Quantization is the process of reducing the number of bits represents a number. In Deep Learning, Quantization normally refers to converting from floating point to fixed point integer (i.e. 8-bit integer between 0 to 255).
Binarization means representing the number in 1 bit with {-1,1} value.
Quantization is supported in Tensorflow & PyTorch, which is normally used by many developers.However, binarization is not supported in Tensorflow & PyTorch. But,Larq framework supports Binarization or Binanry Neural Network.
Let's discuss how Quantzation can be done through Tensorflow & PyTorch. Here is the directory structure of the implementation
Quantization
│ README.md
│
└───tensorflow
│ │ simple_network.py
│ │ tf_dnn.py
| | tf_ptq_dnn.py
| | tf_qat_dnn.py
| | test_tflite_model.py
│ │
│ └───tflite_c++
│ | │
│ | │ ...
| |
│ └───models
| | ...
| |
|
└───pytorch
| | simple_network.py
| | pt_dnn.py
| │ pt_ptq_dnn.py
| | pt_qat_dnn.py
| | test_accuracy.py
| | test_speed.py
| |
| └───c++_port
| | |
| | | ...
| |
| └───models
| |
| | ...
|
|
└───larq
| simple_bnn_network
| lq_qat_bnn.py
| lq_ice_bnn_test.py
| lq_ice_dnn_test.py
└───models
| | ...
| |
|
└───tflite_binary_arm64
| ....
|
import tensorflow as tf
class MyNet(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, classes = 10):
super(MyNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), use_bias=False)
self.bn1 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(scale=False)
self.max_pool1 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))
self.conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), use_bias=False)
self.bn2 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(scale=False)
self.max_pool2 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))
self.conv3 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), use_bias=False)
self.bn3 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(scale=False)
self.flatten = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()
self.dense1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, use_bias=False)
self.bn4 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(scale=False)
self.dense2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(classes, use_bias=False)
self.bn5 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(scale=False)
self.softmax = tf.keras.layers.Activation("softmax")
def call(self, inputs):
x = self.conv1(inputs)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.max_pool1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
x = self.max_pool2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.bn3(x)
x = self.flatten(x)
x = self.dense1(x)
x = self.bn4(x)
x = self.dense2(x)
x = self.bn5(x)
x = self.softmax(x)
return x
Run:
python3 tf_ptq_dnn.py --path models/baseline_32bit.tf
Run:
python3 tf_qat_dnn.py --model models/qat_dnn_8bit.tf
Run:
python3 pt_pqt.py --path models/32_dnn.pth
Run:
python3 pt_pqt.py --path models/32_dnn.pth
Architecture Used:
import tensorflow as tf
import larq as lq
## All quantized layers except the first will use the same options
kwargs = dict(input_quantizer="ste_sign",
kernel_quantizer="ste_sign",
kernel_constraint="weight_clip")
class MyBnnNet(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, classes=10):
super(MyBnnNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = lq.layers.QuantConv2D(32, (3, 3),
kernel_quantizer="ste_sign",
kernel_constraint="weight_clip",
use_bias=False)
self.max_pool1 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))
self.bn1 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(scale=False)
self.conv2 = lq.layers.QuantConv2D(64, (3, 3), use_bias=False, **kwargs)
self.max_pool2 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))
self.bn2 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(scale=False)
self.conv3 = lq.layers.QuantConv2D(64, (3, 3), use_bias=False, **kwargs)
self.bn3 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(scale=False)
self.flatten = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()
self.dense1 = lq.layers.QuantDense(64, use_bias=False, **kwargs)
self.bn4 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(scale=False)
self.dense2 = lq.layers.QuantDense(classes, use_bias=False, **kwargs)
self.bn5 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(scale=False)
self.softmax = tf.keras.layers.Activation("softmax")
def call(self, inputs):
x = self.conv1(inputs)
x = self.max_pool1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.max_pool2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.bn3(x)
x = self.flatten(x)
x = self.dense1(x)
x = self.bn4(x)
x = self.dense2(x)
x = self.bn5(x)
x = self.softmax(x)
return x
python3 lq_bnn_network.py --model models/lq_qat_bnn_1bit.tf
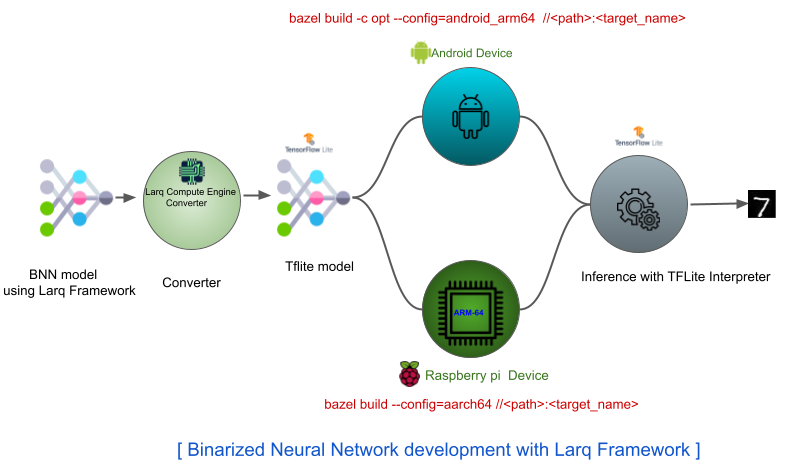
Model development in our case is:
-
1-Bit tensor flow model.
-
Convert to tflite model.
-
Convert to LCE(Larq Compute Engine) compatible tflite model.
This tflite can be tested on raspberry-pi by using tensorflow's label_image tool.
Please follow the steps mentioned inside larq/README.md file to generate "label_image" binary for ARM64 target.
Test the 1-bit model on the Raspberry-Pi by running the below command:
./label_image - tflite_model lq_qat_bnn_1bit.tflite - labels labels.txt - image <image_path> - lcompute 1
Note: must use " - lcompute 1" for using the LCE optimizer from Larq developed specifically for ARM64 device.
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.quantization.fuse_modules.html
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/quantization.html
- https://pytorch.org/blog/quantization-in-practice/
- https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/performance/post_training_quantization
- https://www.tensorflow.org/model_optimization/guide/quantization/training
- https://docs.larq.dev/larq/
- https://docs.larq.dev/compute-engine/end_to_end/
- https://docs.larq.dev/compute-engine/build/arm/
Reach me @