Object-detection-using-yolov2-and-distance-estimation
Object detection using yolov2 and estimation of object from the camera lens
Prerequisite: Download the weights for yolov2 from the below reposotory
https://github.com/sankit1/cv-tricks.com/tree/master/OpenCV/Running_YOLO
This repository provide the approaches that can used to find the distance of objects or the indication of nearness of the objects, to the camera lenses. The codes present in this repository are just the mere attempt to scratch the deep concepts of distance calculation of Objects from the camera lenses.
Assumption:
- These codes are not considering the configuration of cameras.
- Yolov2 is used to detect the objects. Pre-trained weights are used to detect the objects in the images. Yolov2 supports 80 classes. Reference codes for yolov2 - https://github.com/sankit1/cv-tricks.com/tree/master/OpenCV/Running_YOLO
- Camera position is at 1/9 th of the height of the image, just below the center point of the image.
- Width of Bounding box denotes the actual width of the object. We can still reduce the bounding box size but for simplicity purpose the bounding box form yolov2 is used.
2 approaches are coded in separate files:
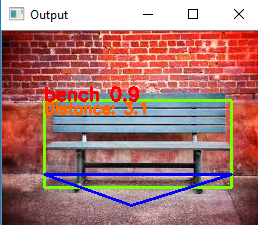
Approach 1: File Name: yolov2_Object_Detection_Distance_Estimation.ipynb Object considered: Bench
- In this approach, the bench is detected and bounding box is drawn around the bench.
- The start and end coordinates of bounding box are identified.
- Coordinates of the triangle are identified : a. Bottom most point – 1/9 of the height of the image and below the center of the input image. b. Left point – 1/7 of the height of bounding box (To touch the outermost point of the bench in the bounding box) c. Right point – 1/7 of the height of bounding box (To touch the outermost point of the bench in the bounding box)
- Identify the angle of vision between the two lines.(Assuming that the bottom most point denotes the camera location. )
- Please refer the link for the formula of calculating the distance between the camera lense and the detected object. https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/webscope/activities/pdfs/measureSize.PDF
- If distance is less than 2 meter then display “Near” and the calculated distance. In other case display “Far” and calculated distance.
Approach 2:
File Name: yolov2_Object_Detection_Distance_by_Area_of_Coutour.ipynb Object considered: Bottle
This is more simple and lean approach. Distance is not calculated in this approach but this approach is good enough for providing the indication of nearness.
-
In this approach the object is detected first. - The start and end coordinates of bounding box are identified.
- Image is cropped with in the bounding box.
- Change the image to gray scale.
- Apply threshold and other filters (filters are not applied in the codes but it is advisable to apply filters for better results)
- Identify the contours
- Find the maximum contour and find the area of that contour(make sure this area is of the contour of car)
- Find the area of the original image.
- Compare the area of the car with that of the total image. Ration = are of car /are of image Assumption: a. Set the threshold of ration to 0.5 b. If ration is greater than 0.5 then we can say that object is closer and far other-wise.