A brute-force GPU implementation of chemical fingerprint similarity searching. Its intended use is to be kept alive as a service with an entire library loaded into graphics card memory. It has python scripts included which use RDKit to generate fingerprints, but the C++/Cuda backend are agnostic to the data once it's been created.
Architecture and benchmarks were presented in a presentation at the 2018 RDKit European UGM.
The commercial GPUSimilarity product ("FPSim GPU") with additional enhancements, maintenance and support is available from Schrödinger. Enhancements to the incentive version will be periodically merged into the open source version, similar to Incentive PyMOL.
On a machine with four Tesla V100, searching one billion compounds takes ~0.2 seconds.
See RDKit Presentation for much more in depth benchmarks (that are slightly out of date).
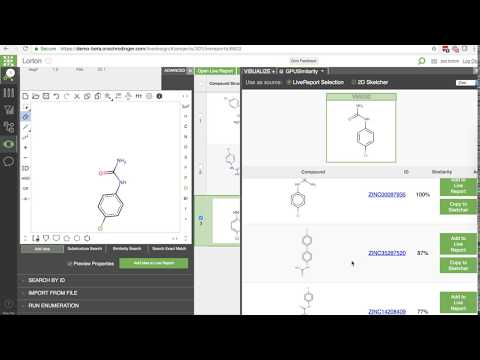
Here is a video of this backend being utilized for immediate-response searching inside Schrödinger's LiveDesign application:
It is highly recommended that you use docker for building/running.
- RDKit (At Python level, not compilation)
- Qt 5.2+ (including QtNetwork)
- PyQt
- Cuda SDK, CUDACXX env variable pointing to nvcc
- cmake 3.10.2+
- C++11 capable compiler
- Boost test libraries
- Optional: Doxygen for generating documents
Recommended only for development, see Docker
From parent directory of source:
mkdir bld
cd bld
ccmake ../gpusimilarity
make -j5
ctest
If Cuda, boost or doxygen are not found, start ccmake with the following options:
ccmake -DCMAKE_CUDA_COMPILER=/path/to/nvcc -DBOOST_ROOT=/path/to/boost/directory -DDOXYGEN_EXECUTABLE=/path/to/doxygen
Install doxygen on system
make doc_doxygen
The result is in bld/doc/html
Recommended only for development, see Docker
From build directory:
python3 ${SRC_DIR}/python/gpusim_server.py <fingerprint fsim file>
From build directory:
python3 ${SRC_DIR}/python/gpusim_server.py <fingerprint fsim file> --http_interface
Easiest from rdkit conda with pyqt installed:
From source python directory:
python3 gpusim_createdb.py <input smi.gz file> <fingerprint fsim file>
From build directory:
./gpusimserver <dbname>.fsim
python3 python ${SRC_DIR}/python/gpusim_search.py <dbname>Note: No .fsim extension is used for gpusim_search.py
This may be useful to determine if the backend is having Cuda/GPU problems.