By applying ideas from information theory Tishby et al [1] proposed a novel theoretical framework to understand Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) – the Information Bottleneck (IB). In a consecutive work Tishby et al [2] analyze the Information Plane (IP) dynamics trough the training process of a DNN and express the generalization increase in terms of MutualInformation of the inputs and the layers. In another work by Zhang et al [3] investigated the effective capacity of DNNs, dismissing the contribution of the regularizers to explain the generalization capabilities of DNNs. In this work, I wish to observe the capacity and memorization capabilities of DNNs from the perspective of the IB.
SGD has two consecutive phases. First, the fitting phase where the layers increase the information about the output. Second, a much longer phase, the compression phase,the layers reduce the information about the input
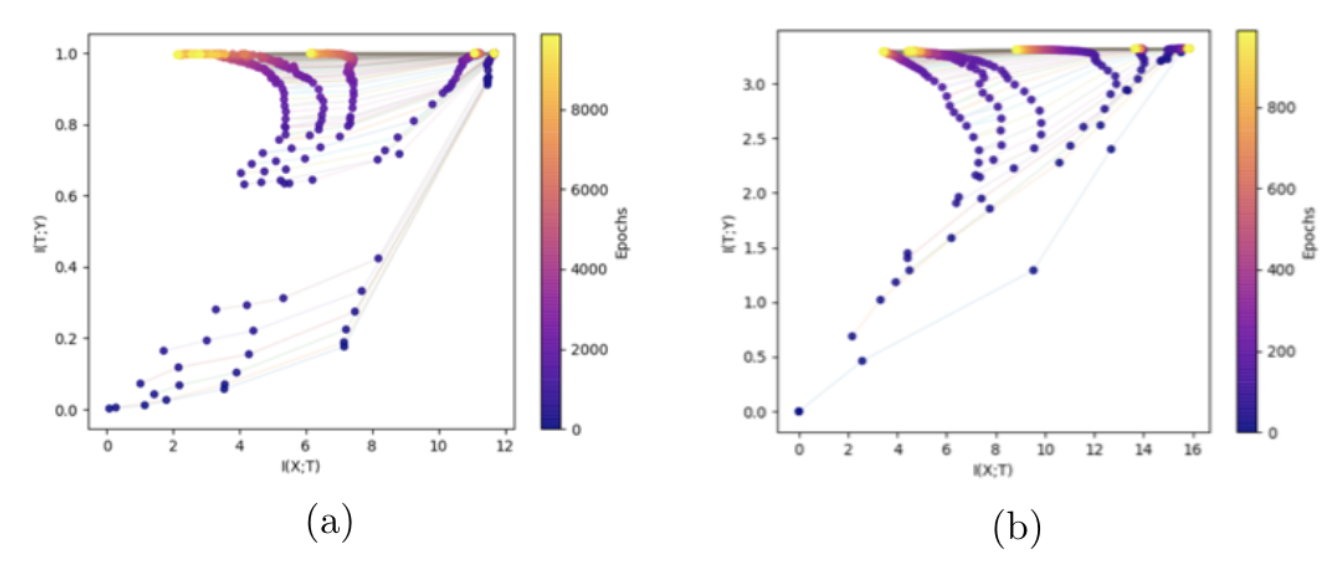
The evolution of layers on the IP (a) for the task of the binary classification with a simple DNN. (b) for multi-class classification on MNIST. The colors indicate the number of trainingepochs with SGD
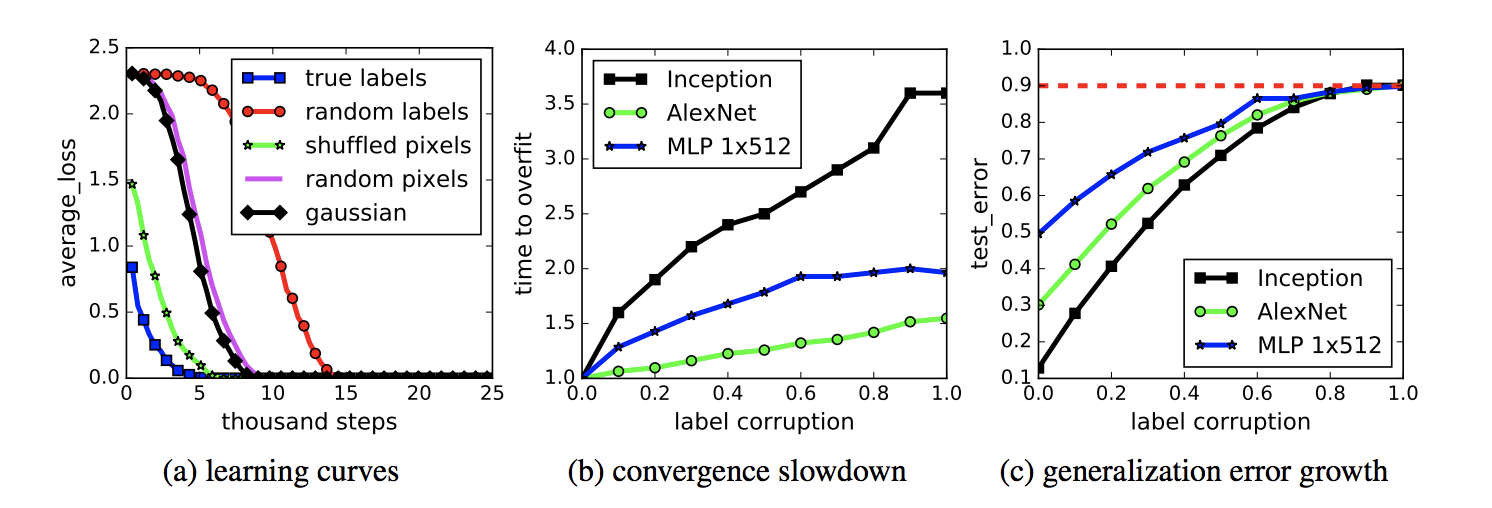 From Zhang et al [3]: Fitting random labels and random pixels on CIFAR10. (a) shows the training loss of
various experiment settings decaying with the training steps. (b) shows the relative convergence
time with different label corruption ratio. (c) shows the test error (also the generalization error since
training error is 0) under different label corruptions
From Zhang et al [3]: Fitting random labels and random pixels on CIFAR10. (a) shows the training loss of
various experiment settings decaying with the training steps. (b) shows the relative convergence
time with different label corruption ratio. (c) shows the test error (also the generalization error since
training error is 0) under different label corruptions
I repeated the experiment on the MNIST data, but this time I randomly shuffle the labels.
Zhang et al [3] showed that it will take more training time but eventually the same DNN will converge to the same training error as in the true label case.
Thus, we can conclude that a DNN, with a big enough capacity, has in fact the ability to memorize a given training set (though with poor generalization error).
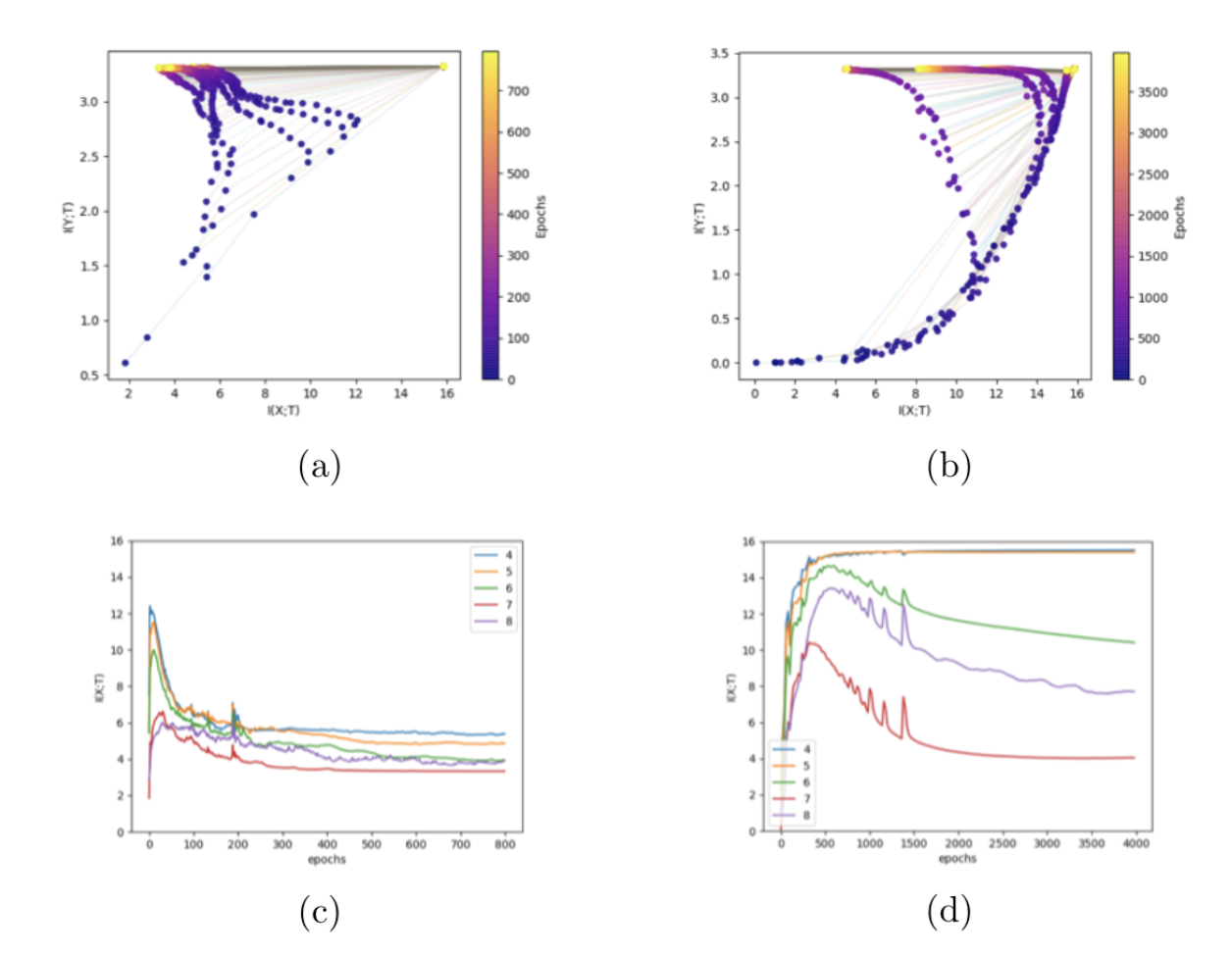 In the upper row, the evolution of layers on the IP in the case of (a) true labels and (b) random labels. In the bottom row, the I(X, T) of the 5 last layers in the case of (c) true labels and (d)random labels as a function of epochs
In the upper row, the evolution of layers on the IP in the case of (a) true labels and (b) random labels. In the bottom row, the I(X, T) of the 5 last layers in the case of (c) true labels and (d)random labels as a function of epochs
- Python 3.6
- PyTorch 1.4
- TorchVision 0.5.0
$ python -m venv venv
$ source venv/bin/activate
$ pip install -r requirements.txt[1]
@inproceedings{tishby2015deep,
title={Deep learning and the information bottleneck principle},
author={Tishby, Naftali and Zaslavsky, Noga},
booktitle={2015 IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW)},
pages={1--5},
year={2015},
organization={IEEE}
}
[2]
@article{shwartz2017opening,
title={Opening the black box of deep neural networks via information},
author={Shwartz-Ziv, Ravid and Tishby, Naftali},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.00810},
year={2017}
}
[3]
@article{zhang2016understanding,
title={Understanding deep learning requires rethinking generalization},
author={Zhang, Chiyuan and Bengio, Samy and Hardt, Moritz and Recht, Benjamin and Vinyals, Oriol},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.03530},
year={2016}
}