This repository benchmarks 7 vector databases for music semantic search, using a shared dataset and query set. It provides both a CLI benchmarking tool and a web UI for side-by-side DB comparison.
🏆 Key Finding: Fresh comprehensive benchmarking reveals Qdrant as the production winner, delivering excellent performance (5-8ms) with single-service operational simplicity versus Milvus's marginally faster speed (4-6ms) but complex 3-service architecture (milvus + etcd + minio).
- Comprehensive benchmarking: ingest time, query latency, recall, hit rate, and throughput (QPS)
- 7 Vector Databases: Qdrant, Milvus, Weaviate, ChromaDB, Pinecone, SQLite, and TopK
- Production-grade testing: Up to 20 iterations for statistical reliability
- Flexible embedding: Use
sentence-transformers(default) or OpenAI embeddings - Heuristic relevance: Weak label matching using tags/genres for recall/hit metrics
- Rich CLI: Many flags for DB selection, concurrency, top-k sweep, teardown, etc.
- Modern UI: FastAPI backend + static frontend for live DB comparison
- Automated result plots: Generates summary charts and per-k metrics tables
- Comprehensive reporting: Detailed analysis with production recommendations
| Database | Deployment | Performance Tier | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🥇 Qdrant | Local/Cloud | Champion | Production systems (excellent speed + single service) |
| 🥈 Milvus | Local | High-Performance | Maximum speed with complex 3-service infrastructure |
| 🥉 Weaviate | Local/Cloud | Good | Feature-rich applications |
| ChromaDB | Local | Solid | Development & moderate workloads |
| Pinecone | Cloud | Managed | Fully managed cloud deployments |
| SQLite | Embedded | Specialized | Embedded/edge applications |
| TopK | Cloud | Managed Service | Cloud vector search with operational simplicity |
Use the Muse Musical Sentiment dataset from Kaggle. Place the CSV as data/muse.csv.
You can test with data/sample_data.csv for a dry run.
- Install dependencies
python -m venv .venv && source .venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt- Configure environment
- Copy
.env.exampleto.envand fill in DB URLs/API keys as needed
- Start local DBs (optional)
docker compose -f scripts/docker-compose.yml up -d- Generate embeddings
python embeddings/embed.py --csv data/muse.csv --out data/embeddings.parquet
# For OpenAI: add --use_openai [--model text-embedding-3-large]- Run the benchmark
python benchmark.py --csv data/muse.csv --embeddings data/embeddings.parquet --dbs qdrant milvus weaviate chroma pinecone sqlite topk --topk 10 --repetitions 15
# For TopK: add 'topk' to --dbs list
# See all CLI flags with: python benchmark.py --help- View results
- Summary and per-k plots:
results/ - Metrics:
results/metrics.json
After starting the Docker services, you can access various database management interfaces:
| Database | UI Access | Credentials | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qdrant | http://localhost:6333/dashboard | None | Built-in web dashboard |
| Milvus | http://localhost:3000 | None | Attu management interface |
| MinIO | http://localhost:9001 | minioadmin/minioadmin | Milvus object storage console |
| Database | API Endpoint | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Weaviate | http://localhost:8080/v1/meta | RESTful API + GraphQL |
| ChromaDB | http://localhost:8001 | HTTP API (v2) |
| Pinecone Local | http://localhost:5080/indexes | Compatible with Pinecone cloud API |
 Qdrant web interface showing collections and search
Qdrant web interface showing collections and search
 Attu interface displaying Milvus collections and data
Attu interface displaying Milvus collections and data
| Service | Internal Port | External Port | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qdrant | 6333, 6334 | 6333, 6334 | Vector database + dashboard |
| Milvus | 19530, 9091 | 19530, 9091 | gRPC API + health check |
| Attu | 3000 | 3000 | Milvus web UI |
| Weaviate | 8080, 50051 | 8080, 50051 | REST + gRPC APIs |
| ChromaDB | 8000 | 8001 | HTTP API |
| Pinecone | 5080-5090 | 5080-5090 | Local API server |
| MinIO | 9000, 9001 | 9000, 9001 | Object storage + console |
| etcd | 2379 | - | Milvus metadata store |
python benchmark.py --csv data/muse.csv --embeddings data/embeddings.parquet --dbs qdrant milvus weaviate chroma pinecone sqlite topk --topk 10 --repetitions 15 [--teardown_after_benchmark]
# TopK included in example aboveKey flags:
--dbs: List of DBs to benchmark (qdrant, milvus, weaviate, chroma, pinecone, sqlite, topk)--topk: Top-k for search (default: 10)--topk_sweep: List of k values to sweep (e.g. 5 10 50)--repetitions: Number of repetitions per query--concurrency: Number of concurrent query workers--teardown_after_benchmark: Delete DB/index after run--query_model: Embedding model for queries--queries: Path to YAML file with queries/expected labels
To run the benchmark across multiple topk values in a single command, use the --topk_sweep argument. The script will loop through each value sequentially for each database. This is more efficient than running the script multiple times.
python benchmark.py --csv data/muse.csv --embeddings data/embeddings.parquet --dbs qdrant milvus weaviate chroma pinecone sqlite topk --repetitions 15 --topk_sweep 5 10 15 20 25 50
# TopK included in example aboveResults:
- Plots and tables in
results/(per-k and summary) - All metrics in
results/metrics.json
By default, uses sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2. To use OpenAI embeddings:
python embeddings/embed.py --csv data/muse.csv --out data/embeddings.parquet --use_openai --model text-embedding-3-largeThe ui/ folder provides a FastAPI backend and static frontend for live, side-by-side DB search and latency comparison.
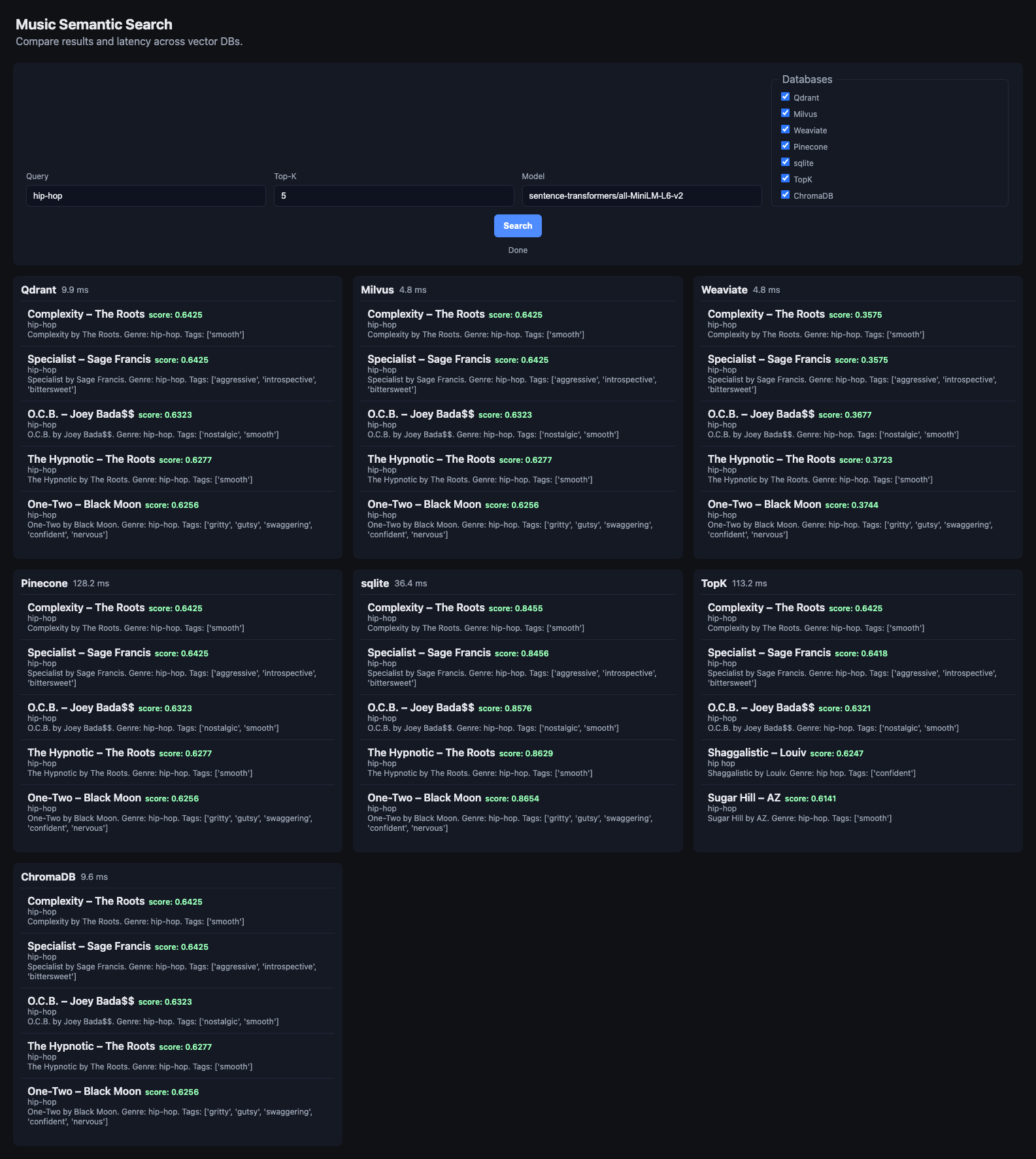 Live comparison of vector databases with real-time latency measurements for music semantic search
Live comparison of vector databases with real-time latency measurements for music semantic search
- Compare Qdrant, Milvus, Weaviate, ChromaDB, Pinecone, SQLite, and TopK in parallel
- Per-DB query latency in ms
- Simple, modern UI (HTML/JS/CSS)
- Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt- Configure
- Create
.envin repo root with DB endpoints and API keys
- Run the server
uvicorn ui.backend.server:app --reload --port 8000- Open the app
- Go to http://localhost:8000
benchmark.py– Main benchmarking script (CLI)embeddings/embed.py– Embedding generation (sentence-transformers or OpenAI)databases/– DB client wrappers (6-7 vector databases including TopK)plot_benchmarks.py– Plots and summary tablesresults/– Output metrics and plots (per-k breakdown + summaries)ui/– Web UI (FastAPI backend + static frontend)BENCHMARK_REPORT.md– Comprehensive analysis and recommendationsrequirements.txt– Python dependencies
- If Docker ports conflict, edit
scripts/docker-compose.yml - If you see dimension mismatch errors, check embedding model and DB index size
- For OpenAI, set
OPENAI_API_KEYin your environment - For Pinecone, set API key in
.env - For TopK, set API key in
.env(includes automatic rate limiting) - Ensure sufficient disk space for Docker volumes (Milvus requires significant storage for 3-service setup)
- ChromaDB v2: Updated to v2 API with improved performance and excellent recall
Cannot connect to Milvus UI (Attu):
- Ensure Attu is running in the Docker network:
docker compose up -d attu - Use container name in connection:
milvus:19530(notlocalhost:19530) - Attu must be in the same Docker network to access Milvus
Port conflicts:
- Check what's using ports:
docker psandlsof -i :PORT - Stop conflicting containers:
docker stop CONTAINER_NAME - Modify ports in
scripts/docker-compose.ymlif needed
Container networking:
- UIs running outside Docker cannot access
localhost- they need container names - Use
docker compose logs SERVICE_NAMEto check for startup errors - Verify containers are healthy:
docker compose ps
This project conducted extensive benchmarking across 7 vector databases with up to 20 iterations for production-grade statistical reliability. Here are the key findings:
🥇 Production Winner: Qdrant
- Speed: 5.0-8.8ms (excellent performance)
- Recall: 0.97-1.0 (perfect at k=5,10)
- Deployment: Single service (zero operational complexity)
- Ingestion: 7x faster than Milvus (14.2s vs 104.4s)
- Best for: 99% of production systems
🥈 Speed Leader: Milvus
- Speed: 4.2-6.4ms (fastest queries)
- Recall: 0.94-1.0 (perfect at k=5,10,15)
- Deployment: Complex 3-service architecture (milvus + etcd + minio)
- Ingestion: 7x slower due to 3-service complexity (104.4s vs 14.2s)
- Best for: Teams with dedicated DevOps needing absolute maximum speed
🥉 Other Notable Performers:
- ChromaDB: Solid for development (8.0-9.8ms), excellent recall with v2 API
- Weaviate: Good performance (9.9-11.3ms) but variable P99 latencies
- Pinecone: Perfect recall but network latency (~102-115ms)
- SQLite: Perfect for embedded use cases (~27-30ms)
- TopK: Managed cloud service with operational simplicity (167-177ms latency)
- Performance vs Complexity Trade-off: Milvus achieves 15-20% faster queries but requires 3-service architecture (3x operational complexity)
- Operational Simplicity: Qdrant delivers excellent performance with single-service deployment and 7x faster ingestion
- Production Reality: Most teams benefit more from operational simplicity than marginal speed gains
- Recall Excellence: Both Qdrant and Milvus deliver perfect recall at critical k=5,10 values
Choose Qdrant for production deployments - it delivers excellent performance (90% of Milvus speed) with 300% operational simplicity advantage. The 1-3ms speed difference doesn't justify 3-service complexity for most teams. See BENCHMARK_REPORT.md for detailed analysis.