The TaskHost PowerShell module and Subatomix.PowerShell.TaskHost NuGet
package provide a thread-safe PowerShell
PSHost
wrapper to improve the clarity of output from long-running, possibly parallel
tasks.
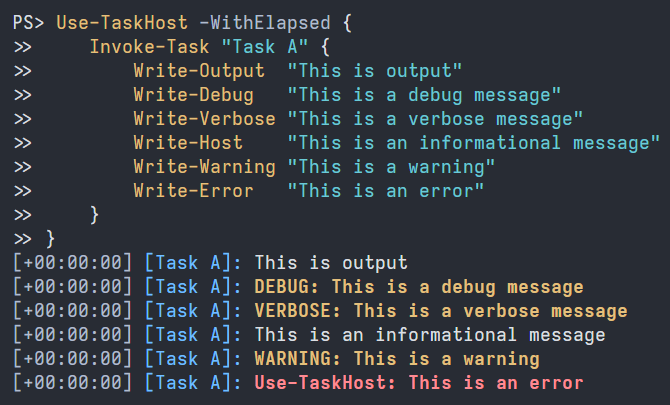
TaskHost adds a header to each line of output, reporting the elapsed time and which task produced the output. Line header components are optional and use color where supported.
- Tested: 100% coverage by automated tests.
- Documented: IntelliSense on everything. Quick-start guide below.
⚠ These instructions are for version 2.0 pre-releases. For version 1.0, see the prior version of these instructions.
From PowerShell 7 or later, install the TaskHost module:
Install-Module TaskHost -AllowPrereleaseUpdate or uninstall the module with Update-Module or Uninstall-Module,
respectively.
Developers wanting to implement similar features in their own software can install the Subatomix.PowerShell.TaskHost NuGet package to get the building blocks of the TaskHost module.
⚠ These instructions are for version 2.0 pre-releases. For version 1.0, see the prior version of these instructions.
Start with a Use-TaskHost command.
Use-TaskHost {
}Optionally, add -WithElapsed to enable the elapsed-time header.
Use-TaskHost -WithElapsed {
}For each task, add an Invoke-Task command.
Use-TaskHost -WithElapsed {
Invoke-Task "Step 1" {
Write-Host "Example output from a task"
}
Invoke-Task "Step 2" {
Write-Host "Example output from another task"
}
}Output:
[+00:00:00] [Step 1]: Example output from a task
[+00:00:00] [Step 2]: Example output from another task
A task is a chunk of code whose output should be distinguishable from that of other tasks and non-task code. Beyond that, what constitutes a task is entirely at the discretion of the user of this module. There is no restriction on the number of or size of tasks or on what can appear in a task's script block.
Tasks are nestable.
Use-TaskHost -WithElapsed {
Invoke-Task "Step 3" {
Invoke-Task "Part 1" {
Write-Host "Example output from a nested task"
}
}
}Output:
[+00:00:00] [Step 3|Part 1]: Example output from a nested task
The PowerShell ForEach-Object -Parallel command complicates the preceding
example. See
this script
for a working example with detailed explanation.
Information about the currently executing task is available via the following expression, which returns null if there is no such task:
[Subatomix.PowerShell.TaskHost.TaskInfo]::CurrentThe TaskInfo object provides a few useful properties:
Id– Unique integer identifier for the task.Name– Name of the task. Writable.FullName–Nameprefixed with theFullNameof the task's parent, if any.Parent– The task in which the current task is nested, if any.
The FullName property determines the text that TaskHost prepends to each
output line. To change the text, set the Name property of the task or of its
ancestors.
[Subatomix.PowerShell.TaskHost.TaskInfo]::Current.Name = "New name"To remove the line header, set the property to an empty string.
[Subatomix.PowerShell.TaskHost.TaskInfo]::Current.Name = ""