Time-stepped radiative-convective solver designed for integration into a coupled atmosphere-interior code.
AGNI relies on SOCRATES (2306) for calculating the radiative-transfer. It makes use of the Julia interface to SOCRATES as written by Stuart Daines (see their branch here). SOCRATES is setup here to include shortwave irradiation from the star, Rayleigh scattering, and continuum absorption / CIA.
Surface boundary conditions are intended to be set by an interior model, so AGNI won't work as well for cooler planets. The model also includes a parameterised conductive 'skin' with a prescribed thickness and conductivity, allowing the surface temperature to be calculated according to the required conductive flux. Two convection parameterisations are included: convective adjustment (directly manipulating the temperature arrays), and mixing length theory (calculating convective energy fluxes). Results are optionally plotted (and animated), and may be saved as NetCDF or CSV files. Integration is primarily via a first-order Euler method with various acceleration options, however it is also possible to activate a high-order stiff integrator with automatic switching (Sundials CVODE Adams-Moulton).
Pronounced: ag-nee. Named after the fire deity of Hinduism.
README.md- This fileLICENSE.txt- License for use and re-usedoc/- Other documentationout/- Output filesres/- Resourcessrc/- AGNI source codesocrates/- Directory containing SOCRATES and associated files (subject to the license therein)agni.jl- AGNI executable for debuggingagni_cli.jl- AGNI executable with command-line interfacedemo_steamrun.jl- Script to demonstrate the pure-steam runaway greenhouse effectdemo_earth.jl- Script to demonstrate solving for Earth's temperature structure
- Julia (version 1.9.1 or later)
- Python (version 3.10 or later)
- NumPy and SciPy
- gfortran
- netcdf-fortran
- make
- OpenMP
- MacOS (ARM and x86-64)
- Ubuntu (x86-64)
$ cd socrates$ cp ../res/Mk_cmd_PLAT ./make/Mk_cmdwhere PLAT is your platform$ ./build_code$ source set_rad_env$ cd julia$ juliajulia> ](@v1.9) pkg> add OffsetArrays(@v1.9) pkg> add Revise(@v1.9) pkg> add PCHIPInterpolation(@v1.9) pkg> add LaTeXStrings(@v1.9) pkg> add Plots(@v1.9) pkg> add NCDatasets(@v1.9) pkg> add DataStructures(@v1.9) pkg> add Glob(@v1.9) pkg> add ArgParse(@v1.9) pkg> add SciMLBase(@v1.9) pkg> add SteadyStateDiffEq(@v1.9) pkg> add Sundials(@v1.9) pkg> activate .- Press backspace
julia> cd("src")julia> include("generate_wrappers.jl")julia> exit()$ cd lib$ make$ cd ../../..
You should end up in the root directory of the repository.
For the command line interface, run $ ./agni_cli.jl (pass --help for help).
To debug the program, run $ ./agni.jl in the root directory of the repository.
To demo the steam runaway greenhouse effect, run $ ./demo_steamrun.jl.
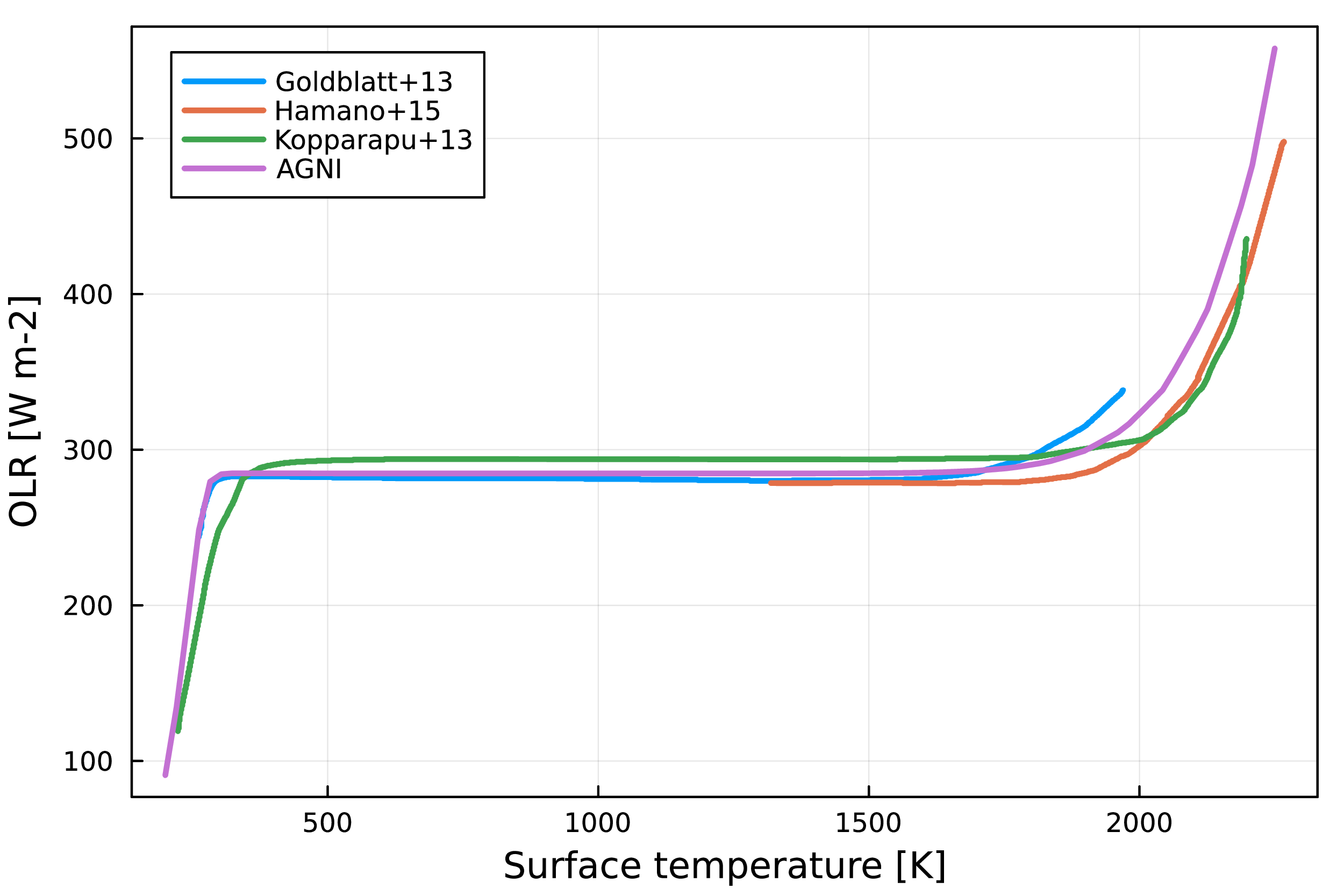
Pure steam runaway greenhouse.
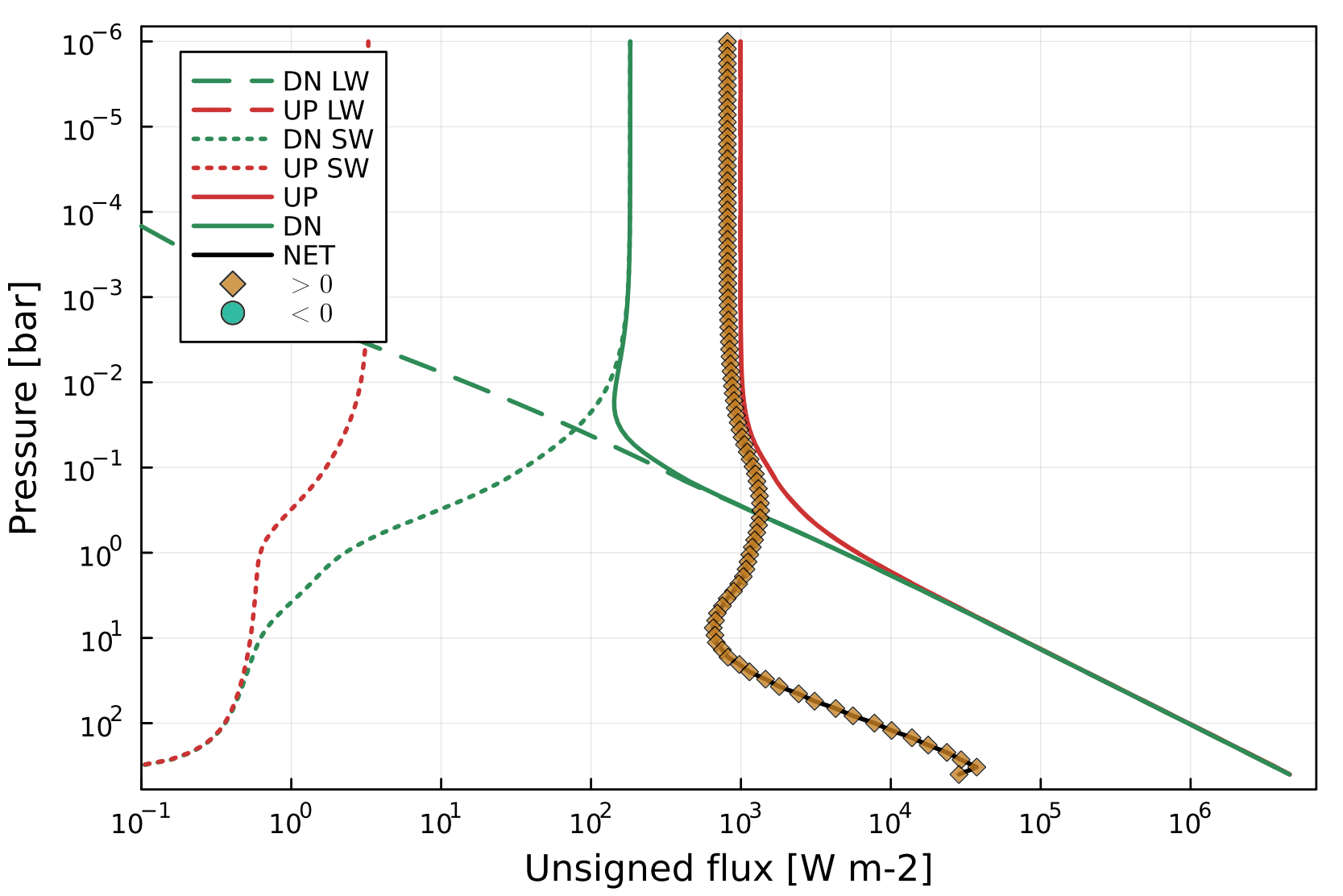
Calculating fluxes with SOCRATES, without solving for RCE.
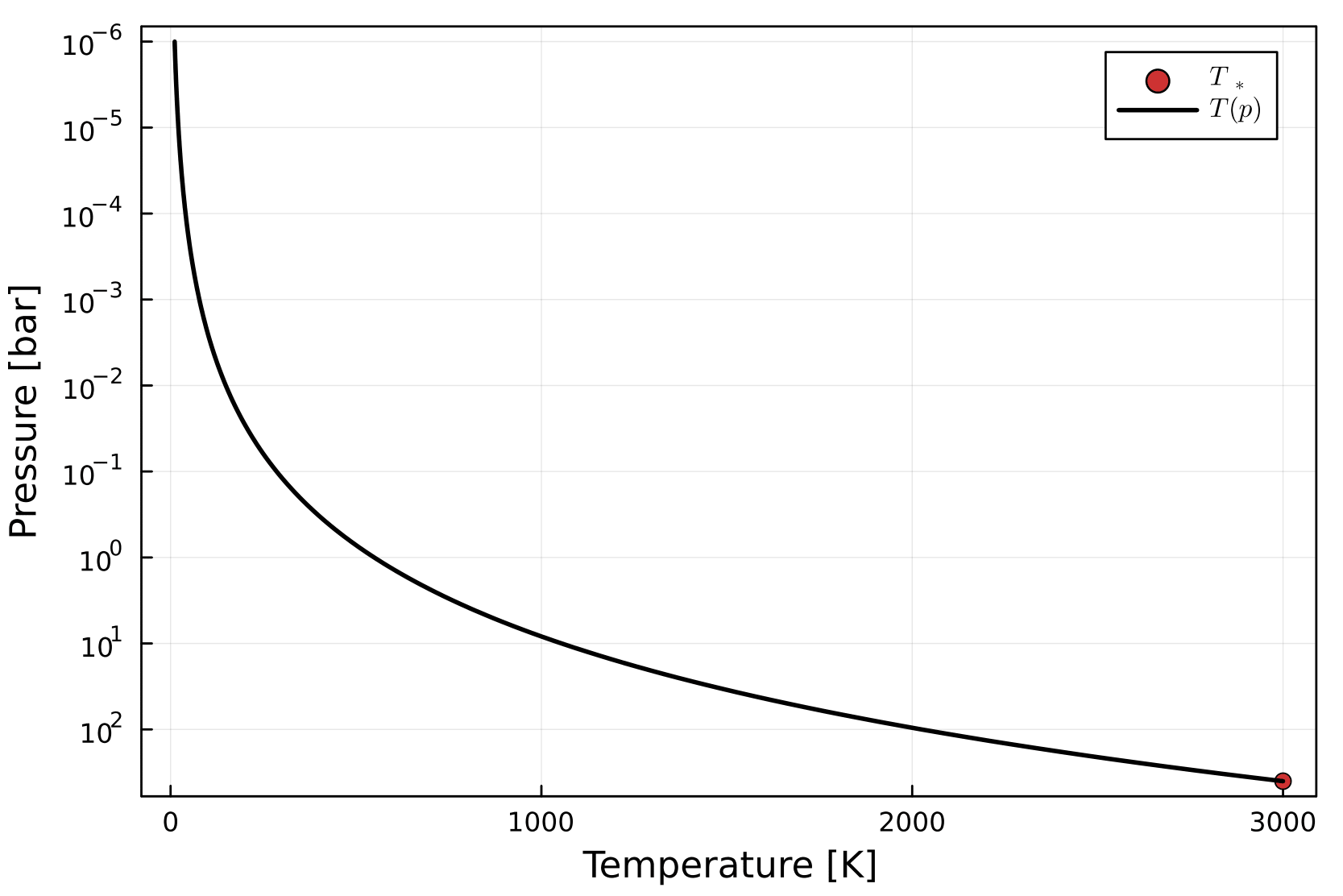
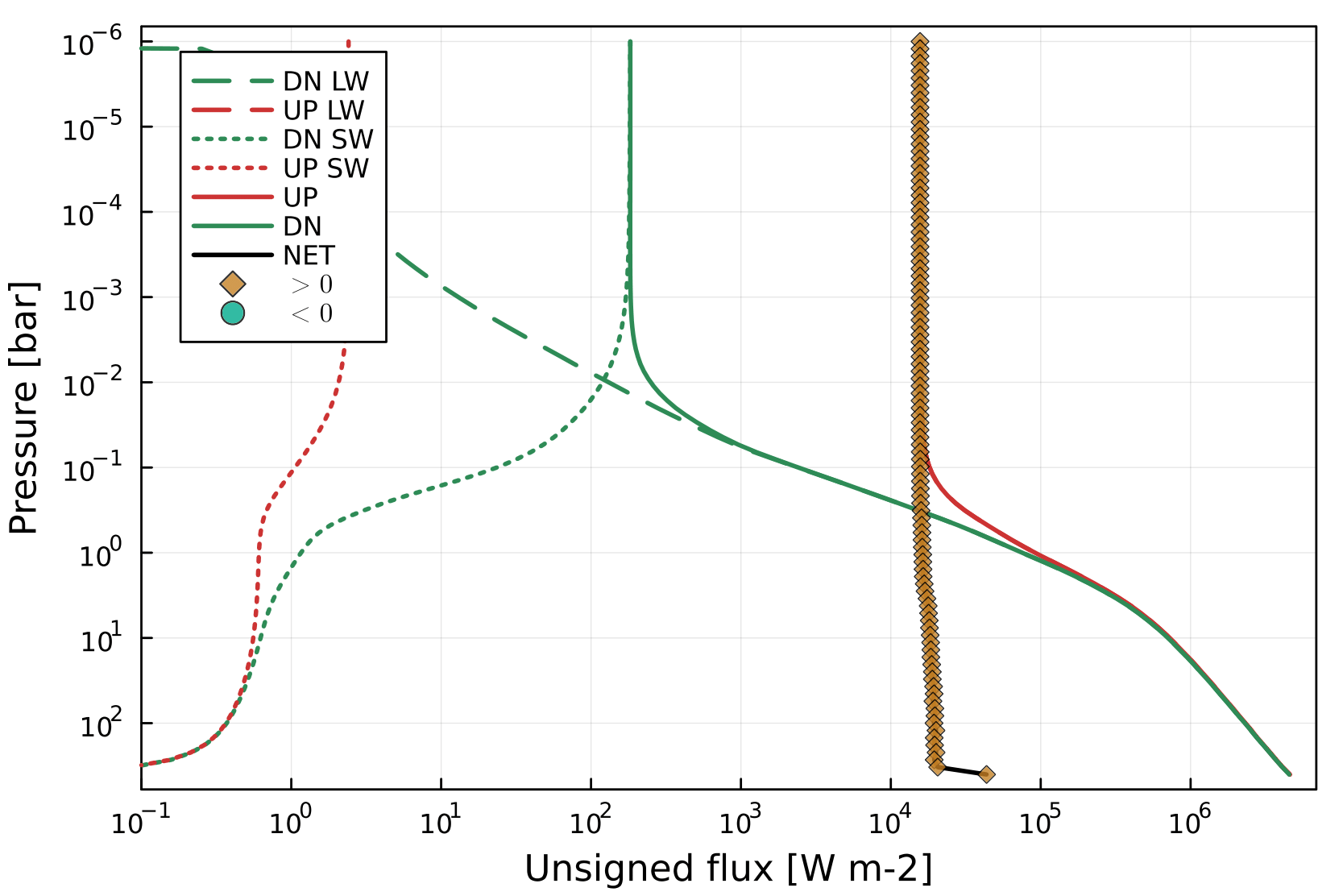
Solving for RCE with accelerated time-stepping. (Outdated plot).
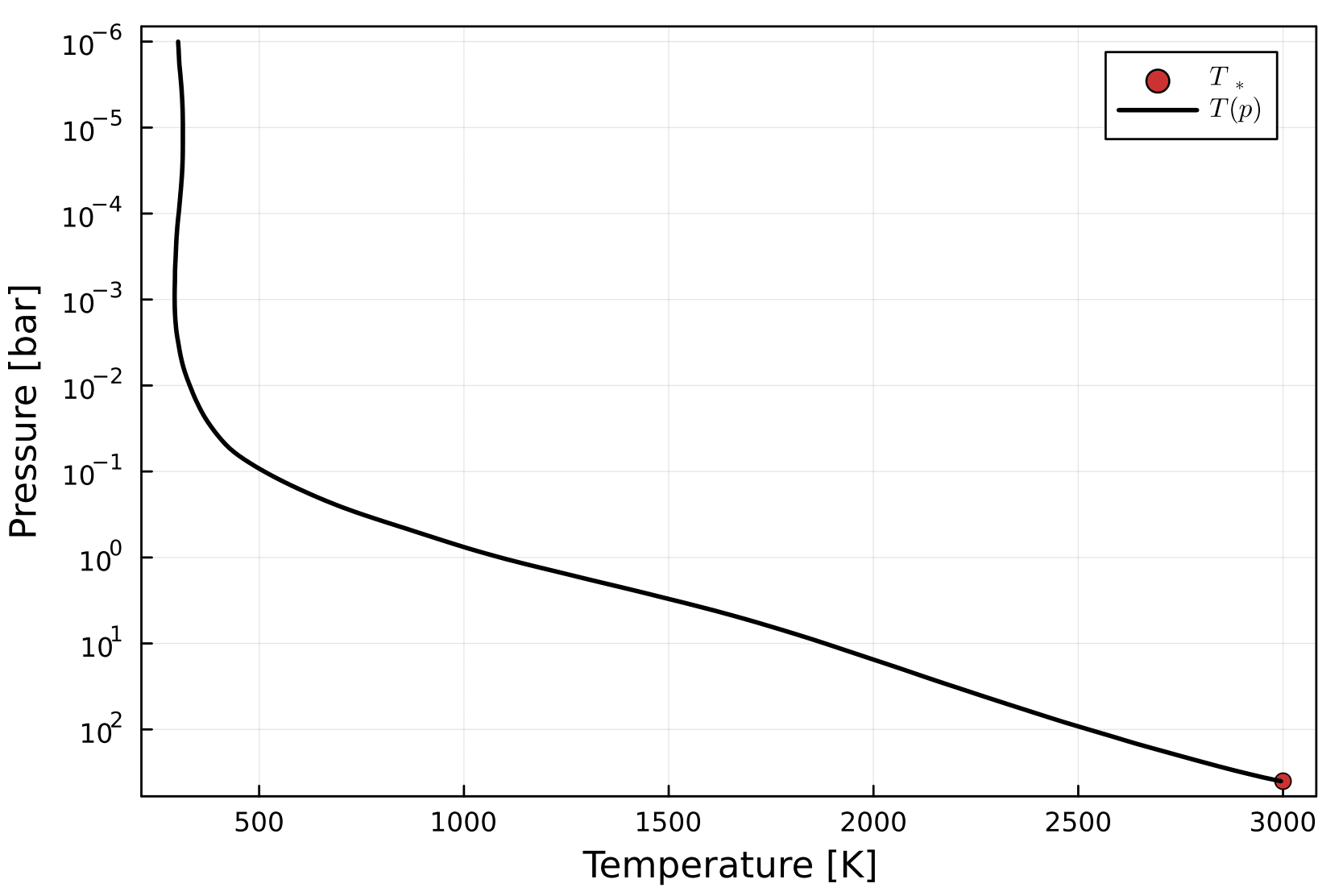
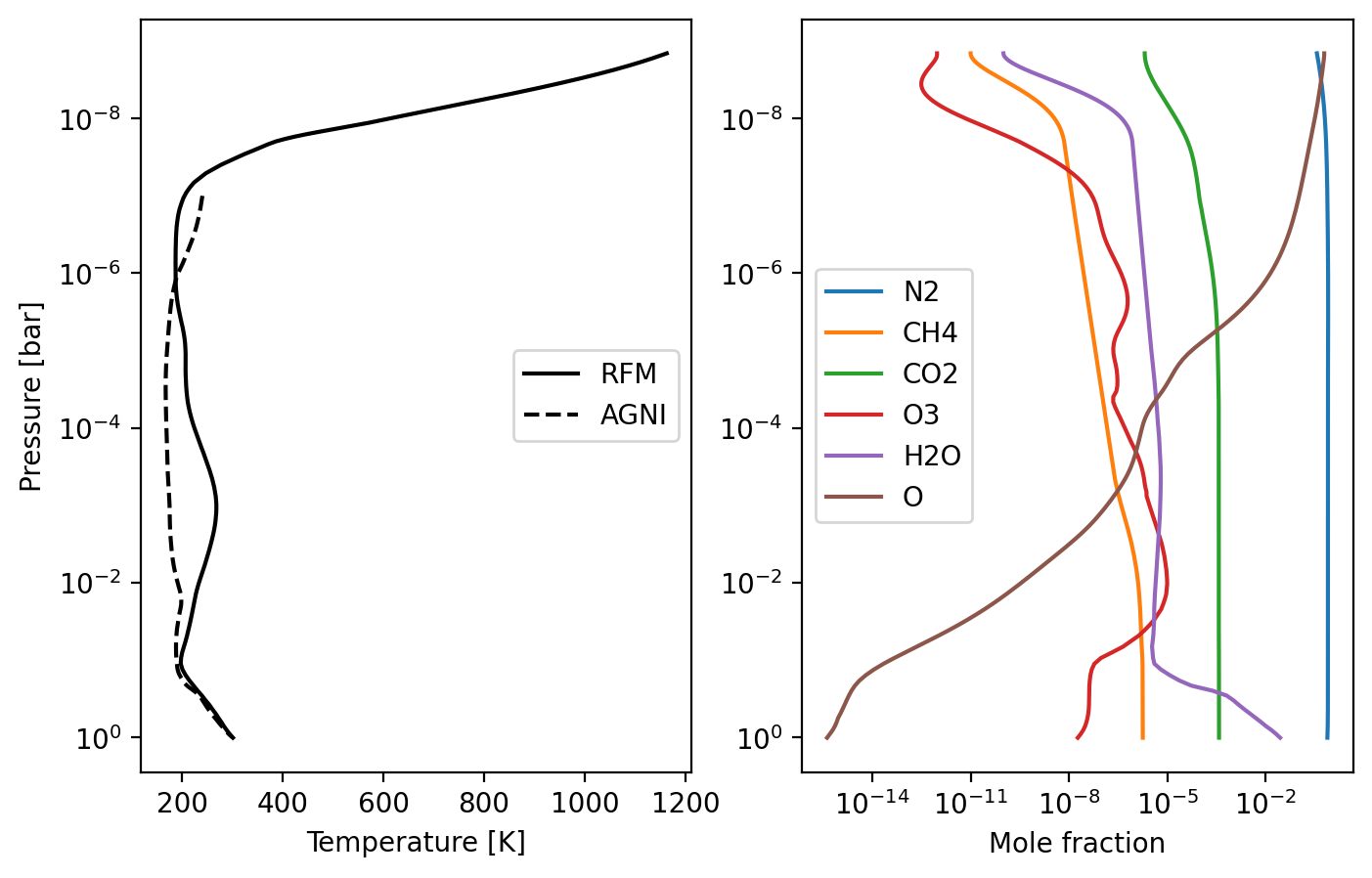
An attempt at solving for Earth's temperature profile. The ~100 K accuracy here wouldn't be good enough for Earth system modelling, but it's probably good enough for magma ocean modelling.