- Features
- Architecture
- Demonstrations
- Specifications
- Virtual Try-on and object manipulation
- Hosting
- About the tech
- License
- References
Here are the main features of the library:
- hand detection and tracking,
- hand side detection (left or right, back or palm),
- hand keypoint detection and tracking.
/demos/: source code of the demonstrations, sorted by 2D/3D engine used,/dist/: core of the library:WebARRocksHand.js: main minified script,HandTracker.module.js: main minified script for use as a module (withimportorrequire),
/helpers/: scripts which can help you to use this library in some specific use cases,/libs/: 3rd party libraries and 3D engines used in the demos,/neuralNets/: neural networks models,/reactThreeFiberDemos: Demos with Webpack/NPM/React/Three Fiber.
The best demos have been ported to a modern front-end development environment (NPM / Webpack / React / Three Fiber / ES6) in the /reactThreeFiberDemos directory. This is a standalone directory.
-
Boilerplate demo (display landmarks): live demo, source code
-
Wrist and ring VTO: live demo, source code
-
Hand based navigation:
- https://webar.rocks like navigation: live demo, source code
- Slideshow presentation (for desktop): live demo, source code
-
Foot tracking:
- Barefoot VTO: live demo, source code
- Shoes on and barefoot VTO: live demo, source code
-
3D Object manipulation:
- Boilerplate: live demo, source code
- Velociraptor demo: live demo, source code
- Cute ghost demo: live demo, source code
- Velociraptor demo with persistency if hand tracking is lost: live demo, source code
To run the demonstrations, serve the content of this directory using a static HTTP server (More info in Hosting section.
On your HTML page, you first need to include the main script between the tags <head> and </head>:
<script src="dist/WebARRocksHand.js"></script>Then you should include a <canvas> HTML element in the DOM, between the tags <body> and </body>. The width and height properties of the <canvas> element should be set. They define the resolution of the canvas and the final rendering will be computed using this resolution. Be careful to not enlarge too much the canvas size using its CSS properties without increasing its resolution, otherwise it may look blurry or pixelated. We advise to fix the resolution to the actual canvas size. Do not forget to call WEBARROCKSHAND.resize() if you resize the canvas after the initialization step.
<canvas width="600" height="600" id='yourCanvas'></canvas>This canvas will be used by WebGL both for the computation and the rendering of the video. It is not costly to render the video using this canvas because the video is already transfered into a WebGLTexture element to feed the neural network. And it allows to apply shader effects to the video.
When your page is loaded you should launch this function:
WEBARROCKSHAND.init({
canvasId: 'yourCanvas',
NNsPaths: [...], // path to JSON neural networks models
callbackReady: function(errCode, spec){
if (errCode){
console.log('AN ERROR HAPPENS. ERROR CODE =', errCode);
return;
}
[init scene with spec...]
console.log('INFO: WEBARROCKSHAND IS READY');
}, //end callbackReady()
// called at each render iteration (drawing loop)
callbackTrack: function(detectState){
// render your scene here
[... do something with detectState]
} //end callbackTrack()
});//end init call<integer> animateDelay: Number of milliseconds during which the browser wait at the end of the rendering loop before starting another detection. The default value is1,<function> onWebcamAsk: Function launched just before asking for the user to allow access to its camera,<function> onWebcamGet: Function launched just after the user has accepted to share its video. It is called with the video element as argument,<dict> videoSettings: override MediaStream API specified video settings, which are by default:
{
'videoElement' // not set by default. <video> element used
// If you specify this parameter,
// all other settings will be useless
// it means that you fully handle the video aspect
'deviceId' // not set by default
'facingMode': 'user', // to use the rear camera, set to 'environment'
'idealWidth': 800, // ideal video width in pixels
'idealHeight': 600, // ideal video height in pixels
'minWidth': 480, // min video width in pixels
'maxWidth': 1280, // max video width in pixels
'minHeight': 480, // min video height in pixels
'maxHeight': 1280, // max video height in pixels,
'rotate': 0 // rotation in degrees possible values: 0,90,-90,180
},<dict> scanSettings: override scan settings - seeset_scanSettings(...)method for more information,<dict> stabilizationSettings: override tracking stabilization settings - seeset_stabilizationSettings(...)method for more information,[<objects>] NNsor[<string>] NNsPaths: trained neural networks models in use,<boolean> followZRot: If the neural network detection window should rotate to better track the hand. Default istrue,<boolean> freeZRot: If the initial rotation value of the detection window should vary or not. If set tofalse, we will only detect hands vertically aligned. Default istrue.
If the user has a mobile device in portrait display mode, the width and height of these parameters are automatically inverted for the first camera request. If it does not succeed, we invert the width and height.
The initialization function ( callbackReady in the code snippet ) will be called with an error code ( errCode ). It can have these values:
false: no error occurs,"GL_INCOMPATIBLE": WebGL is not available, or this WebGL configuration is not enough (there is no WebGL2, or there is WebGL1 without OES_TEXTURE_FLOAT or OES_TEXTURE_HALF_FLOAT extension),"ALREADY_INITIALIZED": the library has been already initialized,"NO_CANVASID": no canvas ID was specified,"INVALID_CANVASID": cannot found the<canvas>element in the DOM,"INVALID_CANVASDIMENSIONS": the dimensionswidthandheightof the canvas are not specified,"WEBCAM_UNAVAILABLE": cannot get access to the camera (the user has no camera, or it has not accepted to share the device, or the camera is already busy),"GLCONTEXT_LOST": The WebGL context was lost. If the context is lost after the initialization, thecallbackReadyfunction will be launched a second time with this value as error code,
We detail here the arguments of the callback functions like callbackReady or callbackTrack. The reference of these objects do not change for memory optimization purpose. So you should copy their property values if you want to keep them unchanged outside the callback functions scopes.
The initialization callback function ( callbackReady in the code snippet ) is called with a second argument, spec, if there is no error. spec is a dictionnary having these properties:
GL: the WebGL context. The rendering 3D engine should use this WebGL context,canvasElement: the<canvas>element,videoTexture: a WebGL texture displaying the camera video. It has the same resolution as the camera video,[<float>, <float>, <float>, <float>]videoTransformMat2: flatten 2x2 matrix encoding a scaling and a rotation. We should apply this matrix to viewport coordinates to rendervideoTexturein the viewport,<HTMLVideoElement> video: the video used as source for the webgl texturevideoTexture,[<string> landmarksLabels]: the list of the landmark labels. This list depends on the neural network model,<int> maxHandsDetected: the maximum number of detected faces.
At each render iteration a callback function is executed ( callbackTrack in the code snippet ). It has one argument ( detectState ) which is a dictionnary with these properties:
<float> detected: the detection probability, between0and1,<float> x,<float> y: The 2D coordinates of the center of the detection frame in the viewport (each between -1 and 1,xfrom left to right andyfrom bottom to top),<float> s: the scale along the horizontal axis of the detection frame, between 0 and 1 (1 for the full width). The detection frame is always square,<float> rx,<float> ry,<float> rz: the Euler angles of the head rotation in radians.<array> landmarks:[[<float> x_0, <float> y_0],...,[<float> x_n, <float> y_n]]: detected landmarks.x_iandy_iare the relative coordinates of theith landmark in the viewport coordinates (between-1and1, from left to right and from bottom to top).
After the initialization (ie after that callbackReady is launched ) , these methods are available:
-
WEBARROCKSHAND.resize(): should be called after resizing the<canvas>element to adapt the cut of the video, -
WEBARROCKSHAND.toggle_pause(<boolean> isPause): pause/resume, -
WEBARROCKSHAND.set_animateDelay(<integer> delay): Change theanimateDelay(seeinit()arguments), -
WEBARROCKSHAND.set_inputTexture(<WebGLTexture> tex, <integer> width, <integer> height): Change the video input by a WebGL Texture instance. The dimensions of the texture, in pixels, should be provided, -
WEBARROCKSHAND.reset_inputTexture(): Come back to the user's video as input texture, -
WEBARROCKSHAND.get_videoDevices(<function> callback): Should be called before theinitmethod. 2 arguments are provided to the callback function:<array> mediaDevices: an array with all the devices founds. Each device is a javascript object having adeviceIdstring attribute. This value can be provided to theinitmethod to use a specific camera. If an error happens, this value is set tofalse,<string> errorLabel: if an error happens, the label of the error. It can be:NOTSUPPORTED,NODEVICESFOUNDorPROMISEREJECTED.
-
WEBARROCKSHAND.set_scanSettings(<object> scanSettings): Override scan settings.scanSettingsis a dictionnary with the following properties:<float> threshold: detection threshold, between0and1. Default value is0.97. You can lower it if you want to make the detection more sensitive (but it will increase the false positive detections),<int> nDetectsPerLoop: specify the number of detection per drawing loop.0for adaptative value. Default:0<int> nScaleLevels: number of detection steps for the scale. Default:4,[<float>, <float>, <float>] overlapFactors: overlap between 2 scan positions forX,Yandscale. Default:[1.5, 1.5, 2],
-
WEBARROCKSHAND.set_stabilizationSettings(<object> stabilizationSettings): Override detection stabilization settings. The output of the neural network is always noisy, so we need to stabilize it using a floatting average to avoid shaking artifacts. The internal algorithm computes first a stabilization factorkbetween0and1. Ifk==0.0, the detection is bad and we favor responsivity against stabilization. It happens when the user is moving quickly, rotating the head or when the detection is bad. On the contrary, ifkis close to1, the detection is nice and the user does not move a lot so we can stabilize a lot.stabilizationSettingsis a dictionnary with the following properties:[<float> minValue, <float> maxValue] qualityFactorRange: Default value:[0.9, 0.98],[<float> minValue, <float> maxValue] alphaRange: it specify how to applyk. Between 2 successive detections, we blend the previousdetectStatevalues with the current detection values using a mixing factoralpha.alpha=<minValue>ifk<0.0andalpha=<maxValue>ifk>1.0. Between the 2 values, the variation is quadratic.
-
WEBARROCKSHAND.update_videoElement(<video> vid, <function|False> callback): change the video element used for the detection (which can be provided viaVIDEOSETTINGS.videoElement) by another video element. A callback function can be called when it is done. -
WEBARROCKSHAND.update_videoSettings(<object> videoSettings): dynamically change the video settings (see Optionnal init arguments for the properties ofvideoSettings). It is useful to change the camera from the selfie camera (user) to the back (environment) camera. APromiseis returned. -
WEBARROCKSHAND.destroy(): Clear both graphic memory and JavaScript memory, uninit the library. After that you need to init the library again. APromiseis returned.
/dist/HandTracker.module.js is exactly the same as /dist/WebARRocksHand.js except that it works as a JavaScript module, so you can import it directly using:
import 'dist/HandTracker.module.js'or using require.
Virtual try-on (VTO) and object manipulation demos are provided in this repository. They rely on the THREE.js VTO helper to instantiate THREE.js objects and especially the scene, the camera and the 3D object tracking specific parts of the hand (the tracker ).
The tracker can follow the wrist for wrist watch or bracelet VTO, or the palm for object manipulation. The 3D mesh of the bracelet will be imported and added as a child of the tracker in the specific demo script.
There are 2 <canvas> elements overlaid in the DOM:
- The canvas used by
WEBARROCKSHANDand to display the video. This canvas is below, - The canvas used by THREE.js to render the scene.
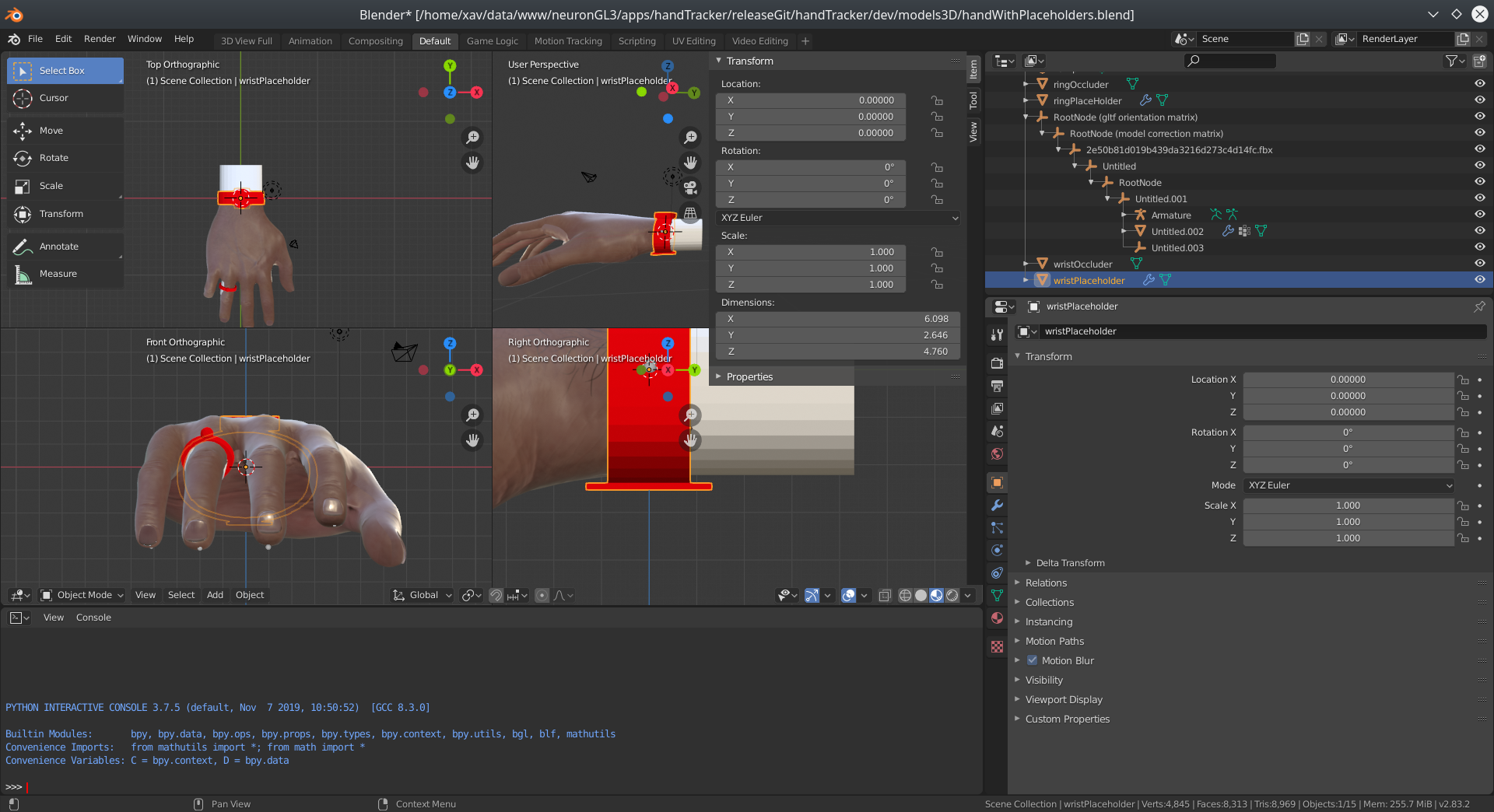
To correctly set the position of the 3D mesh, you can open dev/models3D/handWithPlaceholders.blend using Blender. The place holders are displayed in red and the occluder in white. You can then import your own mesh, scale, rotate and translate it to match the right position, then apply scale rotation and offset and re-export it.
Another solution consist in reporting the scale, position and rotation in the demo.js file and apply them with THREE.js.
The occluders are 3D meshes rendered with a transparent color. They mask part of the tracking object that are normally masked by the user's hand (the interior of a bracelet for example).
You should host the content of this repository using a HTTPS static server.
Be careful to enable gzip HTTP/HTTPS compression for JSON and JS files. Indeed, the .JSON neuron networks files are quite heavy, but very well compressed with GZIP. You can check the gzip compression of your server here.
Neuron network files are loaded through XMLHttpRequest after calling WEBARROCKSHAND.init(). This loading is proceeded after the user has accepted to share its camera. So we won't load this quite heavy file if the user refuses to share it or if there is no camera available. The loading can be faster if you systematically preload the neural network files using a service worker or a simple raw XMLHttpRequest just after the HTML page loading. Then the file will be already in the browser cache when the library will request it.
Some directories of the latest version of this library are hosted on https://cdn.webar.rocks/hand/ and served through a content delivery network (CDN):
This libray uses WebAR.rocks WebGL Deep Learning technology to detect and track the user's hand using a neural network. The accuracy is adaptative: the best is the hardware, the more detections are processed per second. All is done client-side.
- If
WebGL2is available, it usesWebGL2and no specific extension is required, - If
WebGL2is not available butWebGL1, we require eitherOES_TEXTURE_FLOATextension orOES_TEXTURE_HALF_FLOATextension, - If
WebGL2is not available, and ifWebGL1is not available or neitherOES_TEXTURE_FLOATorOES_HALF_TEXTURE_FLOATare implemented, the user is not compatible.
If WebGL2 implementation is lame (like with IOS < 13.3.1), we will force the use of WebGL1.
If a compatibility error is triggered, please post an issue on this repository. If this is a problem with the camera access, please first retry after closing all applications which could use your device (Skype, Messenger, other browser tabs and windows, ...). Please include:
- a screenshot of webglreport.com - WebGL1 (about your
WebGL1implementation), - a screenshot of webglreport.com - WebGL2 (about your
WebGL2implementation), - the log from the web console,
- the steps to reproduce the bug, and screenshots.
Don't panic if you see errors and warning at initialization in the web console. Indeed, we always test all WebGL capabilities. These errors are caught.
This code repository is dual licensed. You have to choose between these 2 licenses:
- GPLv3 (free default option)
- Nominative commercial license (not free)
For more information, please read LICENSE file.