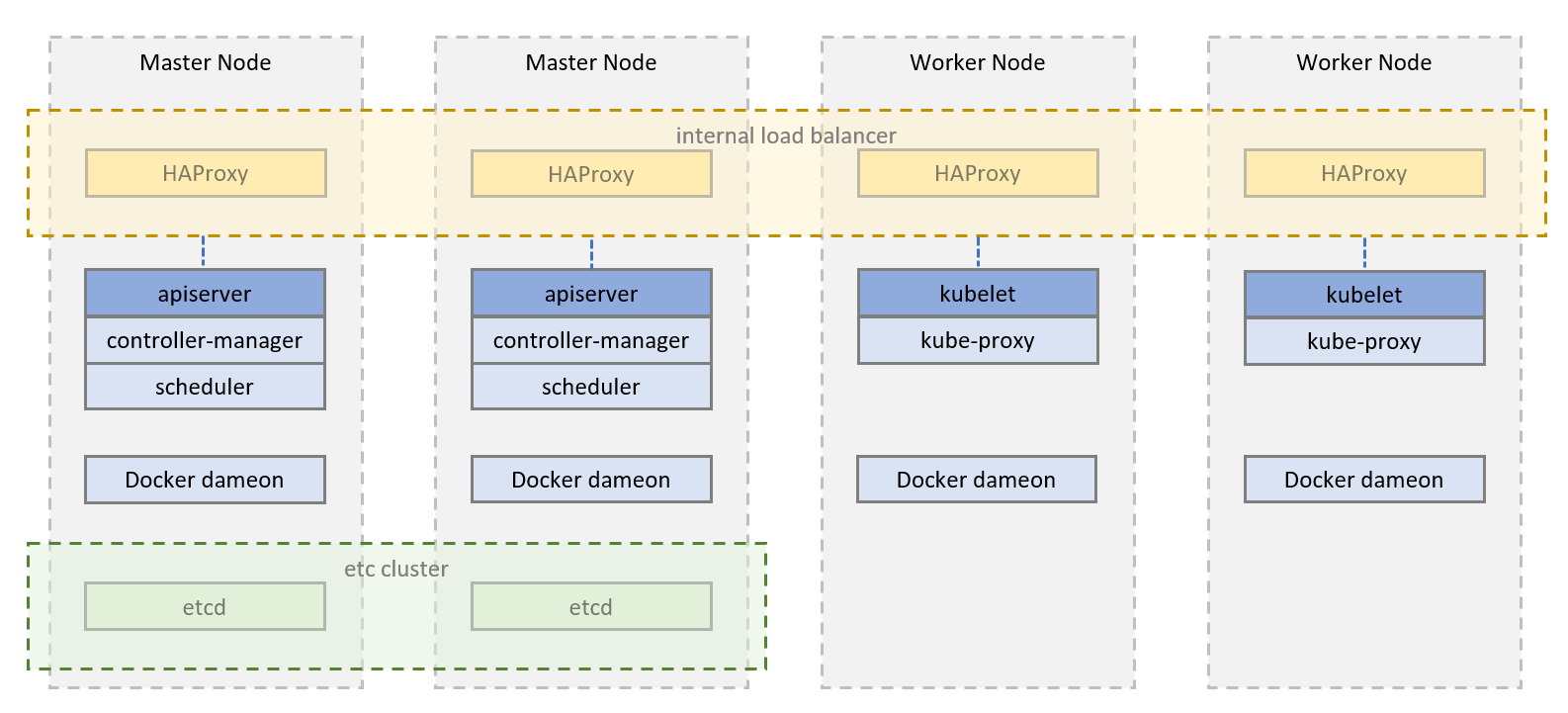
This project includes a Vagrantfile and Ansible Playbook which allows you to deploy a scalable High-Availability Kubernetes cluster in your local cluster running 4 CentOS7 Virtual Machines (using vagrant and virtualbox). This playbook can be easily extended for deployment on Bare Metal/AWS EC2/Google Compute Engine instances and can be used as a foundation for deployment into a production environment. https://medium.com/@nilanthanb1994/kubernetes-ha-cluster-with-ansible-vagrant-centos-a7f5d368dc11
The setup includes the following components:
- 2 Master nodes
- 2 Worker nodes
- HA Proxy running on all nodes within Docker containers
- external etcd cluster running on master nodes within Docker containers
- Canal (Calico + Flannel) for Pod Networking
- Kubernetes Dashboard with admin user service account for Cluster Monitoring
Install latest version of Ansible.
python3 -m pip install -U ansible
virtualbox and vagrant can be installed from the following links: https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads https://www.vagrantup.com/downloads.html
update /etc/hosts file to include the following: 192.168.120.11 node1 192.168.120.12 node2 192.168.120.13 node3
update ~/.ssh/config to include the following: Host 192.168.120.1? node? User vagrant StrictHostKeyChecking no ForwardAgent yes
Run the following to create cluster of VMs.
vagrant up
vagrant status
You can easily destroy the cluster by:
vagrant halt
vagrant destroy -f
If you are deploying this on bare metal / AWS EC2 / Google Compute Engine instances, create new inventory and host_vars files with the correct IPs which can be accessed via SSH.
The following steps will allow you to deploy a Kubernetes HA cluster on your local vagrant cluster.
ansible-playbook -e "ansible_user=vagrant" -i vagrant.inventory install-kubernetes-site.yml
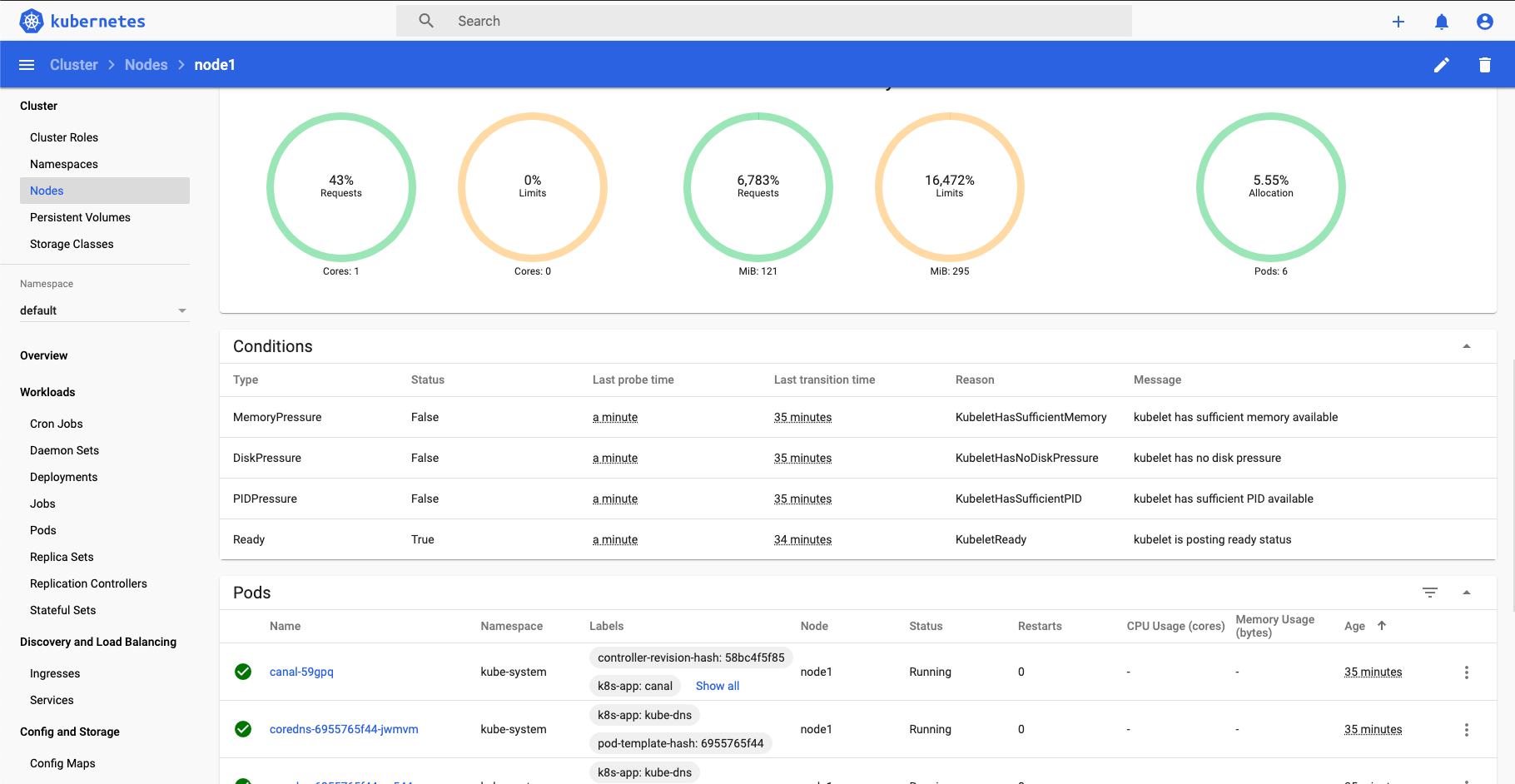
Deployment may take a while but once it's done, you'll need to set up an SSH tunnel to access port 7000 on the admin node and run port-forward on dashboard service.
ssh -L 127.0.0.1:7000:127.0.0.1:7000 root@node1
kubectl port-forward -n kubernetes-dashboard service/kubernetes-dashboard 7000:80 &
Dashboard can be accessed now on http://127.0.0.1:7000/#/login You'll need the token to access the kubernetes dashboard so run this command on the admin node:
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard describe secret $(kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard get secret | grep admin-user | awk '{print $1}')