request thousand per second your API will be got pressure and your system failure was increasing.
If your service call to downstream services by http protocol you're blocking process, network latency is increasing.
- How we improve this process more reliable, async way and adopt with event-driven messaging? Let's take a look a sample design below.
Example you have an API call Payment API that provide the customer to do the payment.
Basically instead provides the clients waits until a whole process completed and response back. We just need to init callback id and return a callback id that tell to the clients, please callback to get your result.
What are the benefits for doing this?
- Make the system more reliable and robust
- We can execute the process asynchronously and finally you just need to update the state.
example:
public CompletableFuture<StackOverflowTagList> fetchTagsFromStackOverFlow(String userId) throws Exception {
log.info("Fetching StackOverflow tags using RestTemplate+CompletableFuture with user id:{}", userId);
CompletableFuture<StackOverflowTagList> stackOverflowTagResponse =
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> restTemplate.getForObject(urlBuilder.fullApiEndpoint(userId),
StackOverflowTagList.class));
log.info("StackOverflow tags of user id:{} is done:{}",
userId, stackOverflowTagResponse.isDone());
return stackOverflowTagResponse;
}
public CompletableFuture<StackOverflowTagList> processBusinessLogic(String callbackId) throws Exception{
CompletableFuture<StackOverflowTagList> result = fetchTagsFromStackOverFlow(callbackId)
.thenApplyAsync(stackOverflowTagList -> {
return applyMyBusinessLogic(stackOverflowTagList);
});
return result;
}
public void execute(String userId, String callBackId) throws Exception {
taskCallbackStorageWorker.processing(callBackId);
processBusinessLogic(userId)
.thenAcceptAsync(stackOverflowTagList ->
taskCallbackStorageWorker.completed(callBackId, stackOverflowTagList)
);
}By doing this all the process are asynchronous.
- We can adopt with event-driven more easily and scale.
If we have a lot of downstream services, we just need to send all the events we need to them to perform through broker like RabbitMQ, ApacheKafka.
When the downstream services completed, they just need send back the result. Then we just need to update the state.
Example: you have two downstream services independent call, you can send the event asynchronously.
- Easy to trace the event, state and result
We can find any state and the result include the details like the root cause and the client can get the result whenever they want.
They just need the callback id. It might be useful for reporting and reconciliation or settle.
All the result with state are storing in memory by default for my design.
We can just store it whatever that we want. It might be good for Redis memory data store or NoSQL for index searching with well document store as my sample design.
- This is interface which provides the callback logic.
public interface TaskCallbackStorageWorker<T> {
void initStorage(BaseResultCallBack baseResultCallBack);
void processing(String callBackId);
void completed(String callBackId, T returnResult);
void updateStatus(String callBackId, String status, T baseResultCallBack);
Optional<T> findResultFromStorage(String callBackId);
default BaseCallBackResponse generateCallBackIdWithInitStatus() {
String callBackId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
BaseCallBackResponse apiResponse = new BaseCallBackResponse(callBackId);
initStorage(new BaseResultCallBack(
callBackId, Status.INIT.toString(), null
));
return apiResponse;
}
}Basically you can implement this class and provides your storage. I am just create a class MemoryCallbackStorageWorker which implemented this interface.
So it's using hashmap with memory storage.
- This is my service abstract that annotation with
@Async. In Spring Boot if you want the method running asynchronously you need to put@Asyncon your method level.
If you want to learn more how to run method asynchronously in spring boot check out here.
import org.soyphea.worker.TaskCallbackStorageWorker;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
public abstract class AsyncBaseService {
protected TaskCallbackStorageWorker taskCallbackStorageWorker;
@Async
abstract public void execute(String userId, String callBackId) throws Exception;
public AsyncBaseService(TaskCallbackStorageWorker taskCallbackStorageWorker) {
this.taskCallbackStorageWorker = taskCallbackStorageWorker;
}
}- For my example, I am going to get all the user tags from stackoverflow by given user id.
@Slf4j
@Service
public class STUserTagFetchingAsync extends AsyncBaseService {
@Autowired
private UrlBuilder urlBuilder;
@Qualifier("bootifulRestTemplate")
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
public STUserTagFetchingAsync(TaskCallbackStorageWorker taskCallbackStorageWorker) {
super(taskCallbackStorageWorker);
}
public CompletableFuture<StackOverflowTagList> fetchTagsFromStackOverFlow(String userId) throws Exception {
log.info("Fetching StackOverflow tags using RestTemplate+CompletableFuture with user id:{}", userId);
CompletableFuture<StackOverflowTagList> stackOverflowTagResponse =
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> restTemplate.getForObject(urlBuilder.fullApiEndpoint(userId),
StackOverflowTagList.class));
log.info("StackOverflow tags of user id:{} is done:{}",
userId, stackOverflowTagResponse.isDone());
return stackOverflowTagResponse;
}
public CompletableFuture<StackOverflowTagList> processBusinessLogic(String callbackId) throws Exception{
CompletableFuture<StackOverflowTagList> result = fetchTagsFromStackOverFlow(callbackId)
.thenApplyAsync(stackOverflowTagList -> {
return applyMyBusinessLogic(stackOverflowTagList);
});
return result;
}
@Async
public StackOverflowTagList applyMyBusinessLogic(StackOverflowTagList stackOverflowTagList) {
log.info("Apply my business logic from result might take some time.");
return stackOverflowTagList;
}
public void execute(String userId, String callBackId) throws Exception {
(1) taskCallbackStorageWorker.processing(callBackId);
processBusinessLogic(userId)
.thenAcceptAsync(stackOverflowTagList ->
(2) taskCallbackStorageWorker.completed(callBackId, stackOverflowTagList)
);
}
}(1) Init a callback
(2) Update state with status COMPLETED.
- This is my controller which get the request and return callback.
@Autowired
private AsyncBaseService asyncBaseService;
@Autowired
private MemoryCallbackStorageWorker memoryCallbackStorageWorker;
@GetMapping("/api/stackoverflow/{user_id}/tags")
BaseCallBackResponse create(@PathVariable("user_id") String userId) throws Exception {
(1) BaseCallBackResponse apiResponse = memoryCallbackStorageWorker.generateCallBackIdWithInitStatus();
log.info("API Response with callback id:{}", apiResponse.getCallBackId());
(2) asyncBaseService.execute(userId, apiResponse.getCallBackId());
return apiResponse;
}
(1) Just init a callback that return callback_id and store it storage defined.
(2) Execute a process include update status PROCESSING, COMPLETED. You should be able to define more, if you want. This is just my an example.
You can combine all the async pipeline or send event in this process, finally just need to update the state.
- This is controller that get the result from callback by given callback_id.
@GetMapping("/api/stackoverflow/{callback_id}/callbacks")
BaseResultCallBack get(@PathVariable("callback_id") String callBackId) {
return memoryCallbackStorageWorker.findResultFromStorage(callBackId).get();
}- Implement DECLINED status with limit of time
- Implement number limit of processing callback
- Implement MongoDB and Redis storage
- Create Event-driven