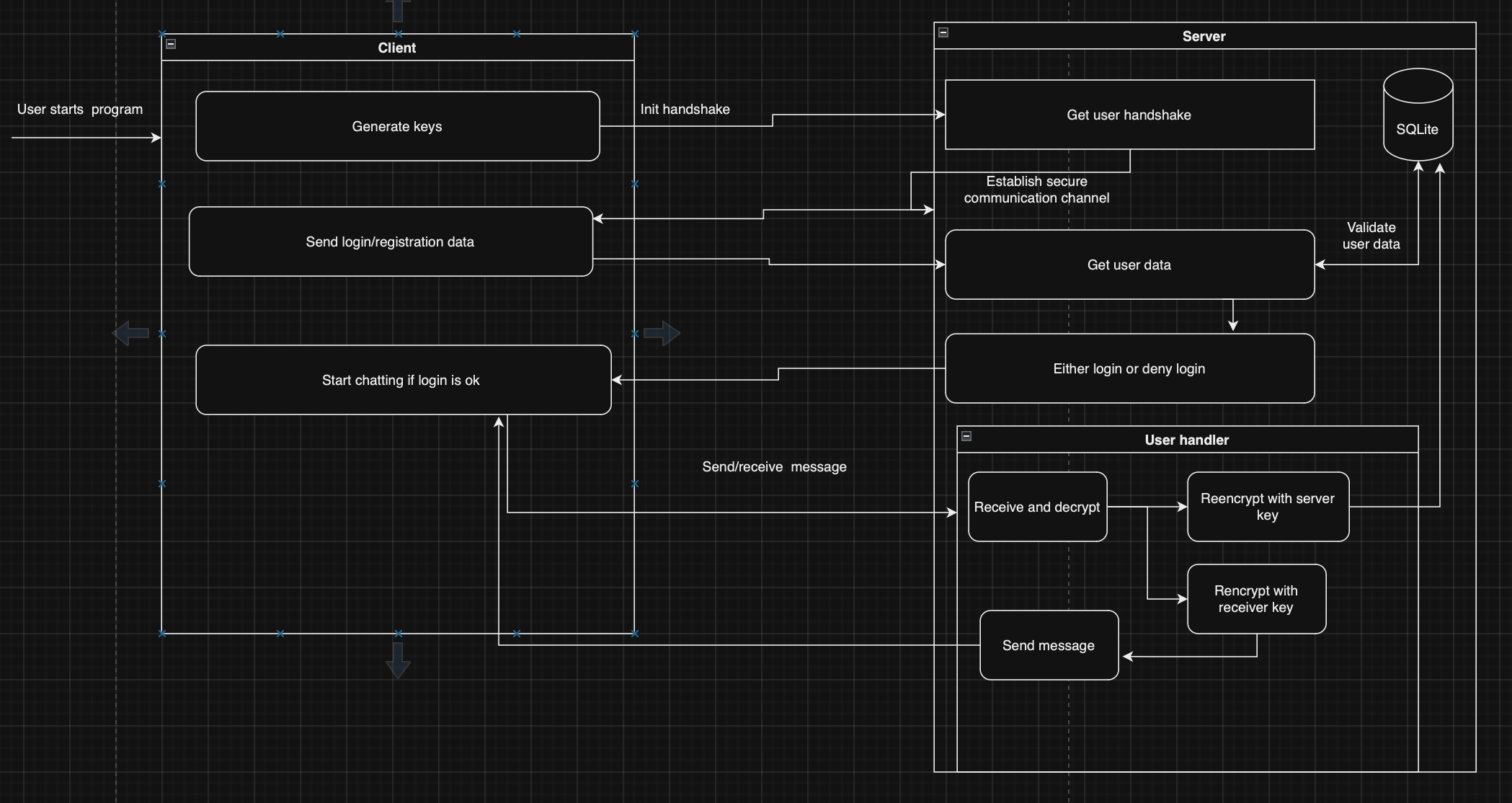
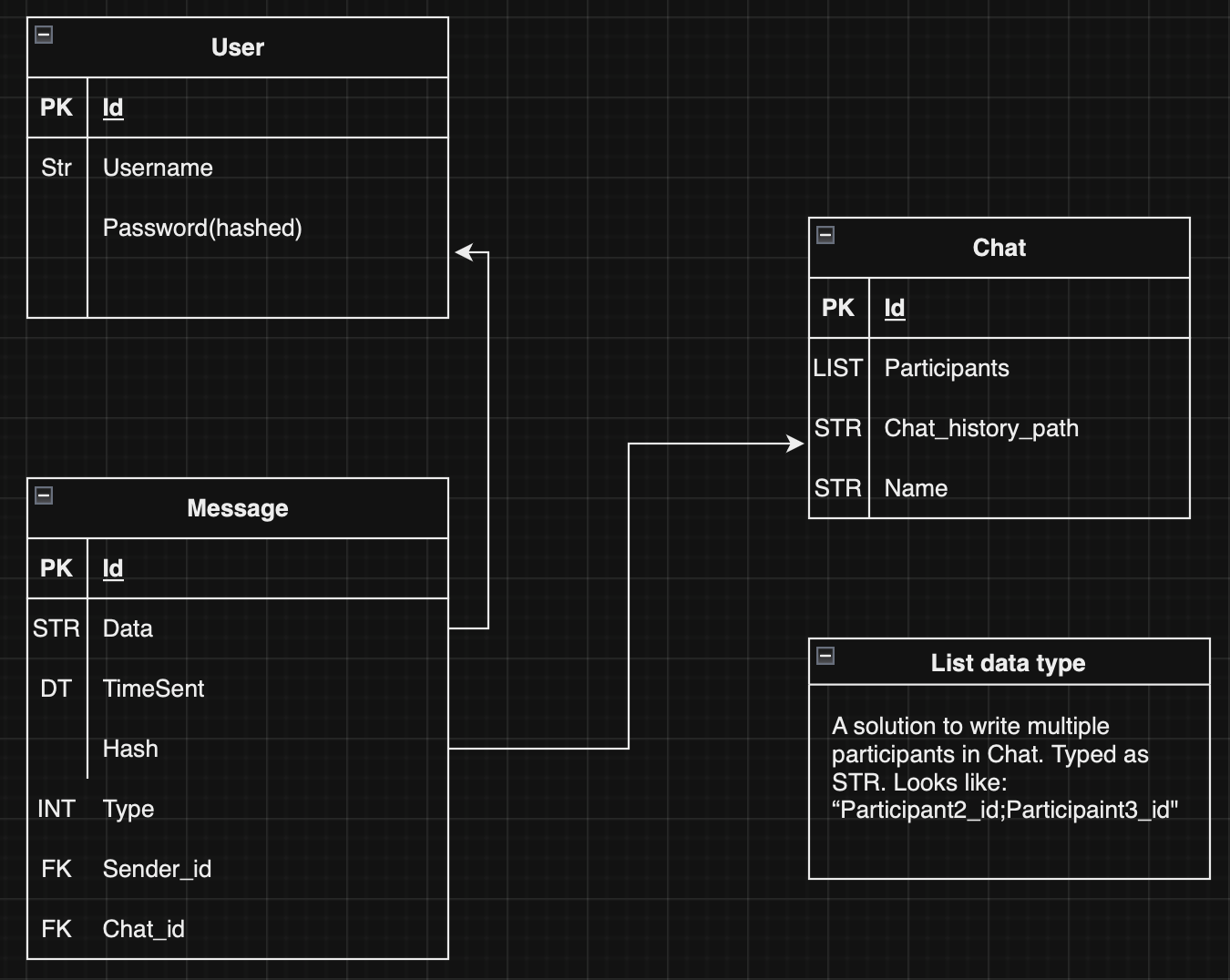
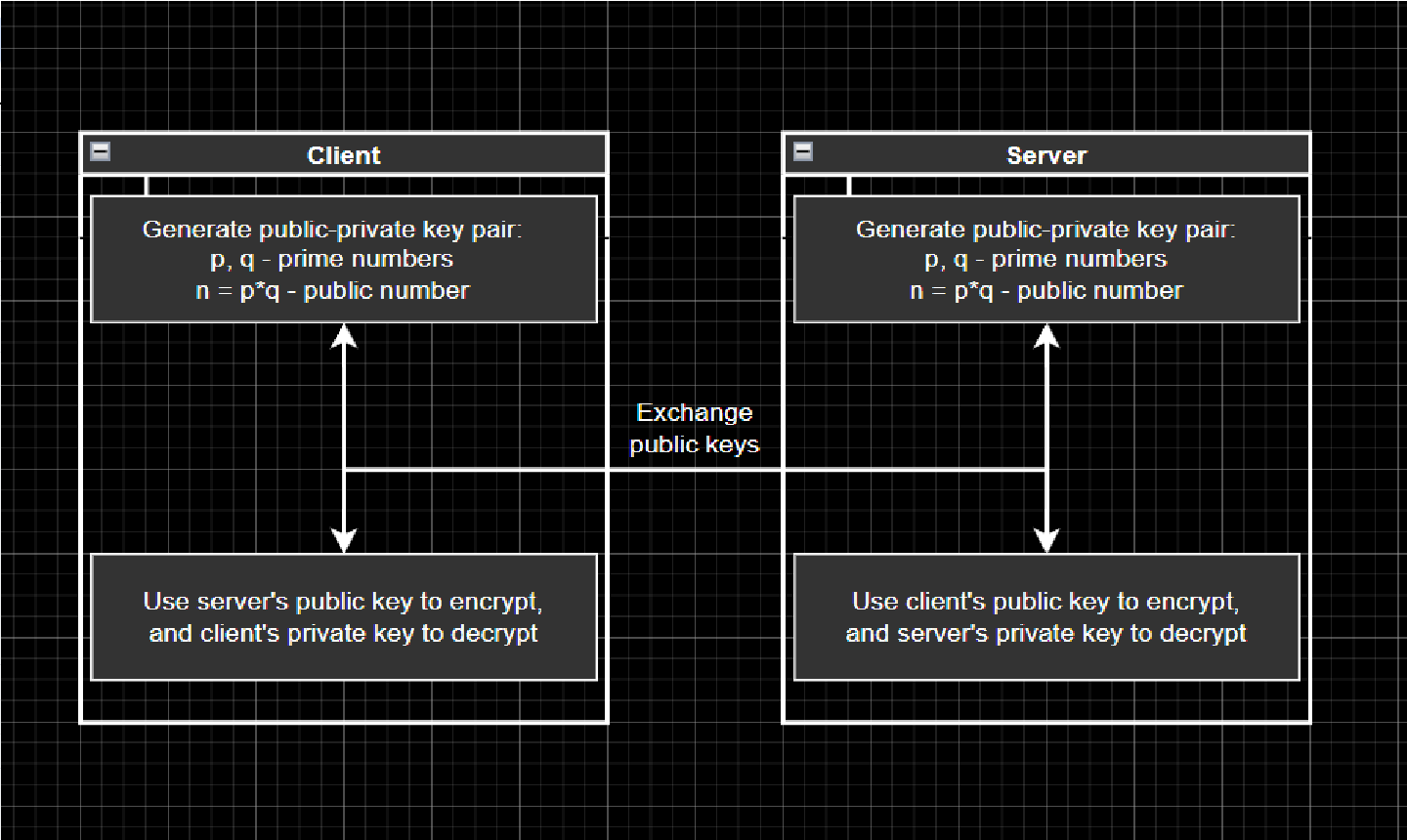
- Ivan Sen - Team lead, server development, RSA and ECC implementation.
- Daniil Bykov - ElGamal implementation, client development.
- Orest Chupa - Rabin implementation
- Edvard Student - DSA implementation
-
- Python 3.8 or higher
- Pipenv
- Git
- For the server: mysql-server
-
git clone https://github.com/senivan/Discrete-math-project2.git
-
cd Discrete-math-project2 -
pipenv shell
-
pipenv install
-
mysql -u root -p
CREATE DATABASE kryptos_app; cd Chat_app/server python3 server.py
-
cd Chat_app/client python3 client.py -
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: './server_utils/server_secret.json'You need to install the cryptography library manually:
touch server_utils/server_secret.json
And in the
server_utils/server_secret.jsonfile, add the following:{}Then run the server again.
In the server_config.json file, you can change the following parameters:
- 'encrypt':The encryption algorithm to use. It can be one of the following:
- 'ECC+AES-128(ECC)'
- 'RSA'
- 'ElGamal'
- 'port': The port to run the server on. Default is 8000
- 'host': The host to run the server on. Default is 'localhost'
- 'db': The database file to use. Default is 'db.sqlite3'
- 'debug_level': The log level to use. Default is 'INFO' - which displays all logs.
-
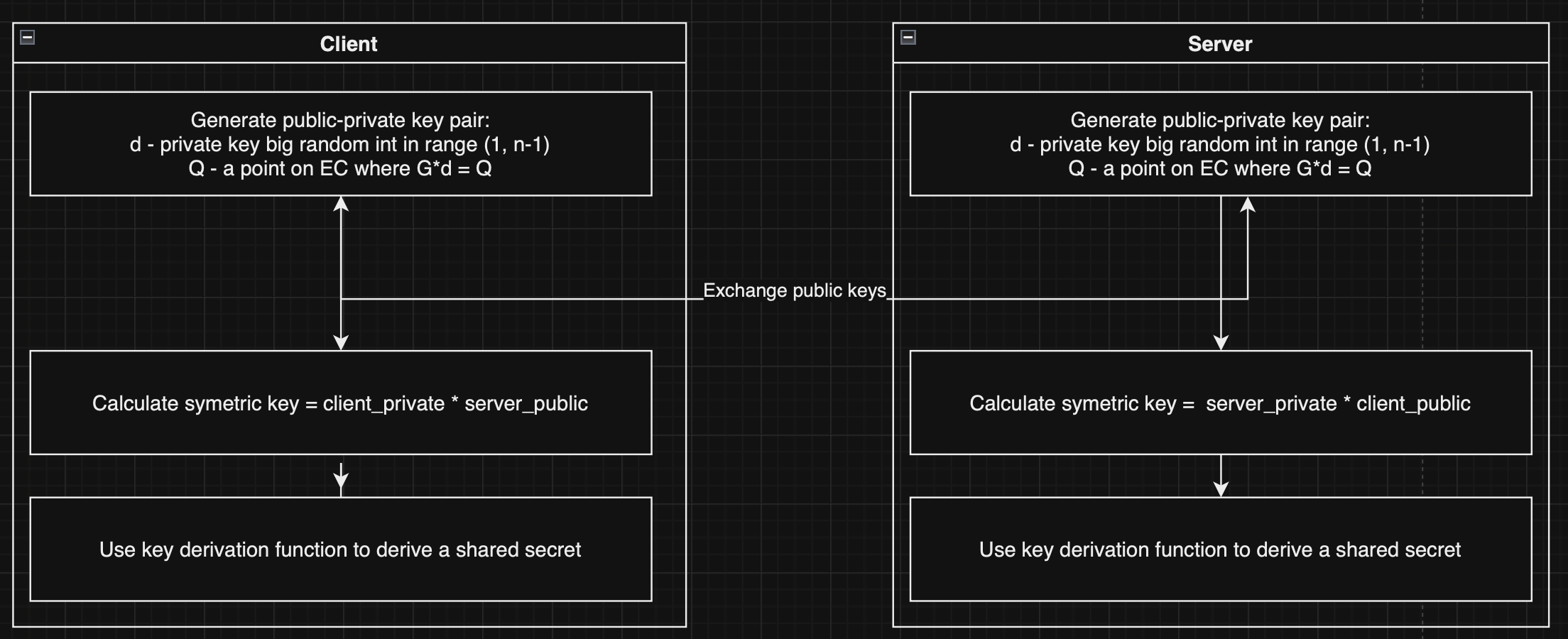
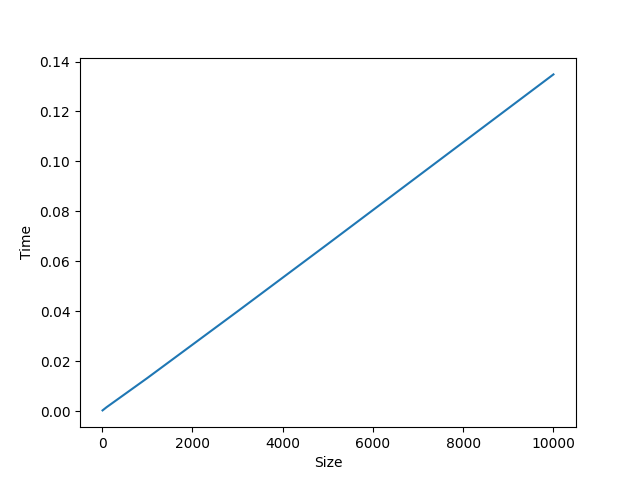
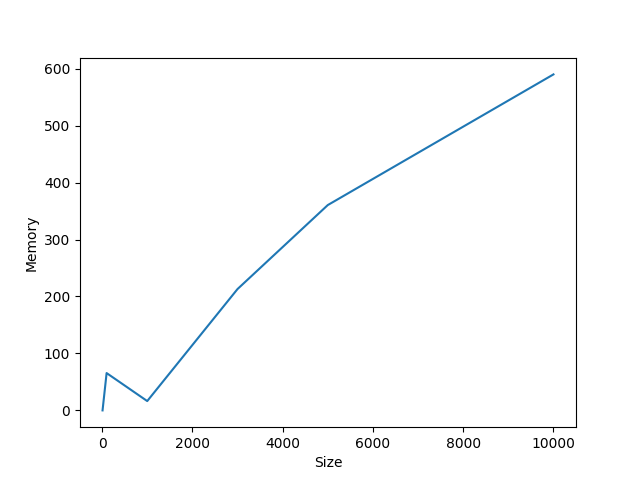
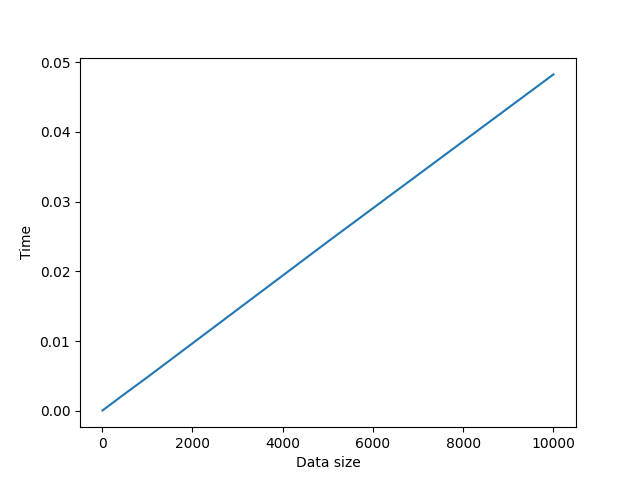
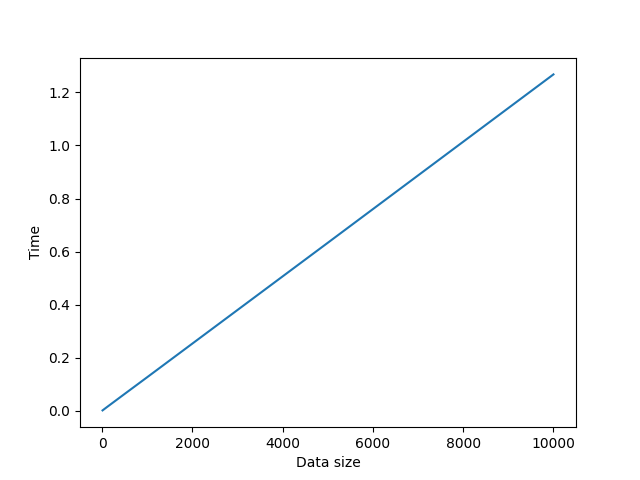
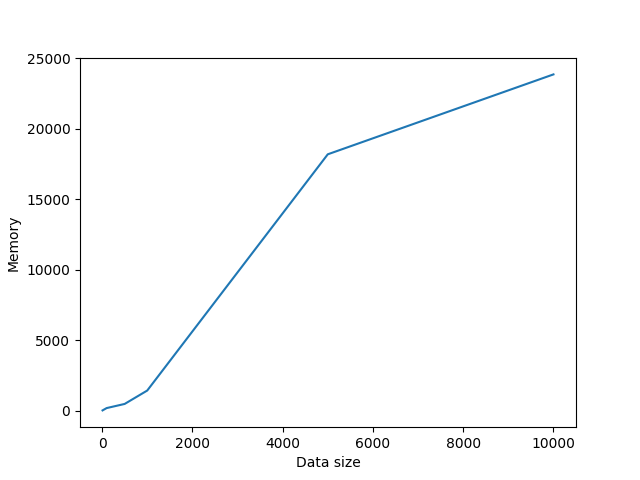
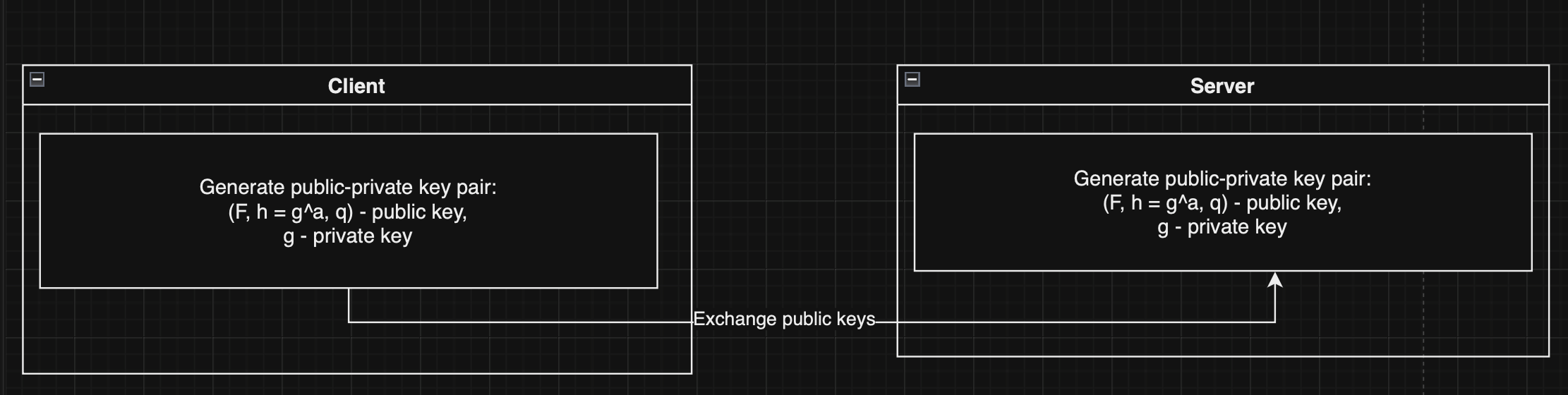
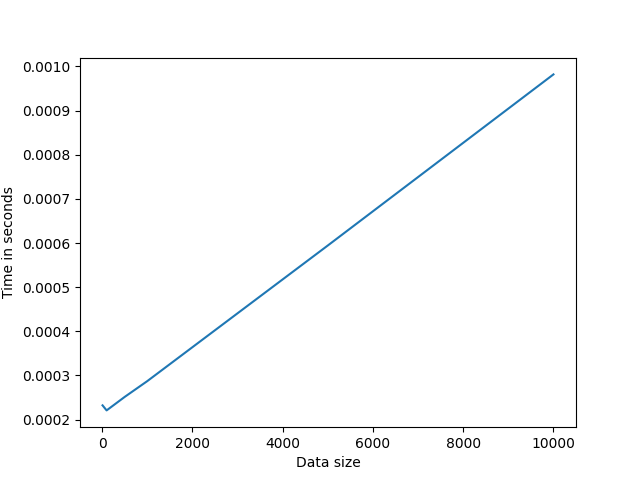
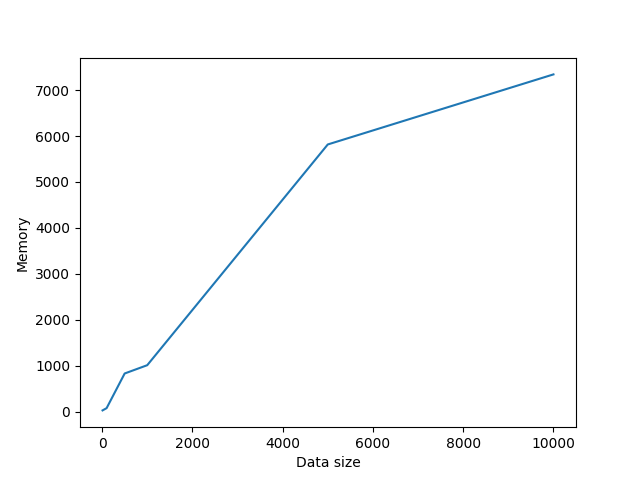
This algorithm uses eliptic curve cryptography to generate key pairs and then generate a symetrci shared key. The shared key is then used to encrypt the message using AES-128 algorithm. It's cons are that it's slower than the other algorithms and uses more memory. But it's more secure than the other algorithms. For example 256-bit ECC key is equivalent to 3072-bit RSA key.
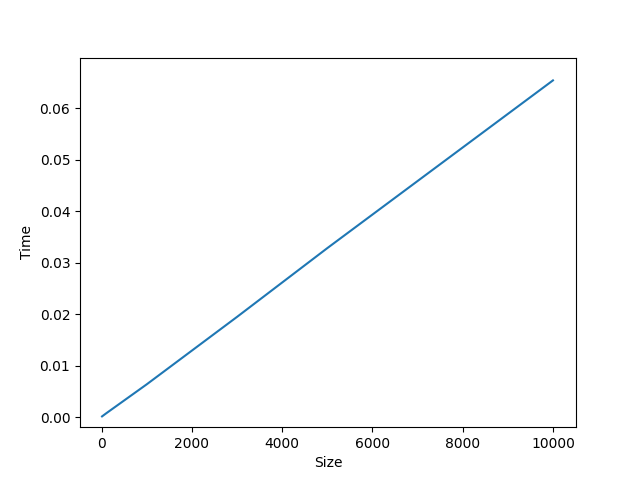
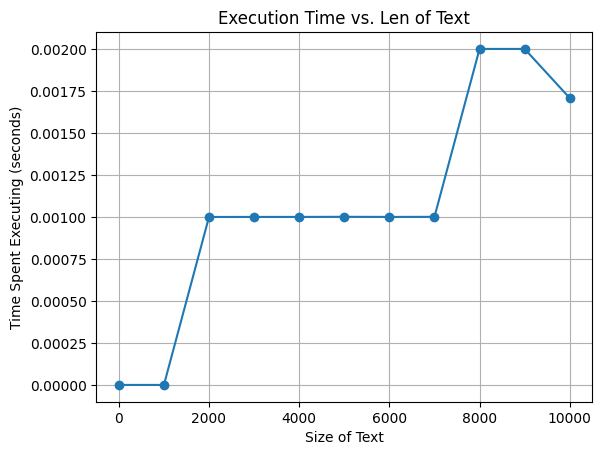
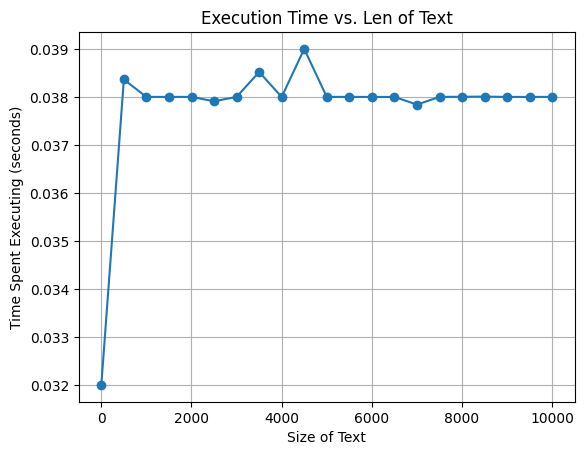
Average time used:
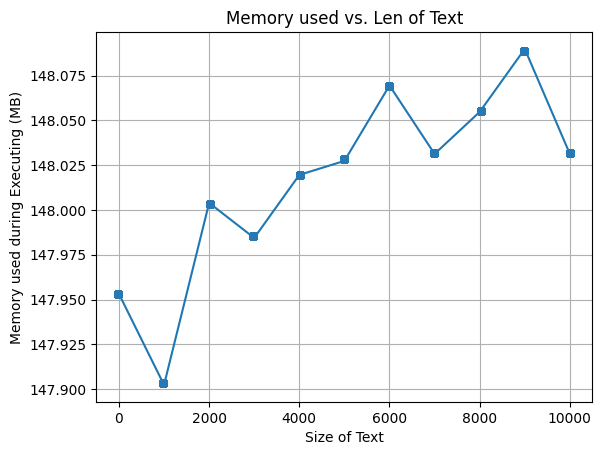
Average memory used:
-
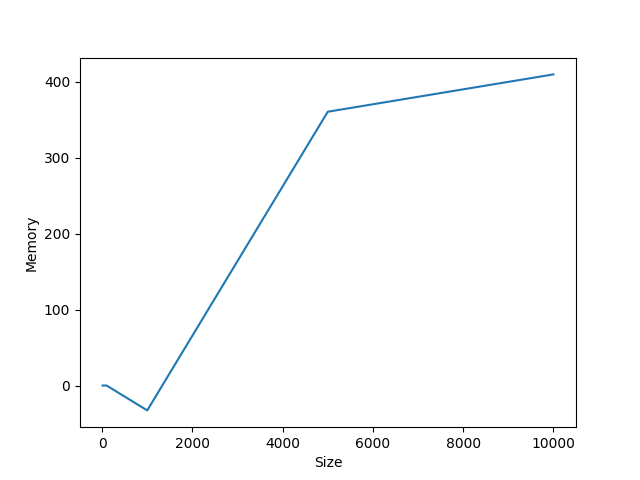
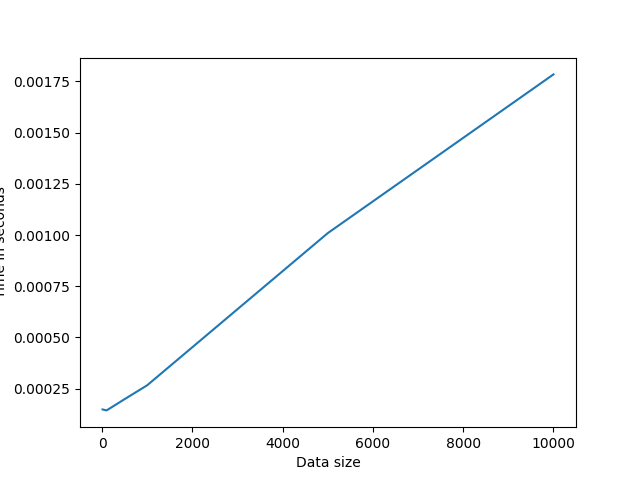
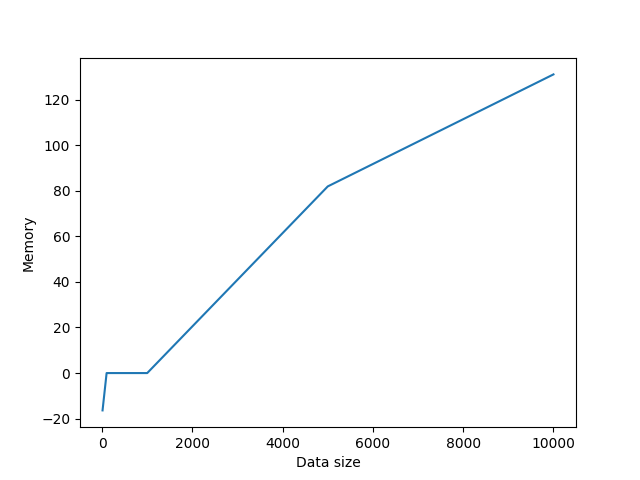
Here we use RSA to generate key pairs and then encrypt the message using the public key. The message is then decrypted using the private key. It's faster than ECC+AES-128 but less secure. It's one of the most used algorithms in the world. It relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers. However, with the advent of quantum computers, it's security is in question, because of Shor's algorithm.
Average time used:
Average memory used:
-
This algorithm is based on the Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm and the problem of computing discrete logorithms of cyclic groups. It's less secure than RSA and ECC+AES-128 but faster. Private keys of these alghoritm can be cracked but you need powerful quantum computer to crack so for now this alghorithm is pretty safe. Also it's security is corelated of hardnes of cyclic group it is based on.
Average time used:
Average memory used:
-
The Rabin cryptosystem is based on the difficulty of factoring large composite numbers, an NP-hard problem. It involves generating a public key from the product of two large primes and using it for encryption. Decryption relies on finding the square roots modulo the product of these primes, which can have multiple solutions. Rabin cryptosystem's security is tied to the challenge of factoring large numbers, making it theoretically secure against classical computers but potentially vulnerable to quantum computing advances. We never used this algorithm in the chat app, because it has a limit on the size of the message that can be encrypted.
Average time used:
Average memory used:
A digital signature is a mathematical technique used to validate the authenticity and integrity of a message, software, or digital document.
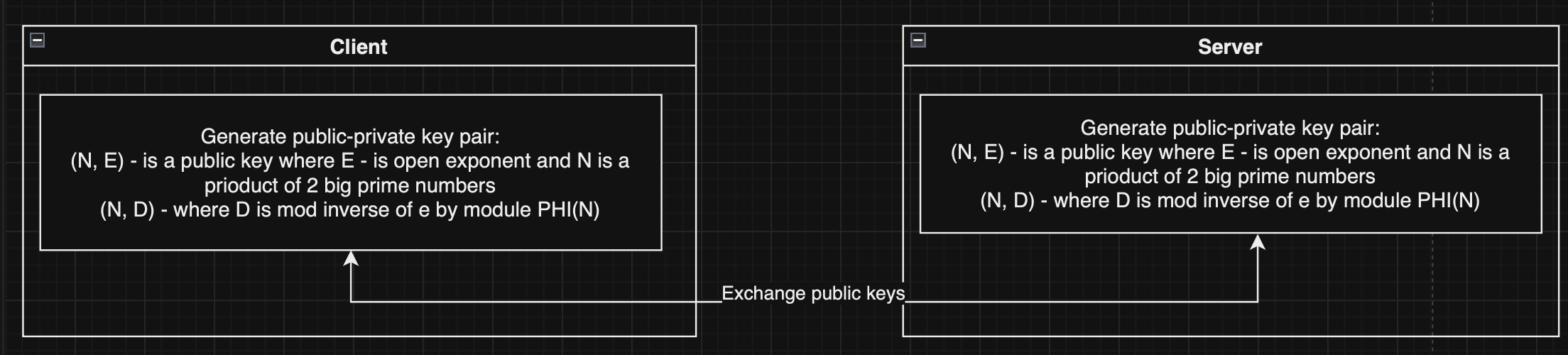
- Key Generation Algorithms: Digital signature is electronic signatures, which assure that the message was sent by a particular sender. While performing digital transactions authenticity and integrity should be assured, otherwise, the data can be altered or someone can also act as if he was the sender and expect a reply.
- Signing Algorithms: To create a digital signature, signing algorithms like email programs create a one-way hash of the electronic data which is to be signed. The signing algorithm then encrypts the hash value using the private key (signature key). This encrypted hash along with other information like the hashing algorithm is the digital signature. This digital signature is appended with the data and sent to the verifier. The reason for encrypting the hash instead of the entire message or document is that a hash function converts any arbitrary input into a much shorter fixed-length value. This saves time as now instead of signing a long message a shorter hash value has to be signed and moreover hashing is much faster than signing.
- Signature Verification Algorithms : Verifier receives Digital Signature along with the data. It then uses Verification algorithm to process on the digital signature and the public key (verification key) and generates some value. It also applies the same hash function on the received data and generates a hash value. If they both are equal, then the digital signature is valid else it is invalid.
ECC is one of the most secure algorithms, but it's slower and uses more memory. DSA is a good substitution for plain hash validation, we find it invaluable. RSA is the most used algorithm in the world, but in our opinion with advencment in quantum computing it's security is in question. ElGamal is a good algorithm for small messages, but it's less secure than RSA and ECC. We couldn't use Rabin algorithm in our chat app, because it has a limit on the size of the message that can be encrypted.