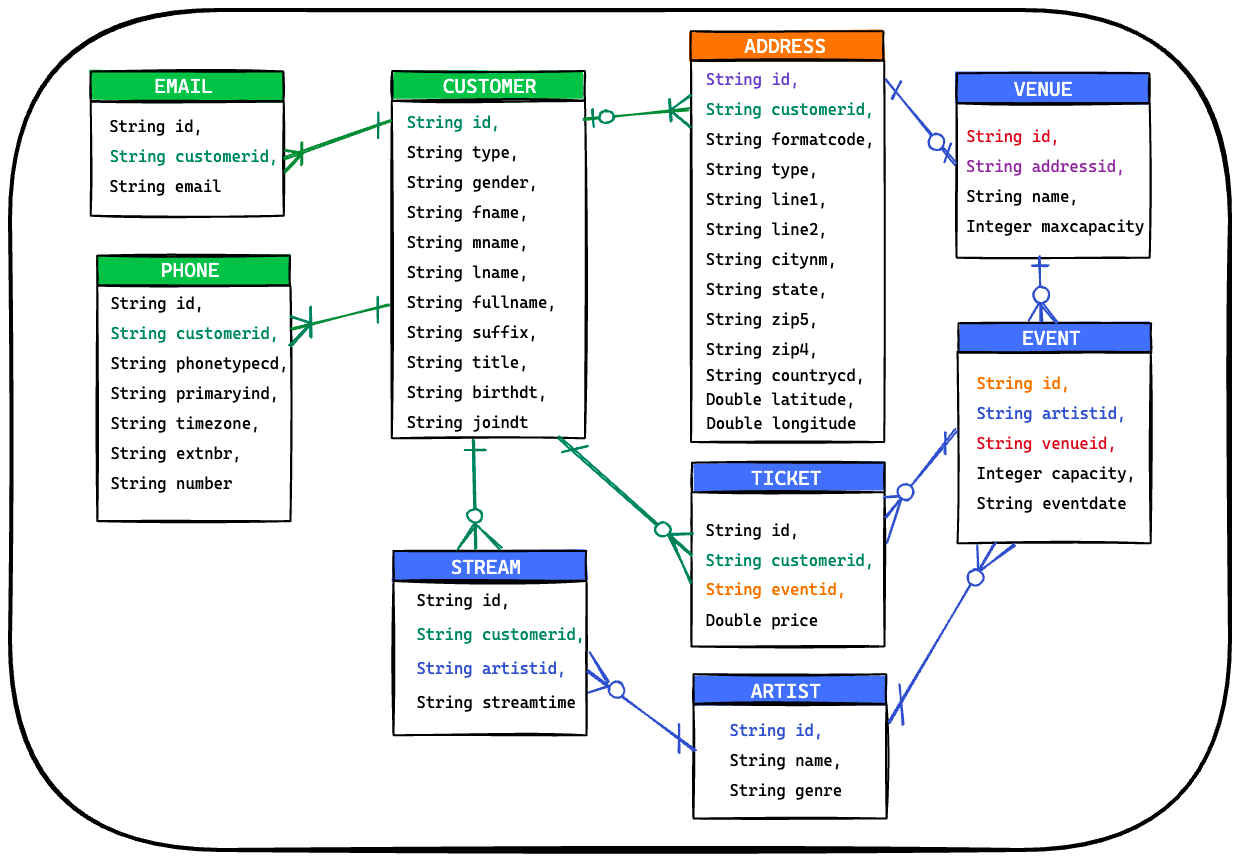
The Data Demo generates fake data aligned with the ERD below.
The Data Demo can throw data into the following environments -
- Local Kafka (Confluent) (Docker)
- Local Kafka (Redpanda) (Docker)
- Local Postgres (Docker)
- Local Postgres -> Kafka Connect -> Kafka (Docker)
- Confluent Cloud (tf-ccloud)
For more details on running the Data Demo, jump ahead to the getting started section after installing the prerequisites.
- In the root gradle.properties file, select your
runtimeMode(brief descriptions below).postgres: data-demo will inject mock data into a local postgres database.kafka: data-demo will produce mock data into Kafka. A redis cache is used to keep track of the produced mock entities.kafka-cloud: data-demo will connect to a Confluent Cloud cluster and produce mock data. A local redis cache is still used to keep track of the produced mock entities.
- Start the environment for your selected
runtimeMode - If you're enabling tracing, start the tracing environment and set
tracingEnabled=truein thegradle.propertiesfile. - Configure the initial load volumes (these do not apply if running the
mockdata-api). These properties are in thegradle.propertiesfile.initialLoadCustomers=20 initialLoadArtists=20 initialLoadVenues=15 initialLoadEvents=100 initialLoadTickets=10000 initialLoadStreams=50000
- Run
data-demo. There are 2 modes of operation, a daemon and an API. More details can be found on each below.mockdata-daemon, run via./gradlew bootRunDaemon- The daemon will hydrate the configured initial load volumes and then continue to run and inject random data into the environment.
mockdata-api, run via./gradlew bootRunAPI- The API exposes endpoints to manually create entities. Import the Insomnia Collection to explore the available endpoints.
- To validate the API, you can fire off a sample request with this command ->
curl -X POST localhost:8080/customers | jq
- To validate the API, you can fire off a sample request with this command ->
- The API exposes endpoints to manually create entities. Import the Insomnia Collection to explore the available endpoints.
The docker-compose gradle plugin is used to start the services in appropriate docker-compose files.
- Start Kafka Services
-
Typical set-up of 3 brokers with replication of data between brokers.
# KAFKA ./gradlew kafkaComposeUp ./gradlew kafkaComposeDown ./gradlew kafkaComposeDownForced -
Minimal set-up of 1 broker (use on limited hardware)
# KAFKA ./gradlew kafka1ComposeUp ./gradlew kafka1ComposeDown ./gradlew kafka1ComposeDownForced
- Validate Environment
-
In each directory there is a bin directory of kafka command line tools. These are actually scripts to run the command on the broker (to avoid additional software installed on your machine).
-
Be sure to run from either
kafka-1orkafka-3as container names are different between them. -
./bin/kafka-topics --list- Will list all the topics on the cluster, you should see 5 topics in a newly created cluster.
__consumer_offsetsis a topic internally created for Kafka._schemasis used by the schema-registry which is used for data governance.connect-cluster-*topics will be used by the Kafka Connect service that will be used to connect Kafka to external systems.
__consumer_offsets _schemas connect-cluster-config connect-cluster-offsets connect-cluster-status - Will list all the topics on the cluster, you should see 5 topics in a newly created cluster.
-
./bin/kafka-topics --create --topic test --partitions 2 -
./bin/kafka-console-producer --topic test- each line you type will create a message to a topic
- hit
ctrl-dto exit
-
./bin/kafka-console-consumer --topic test --from-beginning- Each line sent sent by the producer will show up here in the consumer.
--from-beginningwill have it start with the earliest message, omitting this means it will only display messages after it is started.
-
Starting a producer and consumer in two separate consoles is the best way to start seeing how Kafka works.
- Advance concepts to be learned through the course will be:
- Keys for Messages
- Partitioning of Messages
- Replication of Messages
- Consumer Groups
- Advance concepts to be learned through the course will be:
- Validate Environment
- If all containers seem to be running (healthy), navigate to Control Center at http://localhost:9021 and poke around a bit. You should see a few things but feel free to explore as much as you want.
- A single cluster named "controlcenter.cluster"
- When clicking on the "controlcenter.cluster" cluster, 1 Broker
- When clicking on Topics, No Topics
- If you unselect "Hide internal topics", you should see the topics used by CC itself to manage its own state.
- If all containers seem to be running (healthy), navigate to Control Center at http://localhost:9021 and poke around a bit. You should see a few things but feel free to explore as much as you want.
-
Start Kafka Services
- Redpanda is a Kafka-compatible streaming data platform that is JVM-free & ZooKeeper®-free. It starts fast and requires fewer resources, making it great for local environments.
# KAFKA ./gradlew redpandaComposeUp ./gradlew redpandaComposeDown ./gradlew redpandaComposeDownForced -
Validate Environment
- Redpanda Console available at
http://localhost:3000
- Redpanda Console available at
-
Start Postgres Services
# POSTGRESQL ./gradlew postgresComposeUp ./gradlew postgresComposeDown ./gradlew postgresComposeDownForced -
Validate Environment
- pgAdmin4 (Postgres Exploration UI) available at
http://localhost:5433- username:
root@email.com - password:
root - postgres database password:
postgres
- username:
- pgAdmin4 (Postgres Exploration UI) available at
If you're planning to load data from Postgres into Kafka via Kafka Connect, run the following commands.
-
Start All Services (Postgres & Kafka)
./gradlew fullComposeUp ./gradlew fullComposeDown ./gradlew fullComposeDownForced
-
Validate Environment
- Postgres
- pgAdmin4 (Postgres Exploration UI) available at
http://localhost:5433- username:
root@email.com - password:
root - postgres database password:
postgres
- username:
- pgAdmin4 (Postgres Exploration UI) available at
- Kafka
- Redpanda Console available at
http://localhost:3000
- Redpanda Console available at
- Postgres
The Confluent Cloud environment is provisioned via Terraform. You will need the Confluent CLI installed and logged in.
- Provision Confluent Cloud Environment - see the tf-ccloud readme for more details.
- After the environment is provisioned, configure the bootstrap-servers, api-key, and api-secret. These values are expected by the application-ccloud.yaml properties file.
terraform output resource-ids export CONFLUENT_CLOUD_BOOTSTRAP_SERVER="pkc-mg1wx.us-east-2.aws.confluent.cloud:9092" export DATA_DEMO_CONFLUENT_CLOUD_API_KEY="**REDACTED**" export DATA_DEMO_CONFLUENT_CLOUD_API_SECRET="**REDACTED**"
- You will still need to start Redis locally, as it is needed by data-demo for caching the created entities. This allows the tool to generate data with referential integrity.
./gradlew redisComposeUp ./gradlew redisComposeDown ./gradlew redisComposeDownForced
- Redis Commander available at http://localhost:6380
If you want to run the OpenTelemetry stack and enable distributed tracing, start up the tracing services (Jaeger).
This command is run separate from the above commands that start postgres/kafka. The networking between the two docker compose files is configured to allow them to communicate.
./gradlew tracingComposeUp
./gradlew tracingComposeDown
./gradlew tracingComposeDownForced- Validate Environment
- Jaeger (Tracing UI) available at
http://localhost:16686
- Jaeger (Tracing UI) available at
Once the tracing backend is started, flip the tracingEnabled flag to true in the root gradle.properties file before starting up the API or Daemon.
Want to run Grafana Tempo instead of Jaeger? Update the tracing dockerCompose config in the root build.gradle to point to the tempo folder as shown below.
tracing {
useComposeFiles = [
'./observability/tempo/docker-compose.yml'
]
}Ready to do something with this data? Go check out the stream-processing-workshop.
The following error is likely the cause of not having Java 17 installed.
> error: invalid source release: 17./network.sh doesn't work
Ideally, use git bash to run the ./gradlew kafkaComposeUp
OR
- Create the network manually -
docker network create dev-local - Comment out the
kafkaComposeUp.dependsOn dockerCreateNetworkline in the rootbuild.gradle - Run
./gradlew kafkaComposeUp
- add user to permission group to use docker (without sudo)
- install
docker-composemanually:sudo apt install docker-compose