The goal of this project was optimizing a robot's navigation around obstacles using the A* (A Star) algorithm. A* is a artificial intelligence method that helps the robot decide its best path. Throughout the project, I explored an adaptive "online" version of the algorithm, which deals with obstacles discovered while the robot is moving. This meant that the robot could not react to some objects until it was very close to them. Another challenge was implementing a PID controller to enable the robot to follow the path found by the A* algorithm. This controller
To run the A* algorithm and generate and plot all the paths, run run.py. All planning tasks are completed using the .a_star_navigation_interface() function in the Robot class.
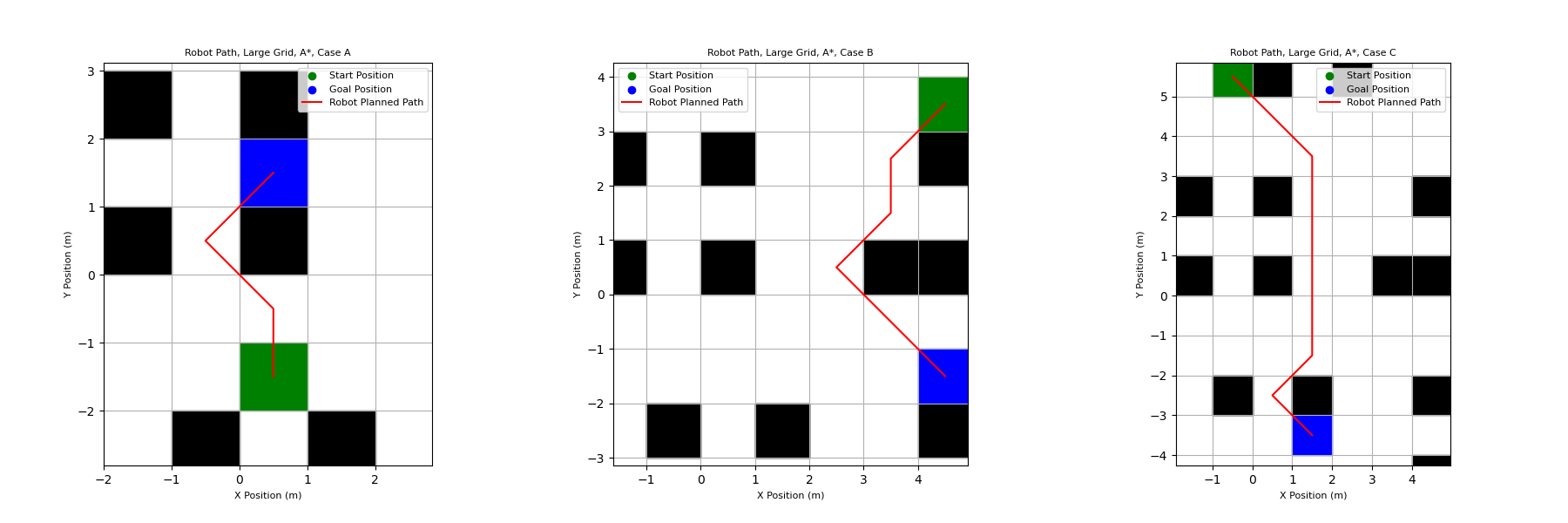
The A* algorithm is used in this assignment to find a path between two cells on a grid while navigating around cells that contain obstacles. This algorithm uses a heuristic equation to direct its search toward the goal cell, as opposed to uniformed search algorithms which would search equally in all directions. The current and goal cells are both known, allowing the heuristic to be used to direct the search toward the goal.
The robot is able to move to any of the eight cells that surround it, and the algorithm determines which cell to move to next by estimating the total distance to the goal if it moves in each direction. It does this using the equation below:
f = h + g
The estimated total cost from the start to the goal is given by f, g is the cost of moving from the start cell to the cell being evaluated, and h is the estimated cost of moving from the cell being evaluated to goal cell. The variable g is calculated by adding the cost of moving from the current cell to the cell being evaluated and the cost of moving from the start cell to the current cell. The cost of moving to an open cell is given as 1, while moving into a cell occupied by an obstacle is 1000. The high cost of movements into cells with obstacles is what allows the algorithm to navigate around obstacles. Below are the paths output by the algorithm for three different start and goal locations on the grid.