This project focuses on classifying respiratory diseases based on chest X-ray images. The model classifies images into four categories: normal, tuberculosis, COVID-19, and pneumonia. The final model achieved an accuracy of 94% and a loss of 0.12.
The dataset comprises chest X-ray images for each class. These images underwent preprocessing and augmentation using ImageDataGenerator for both training and validation purposes.
The model is a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with the following structure:
- Three convolutional layers with ReLU activation and max pooling.
- Flatten layer followed by two dense layers with ReLU and softmax activation for classification.
The model was trained for 20 epochs using the Adam optimizer and categorical crossentropy loss function. Callbacks were employed to save the best model based on validation accuracy. Monitoring of training and validation accuracy and loss helped mitigate overfitting.
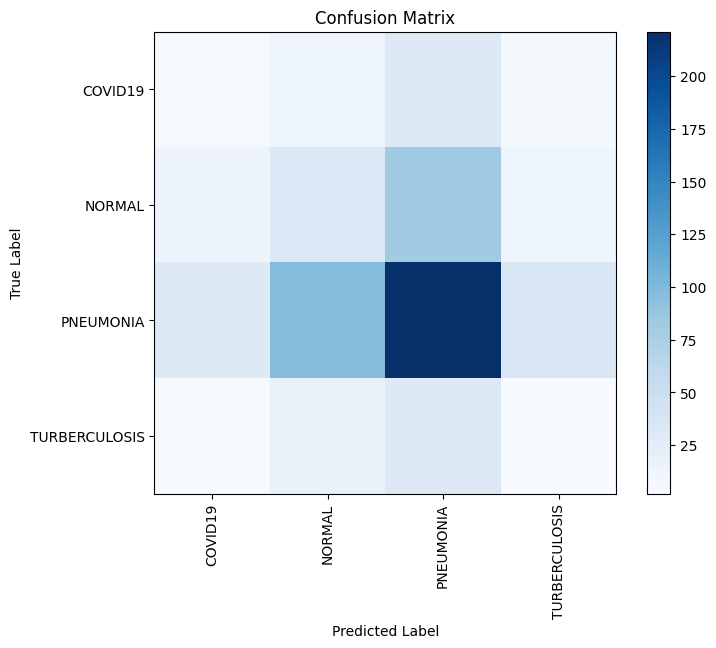
The confusion matrix illustrates the model's performance on the validation set, with rows representing actual classes and columns representing predicted classes.
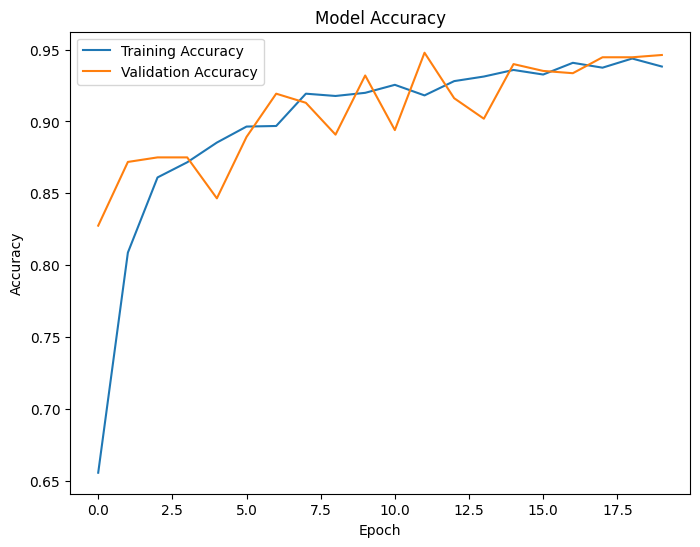
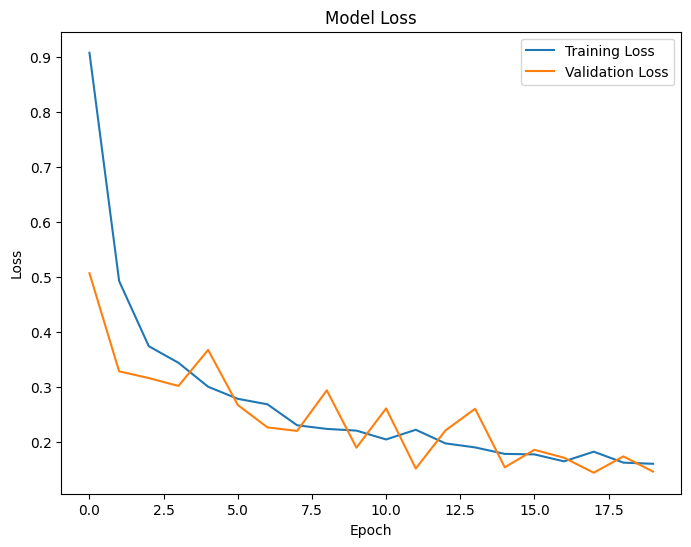
The training history plots showcase the training and validation accuracy and loss over epochs, aiding in visualizing the model's learning progression and identifying overfitting.
The CNN model achieved an accuracy of 94% on the validation set, demonstrating its effectiveness in classifying respiratory diseases based on chest X-ray images. Future enhancements could involve fine-tuning the model architecture and hyperparameters.