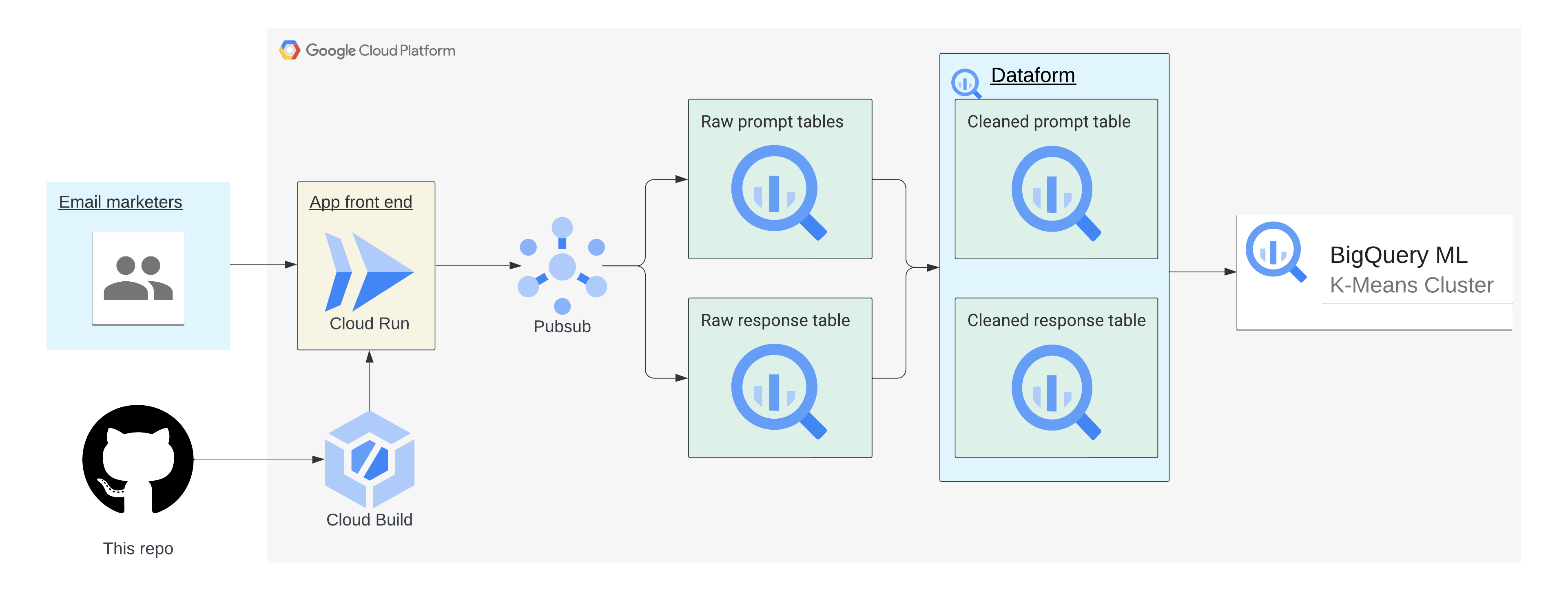
This repo provides an example LLM app to generate marketing emails to demonstrate how you can establish prompt lineage and response lineage around LLM usage. The following instructions should help you get started. It is intended to demonstration:
- How you can enable non-technical users (in this case, email marketing professionals) to use LLMs
This app puts a user interface over some of Google Cloud's LLMs APIs for text generation that makes it easier for non-technical users to benefit from LLMs - Provide some boundaries around how LLMs are used within your company while still leveraging the expertise of users
This app has a narrowly defined use case: Generating marketing emails. This is accomplished by providing a place for user input that is part of the prompt while still providing structure around what the prompt will produce by telling it to write a marketing email. This provides some boundaries around the use case rather than giving users a "blank canvas" that allows them to generate content for an unsupported use case. - Begin to implement "prompt & response lineage" by capturing the prompt and response (along with associated metadata) to a Pub/Sub topic
This is a first step to implementing full lineage and governance for workloads that use LLMs. The Pub/Sub topics used in this app write to BigQuery, allowing you to analyze LLM usage over time. - How Terraform can be used to support simplified infrastructure deployments
Terraform can be used to scalably manage infrastructure for deployments, specifically for repeatable tasks such as launching LLM apps with varying use cases.
Note
Before you start: Though it's not a requirement, using a new GCP project for this demo is easiest. This makes cleanup much easier, as you can delete the whole project to ensure all assets are removed and it ensures no potential conflicts with existing resources. You can also remove resources by running terraform destroy after you deploy the resources, but it will miss some of the resources deployed by Terraform.
1. You'll need to set your Google Cloud project in Cloud Shell, clone this repo locally first, and set the working directory to this folder using the following commands.
gcloud config set project <PROJECT ID>
git clone https://github.com/shanecglass/llms-for-email-marketing.git
cd llms-for-email-marketing
Check to make sure the Cloud Resource Manager API is enabled
This app uses Cloud Run, Cloud Build, BigQuery, and PubSub. Run the following to execute the Terraform script to setup everything.
First, initialize Terraform by running
terraform init
touch ./terraform.tfvars
nano ./terraform.tfvars
3. Copy and paste the following code snippet. Edit the values for the required variables, save the file, and exit.
# This is an example of the terraform.tfvars file.
# The values in this file must match the variable types declared in variables.tf.
# The values in this file override any defaults in variables.tf.
# ID of the project in which you want to deploy the solution
project_id = "PROJECT_ID"
# Google Cloud region where you want to deploy the solution
# Example: us-central1
region = "REGION"
# Whether or not to enable underlying apis in this solution.
# Example: true
enable_apis = true
# Whether or not to protect BigQuery resources from deletion when solution is modified or changed.
# Example: false
force_destroy = false
# Whether or not to protect Cloud Storage resources from deletion when solution is modified or changed.
# Example: true
deletion_protection = true
Run the following:
terraform validate
If the command returns any errors, make the required corrections in the configuration and then run the terraform validate command again. Repeat this step until the command returns Success! The configuration is valid.
Review the resources that are defined in the configuration:
terraform plan
terraform apply
When you're prompted to perform the actions, enter yes. Terraform displays messages showing the progress of the deployment.
If the deployment can't be completed, Terraform displays the errors that caused the failure. Review the error messages and update the configuration to fix the errors. Then run terraform apply command again. For help with troubleshooting Terraform errors, see Errors when deploying the solution using Terraform.
After all the resources are created, Terraform displays the following message:
Apply complete!
The Terraform output also lists the following additional information that you'll need:
- A link to the Dataform repository that was created
- The link to open the BigQuery editor for some sample queries
Create and initialize your Dataform workspace. Then copy and paste the Dataform queries found in prompt_cleaned.sqlx and response_cleaned.sqlx, then start the workflow execution for all actions. These will incrementally clean and write the data to analysis-ready tables.
From the BigQuery console SQL Workspace, run the CREATE MODEL query to create the BQML model.
From here, you can get started analyzing the data and the results of the BQML model. Check out this blog post to learn more about how you can get started with K-Means clustering in BQML.
Training a clustering model helps you identify similar questions/prompts that the end-users are asking, so that you can learn from how your users are using your product and take actions to cater your business. In this example, it helps you identify similar requests for email marketing support, but this demo can be adapted to support a customer-facing chat bot as well. In that case, BigQuery Machine Learning makes it simple to build a k-means clustering model that can help you better understand the types of products customers are asking a chatbot about. This understanding of customer intent would allow you to better align your product offerings & inventory to match that demand!