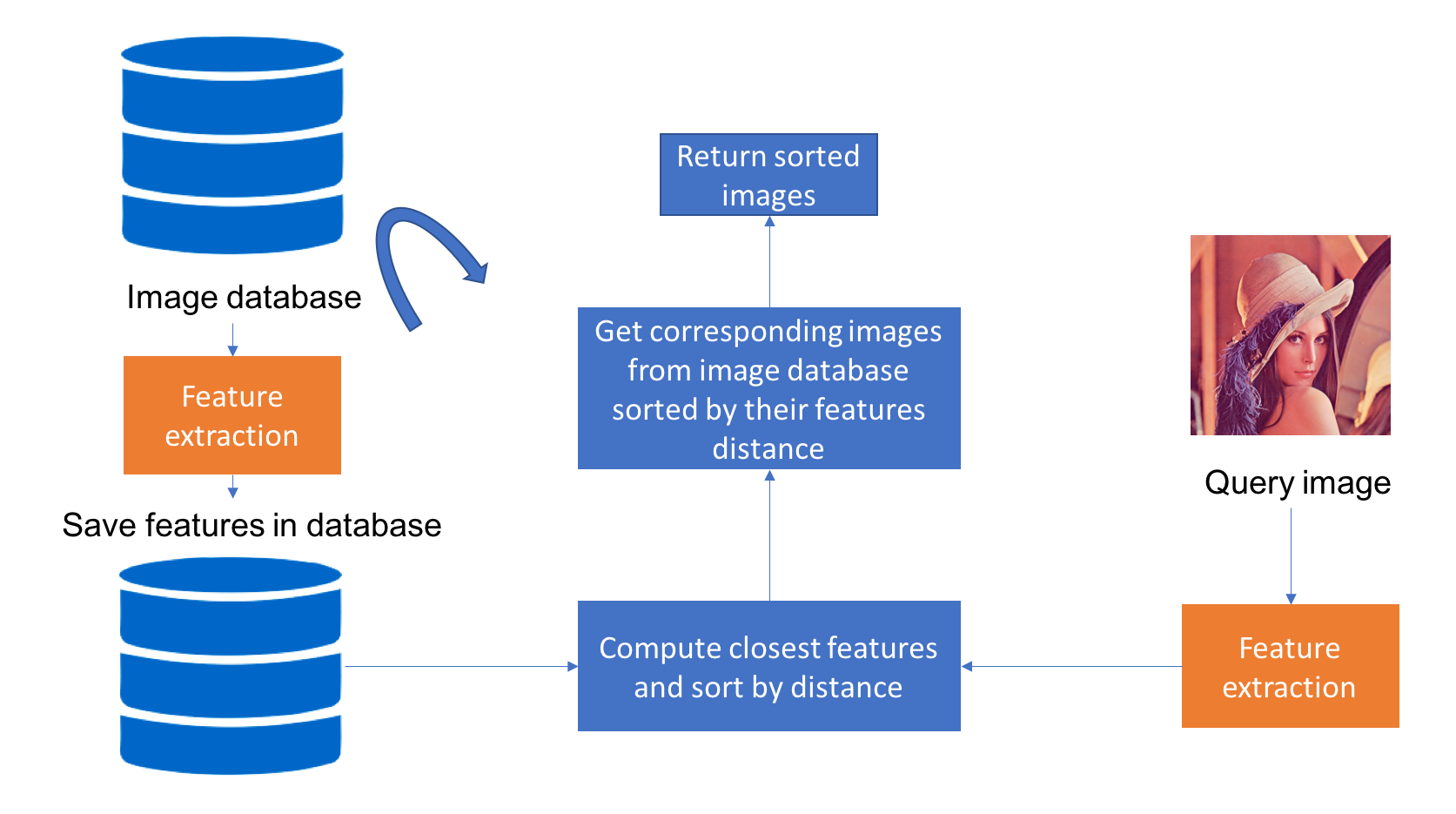
Content-based image retrieval (CBIR) is the application of computer vision techniques to the image retrieval problem, which involves searching for digital images in large databases.
Content-based means that the search analyzes the contents of the image rather than metadata such as keywords, tags, or descriptions associated with the image.
The process consists of four steps:
- Extraction of features from an image database to form a feature database.
- Extraction of features from the input image.
- Finding the most similar features in the database.
- Returning the image associated with the found features.
The goal is to determine the most suitable model and distance similarity for finding similar images. To achieve this, we explore three different similarity measurements and five models for feature extraction.
The objective is to find the right combination (extraction algorithm & similarity measure) that allows us to obtain relevant answers.
In our exploration, we used the Fashion dataset Apparel available on Kaggle. To evaluate different combinations (model + measurement), we utilized three metrics:
- Mean Average Precision (MAP) for the system's robustness.
- Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR) for the relevance of the first element.
- Average time per query.
The evaluation formulas are referred to in this Stanford course.
All the experiments can be reproduced using the Makefile:
- Create the necessary virtual environment for all tests:
make venv- Create a repository for features and the .env file with different paths:
make prepare- Create the feature dataset:
make featuresExperimental results are presented in the report folder. Consult the PDF file and graphs to analyze the performance of different combinations.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.