ffmpeg-go is golang port of https://github.com/kkroening/ffmpeg-python
check examples/example_test.go and ffmpeg_test.go for more examples.
You can get this package via:
go get -u github.com/schaffung/ffmpeg-go
Note:
ffmpeg-gomakes no attempt to download/install FFmpeg, asffmpeg-gois merely a pure-Go wrapper - whereas FFmpeg installation is platform-dependent/environment-specific, and is thus the responsibility of the user, as described below.
Before using ffmpeg-go, FFmpeg must be installed and accessible via the $PATH environment variable.
There are a variety of ways to install FFmpeg, such as the official download links, or using your package manager of choice (e.g. sudo apt install ffmpeg on Debian/Ubuntu, brew install ffmpeg on OS X, etc.).
Regardless of how FFmpeg is installed, you can check if your environment path is set correctly by running the ffmpeg command from the terminal, in which case the version information should appear, as in the following example (truncated for brevity):
$ ffmpeg
ffmpeg version 4.2.4-1ubuntu0.1 Copyright (c) 2000-2020 the FFmpeg developers
built with gcc 9 (Ubuntu 9.3.0-10ubuntu2)
Note: The actual version information displayed here may vary from one system to another; but if a message such as
ffmpeg: command not foundappears instead of the version information, FFmpeg is not properly installed.
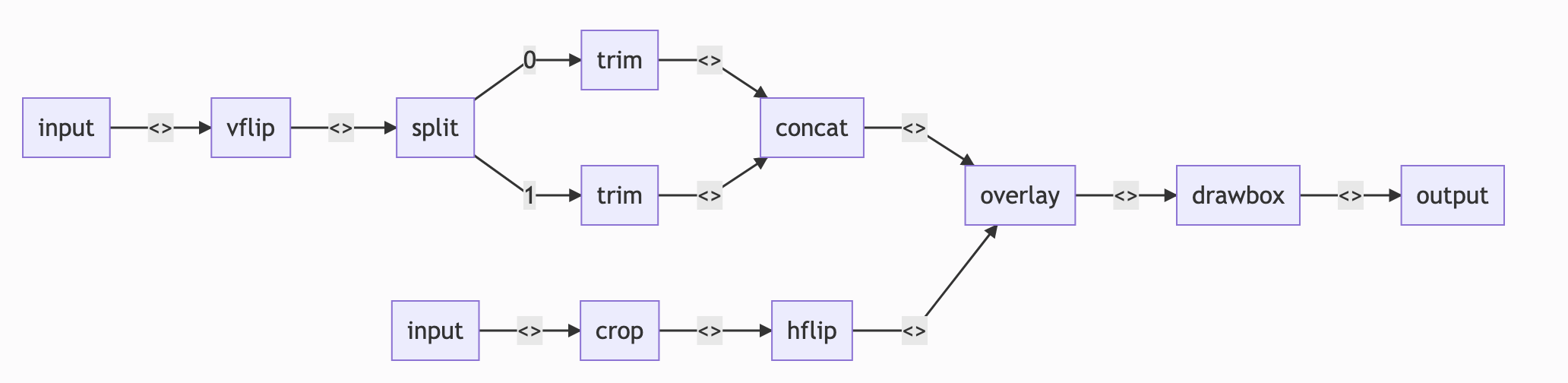
split := Input(TestInputFile1).VFlip().Split()
split0, split1 := split.Get("0"), split.Get("1")
overlayFile := Input(TestOverlayFile).Crop(10, 10, 158, 112)
err := Concat([]*Stream{
split0.Trim(KwArgs{"start_frame": 10, "end_frame": 20}),
split1.Trim(KwArgs{"start_frame": 30, "end_frame": 40})}).
Overlay(overlayFile.HFlip(), "").
DrawBox(50, 50, 120, 120, "red", 5).
Output(TestOutputFile1).
OverWriteOutput().
Run()err := ffmpeg.Input("./sample_data/in1.mp4").
Output("./sample_data/out1.mp4", ffmpeg.KwArgs{"c:v": "libx265"}).
OverWriteOutput().ErrorToStdOut().Run()err := ffmpeg.Input("./sample_data/in1.mp4", ffmpeg.KwArgs{"ss": 1}).
Output("./sample_data/out1.mp4", ffmpeg.KwArgs{"t": 1}).OverWriteOutput().Run()
assert.Nil(t, err)// show watermark with size 64:-1 in the top left corner after seconds 1
overlay := ffmpeg.Input("./sample_data/overlay.png").Filter("scale", ffmpeg.Args{"64:-1"})
err := ffmpeg.Filter(
[]*ffmpeg.Stream{
ffmpeg.Input("./sample_data/in1.mp4"),
overlay,
}, "overlay", ffmpeg.Args{"10:10"}, ffmpeg.KwArgs{"enable": "gte(t,1)"}).
Output("./sample_data/out1.mp4").OverWriteOutput().ErrorToStdOut().Run()result:
err := ffmpeg.Input("./sample_data/in1.mp4", ffmpeg.KwArgs{"ss": "1"}).
Output("./sample_data/out1.gif", ffmpeg.KwArgs{"s": "320x240", "pix_fmt": "rgb24", "t": "3", "r": "3"}).
OverWriteOutput().ErrorToStdOut().Run()result:
func ExampleReadFrameAsJpeg(inFileName string, frameNum int) io.Reader {
buf := bytes.NewBuffer(nil)
err := ffmpeg.Input(inFileName).
Filter("select", ffmpeg.Args{fmt.Sprintf("gte(n,%d)", frameNum)}).
Output("pipe:", ffmpeg.KwArgs{"vframes": 1, "format": "image2", "vcodec": "mjpeg"}).
WithOutput(buf, os.Stdout).
Run()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return buf
}
reader := ExampleReadFrameAsJpeg("./sample_data/in1.mp4", 5)
img, err := imaging.Decode(reader)
if err != nil {
t.Fatal(err)
}
err = imaging.Save(img, "./sample_data/out1.jpeg")
if err != nil {
t.Fatal(err)
}result :
// get multiple output with different size/bitrate
input := ffmpeg.Input("./sample_data/in1.mp4").Split()
out1 := input.Get("0").Filter("scale", ffmpeg.Args{"1920:-1"}).
Output("./sample_data/1920.mp4", ffmpeg.KwArgs{"b:v": "5000k"})
out2 := input.Get("1").Filter("scale", ffmpeg.Args{"1280:-1"}).
Output("./sample_data/1280.mp4", ffmpeg.KwArgs{"b:v": "2800k"})
err := ffmpeg.MergeOutputs(out1, out2).OverWriteOutput().ErrorToStdOut().Run()see complete example at: showProgress
func ExampleShowProgress(inFileName, outFileName string) {
a, err := ffmpeg.Probe(inFileName)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
totalDuration := gjson.Get(a, "format.duration").Float()
err = ffmpeg.Input(inFileName).
Output(outFileName, ffmpeg.KwArgs{"c:v": "libx264", "preset": "veryslow"}).
GlobalArgs("-progress", "unix://"+TempSock(totalDuration)).
OverWriteOutput().
Run()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
ExampleShowProgress("./sample_data/in1.mp4", "./sample_data/out2.mp4")result
progress: .0
progress: 0.72
progress: 1.00
progress: donesee complete example at: opencv
e := ComplexFilterExample("./sample_data/in1.mp4", "./sample_data/overlay.png", "./sample_data/out2.mp4")
err := e.RunWithResource(0.1, 0.5)
if err != nil {
assert.Nil(t, err)
}result from command top: we will see ffmpeg used 0.5 core as expected.
> top
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
1386105 root 20 0 2114152 273780 31672 R 50.2 1.7 0:16.79 ffmpegfunction view generate mermaid chart, which can be use in markdown or view online
split := Input(TestInputFile1).VFlip().Split()
split0, split1 := split.Get("0"), split.Get("1")
overlayFile := Input(TestOverlayFile).Crop(10, 10, 158, 112)
b, err := Concat([]*Stream{
split0.Trim(KwArgs{"start_frame": 10, "end_frame": 20}),
split1.Trim(KwArgs{"start_frame": 30, "end_frame": 40})}).
Overlay(overlayFile.HFlip(), "").
DrawBox(50, 50, 120, 120, "red", 5).
Output(TestOutputFile1).
OverWriteOutput().View(ViewTypeFlowChart)
fmt.Println(b)