DBMS Language
To communicate database updates and queries, DBMS language is used. Different types of database languages are explained below:
- Data Definition Language (DDL): It is used to save information regarding tables schemas, indexes, columns, constraints, etc.
- Data Manipulation Language (DML): It is used for accessing and manipulating databases.
- Data Control Language (DCL): It is used to access the saved data. It also allows to give or revoke access from a user.
- Transaction Control Language (TCL): It is used to run or process the modifications made by the DML.
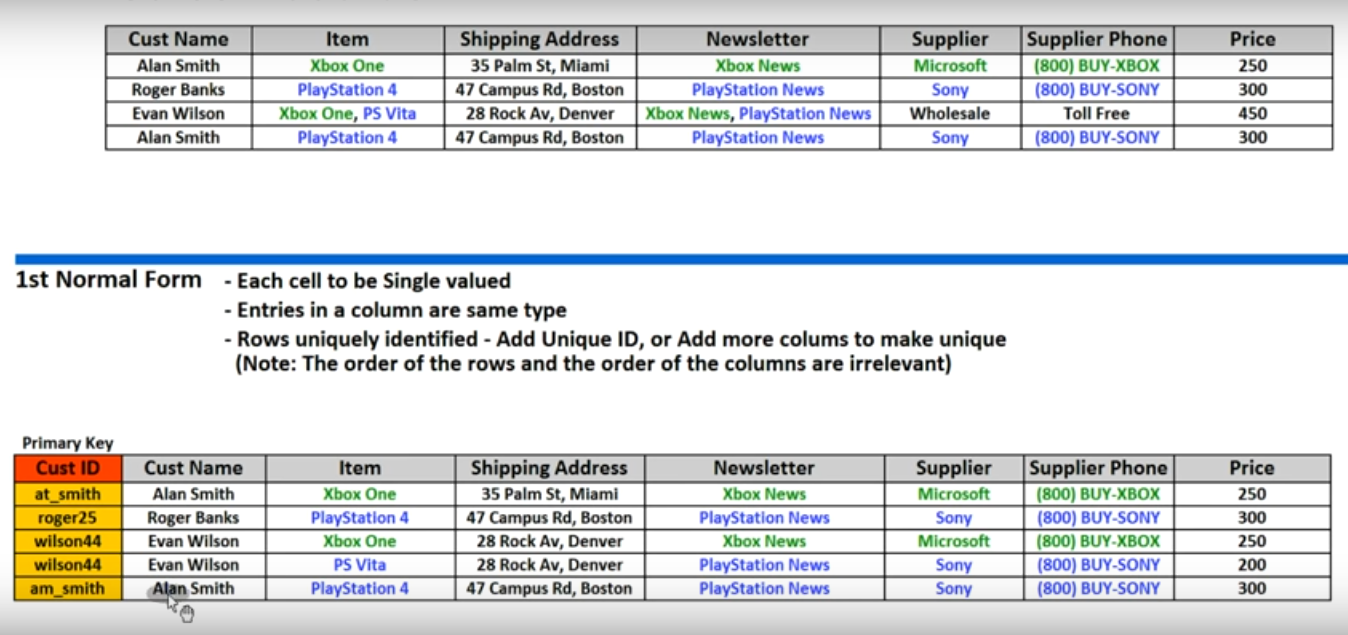
- Each cell to be single valued
- Entries in a column are same type
- Rows uniquely identified - Add unique ID, or add more columns to be unique.
- (Note: the order of the rows and the order of the columns are irrelevant)
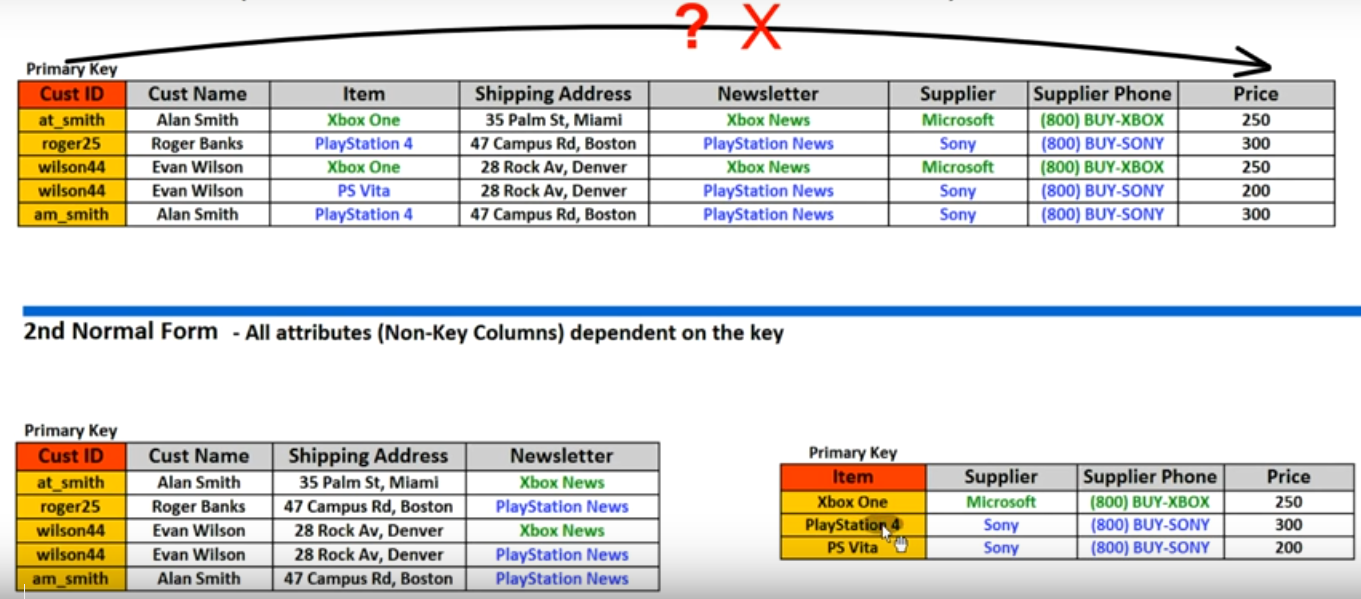
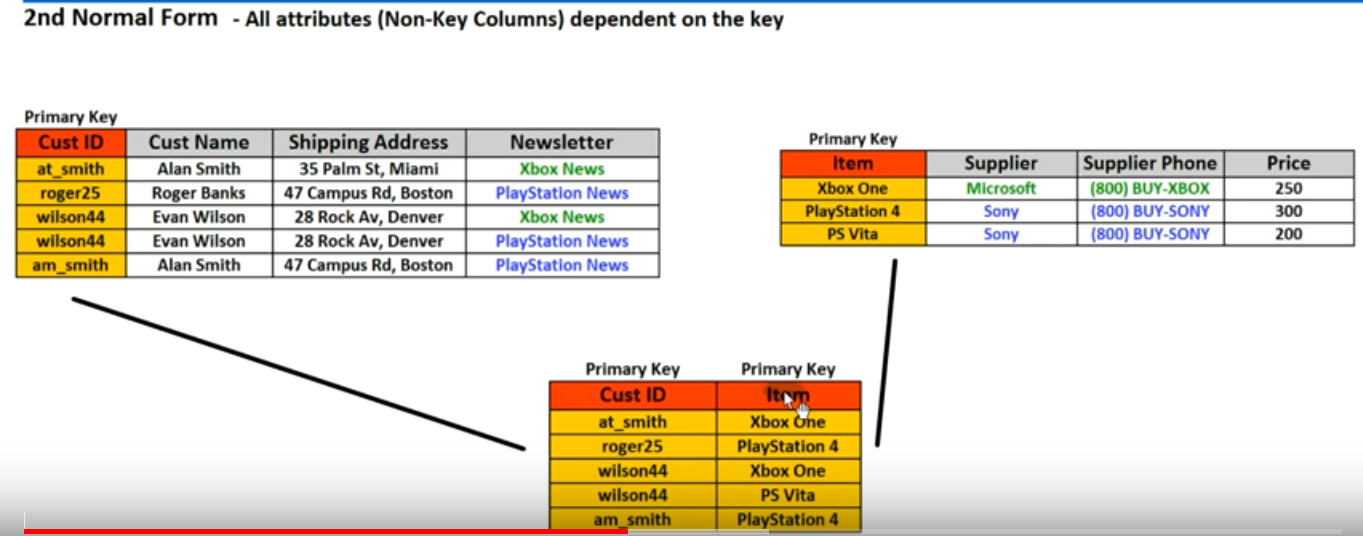
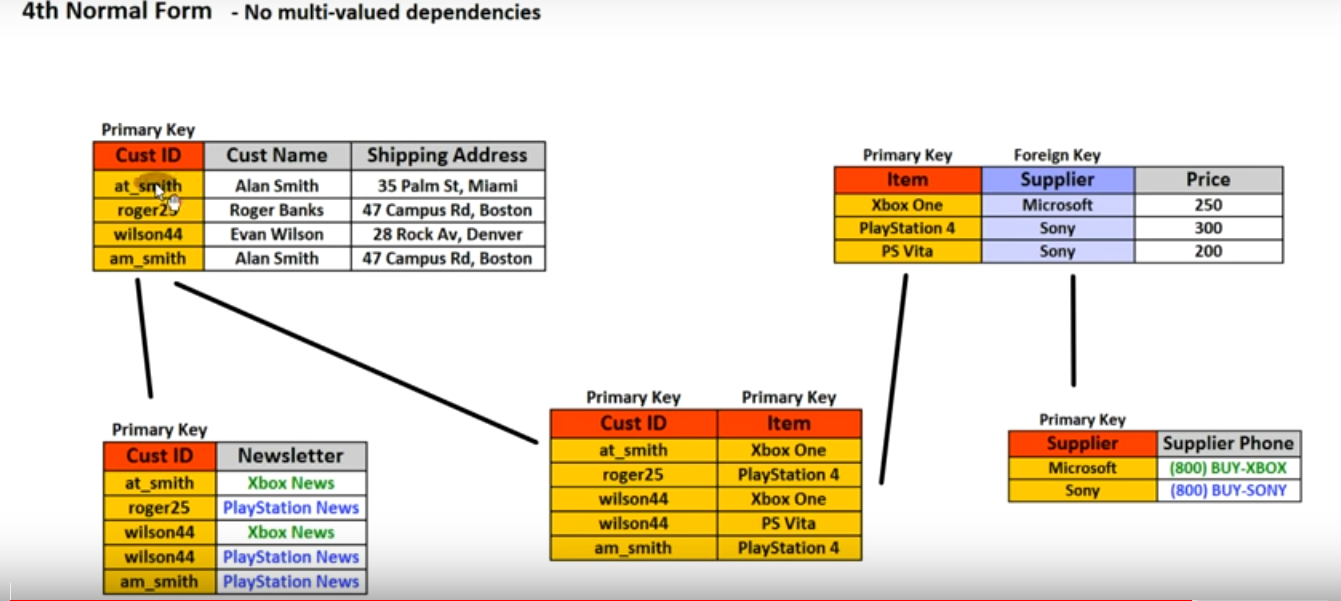
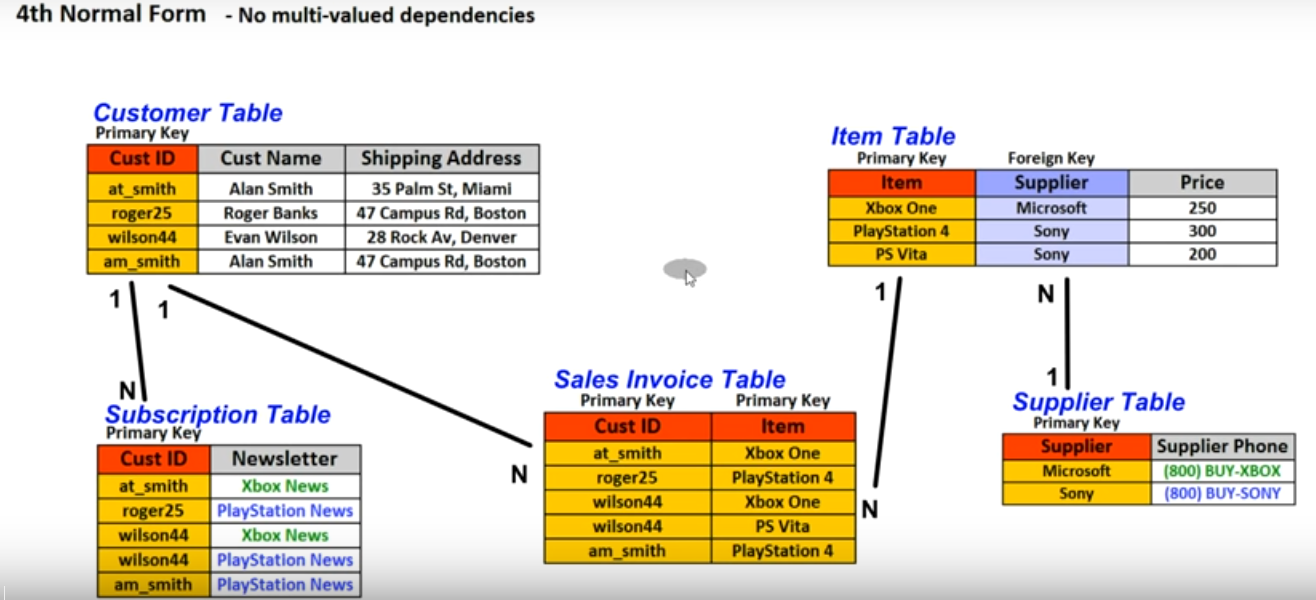
- All attributes(Non-key columns) dependent an the key (Means than of columns to depended to key columns we should seperate its to another table)
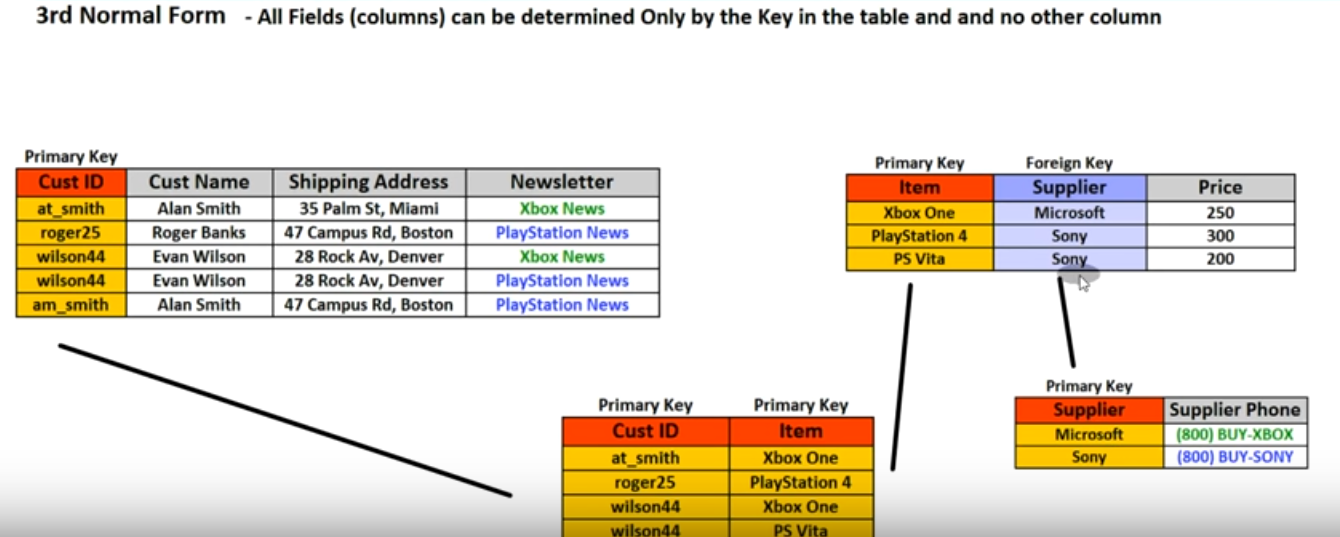
- All fiedls(columns) can be determined only by the key in the table and no other columns (Means that if two or three columns has 1 to 1 relationship we can seperate its to another table)
- No multi-valued dependencies
select * from `User_Table` where id not in(
select id from
(select id, max(registration_date) as registration_date, productkey from `User_Table`
where
productkey in
(select productkey
from
(SELECT count(productkey) as repeat_productkey, productkey FROM `User_Table` where os = '' group by productkey having count(productkey)>=2) as s
)group by productkey) as t6)
AND
productkey in (
select productkey from
(select id, max(registration_date) as registration_date, productkey from `User_Table`
where
productkey in
(select productkey
from
(SELECT count(productkey) as repeat_productkey, productkey FROM `User_Table` where os = '' group by productkey having count(productkey)>=2) as s
)group by productkey) as t6
)
DROP SCHEMA public CASCADE;
CREATE SCHEMA public;
GRANT ALL ON SCHEMA public TO postgres;
GRANT ALL ON SCHEMA public TO public;
CREATE FUNCTION dup(int) RETURNS TABLE(f1 int, f2 text)
AS $$ SELECT $1, CAST($1 AS text) || ' is text' $$
LANGUAGE SQL;
SELECT * FROM dup(42);
do $$
begin
for counter in 1..6 by 2 loop
raise notice 'counter: %', counter;
end loop;
end; $$
yum update
sudo yum install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm
sudo /usr/pgsql-10/bin/postgresql-10-setup initdb
sudo systemctl start postgresql-10
sudo systemctl enable postgresql-10
create database database_name
create user username with password 'password'
GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE database_name TO username;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE database_name TO username;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON mtn_cfg_descripancy TO rpat
ALTER USER username CREATEDB;
CREATE TABLE order_details
( order_detail_id integer CONSTRAINT order_details_pk PRIMARY KEY,
order_id integer NOT NULL,
order_date date,
quantity integer,
notes varchar(200),
CONSTRAINT order_date_unique UNIQUE (order_id, order_date)
);
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD CONSTRAINT constraint_name UNIQUE (column1, column2, ... column_n);
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP CONSTRAINT constraint_name;
select max(date_tiem, formula_cal) from table;
COPY(select region,province, city,device_name,resource_name,type,port_level, capacity, subtype, link_name from mtn_transmission_mapping where deleted = false) to '/tmp/mapping_2020_10_04.csv' with csv;
pg_dump --data-only -d 'moniaz' -U 'moniazuser' < ~/Downloads/moniaz_d.dump
COPY(region,province, city,device_name,resource_name,type,port_level, capacity, subtype, link_name) from '/tmp/mapping_2020_10_04.csv' with csv;
expalin select ...
explain analyze select ....
create foreign table mtn_huawei_lte_cell_hrly_r7r8 () inherits(mtn_huawei_lte_cell_hrly) server master_server;
to_char(collection_date::Date, 'YYYY')
to_char(collection_date::Date, 'YYYY/mm/dd')
sudo -u postgres pg_dump -d rpat -t mtn_dump_mapping > mtn_dump_mapping.sql
sudo pg_restore --host "localhost" --port "5432" --username "moniazuser" -W --dbname "moniaz" --verbose "/home/ubuntu/moniaz/moniaznew.dump"
SELECT table_name FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema = 'public';
The NULLIF function returns a null value if value1 equals value2; otherwise it returns value1. This can be used to perform the inverse operation of the COALESCE example given above:
SELECT NULLIF(value, '(none)') ...
clickhouse-client --format_csv_delimiter="," --query="INSERT INTO rpat.mtn_transmission_mapping (region, province, city,device_name,resource_name,type,port_level, capacity, subtype,link_name) FORMAT CSV" < /tmp/mapping_2020_10_04.csv
Buffers the data to write in RAM, periodically flushing it to another table. During the read operation, data is read from the buffer and the other table simultaneously.
Buffer(database, table, num_layers, min_time, max_time, min_rows, max_rows, min_bytes, max_bytes)
Engine parameters:
database – Database name. Instead of the database name, you can use a constant expression that returns a string.
table – Table to flush data to.
num_layers – Parallelism layer. Physically, the table will be represented as num_layers of independent buffers. Recommended value: 16.
min_time, max_time, min_rows, max_rows, min_bytes, and max_bytes – Conditions for flushing data from the buffer.
Data is flushed from the buffer and written to the destination table if all the min* conditions or at least one max* condition are met.
min_time, max_time – Condition for the time in seconds from the moment of the first write to the buffer.
min_rows, max_rows – Condition for the number of rows in the buffer.
min_bytes, max_bytes – Condition for the number of bytes in the buffer.
During the write operation, data is inserted to a num_layers number of random buffers. Or, if the data part to insert is large enough (greater than max_rows or max_bytes), it is written directly to the destination table, omitting the buffer.
The conditions for flushing the data are calculated separately for each of the num_layers buffers. For example, if num_layers = 16 and max_bytes = 100000000, the maximum RAM consumption is 1.6 GB.
Example:
CREATE TABLE merge.hits_buffer AS merge.hits ENGINE = Buffer(merge, hits, 16, 10, 100, 10000, 1000000, 10000000, 100000000) Creating a merge.hits_buffer table with the same structure as merge.hits and using the Buffer engine. When writing to this table, data is buffered in RAM and later written to the ‘merge.hits’ table. 16 buffers are created. The data in each of them is flushed if either 100 seconds have passed, or one million rows have been written, or 100 MB of data have been written; or if simultaneously 10 seconds have passed and 10,000 rows and 10 MB of data have been written. For example, if just one row has been written, after 100 seconds it will be flushed, no matter what. But if many rows have been written, the data will be flushed sooner. When the server is stopped, with DROP TABLE or DETACH TABLE, buffer data is also flushed to the destination table.
+ When reading from a Buffer table, data is processed both from the buffer and from the destination table (if there is one).SELECT if(cond, then, else)
endsWith(s, suffix)
Returns whether to end with the specified suffix. Returns 1 if the string ends with the specified suffix, otherwise it returns 0.
startsWith(str, prefix)
Returns 1 whether string starts with the specified prefix, otherwise it returns 0.
SELECT startsWith('Spider-Man', 'Spi');
``` :) SELECT :-] number, :-] CASE number :-] WHEN 0 THEN number+1 :-] WHEN 1 THEN number*10 :-] ELSE number :-] END :-] FROM system.numbers :-] WHERE number < 10 :-] LIMIT 10;
```
clickhouse-clien -u root --password ***
mysql -h 192.168.*.* -u root --delimiter="," -p -e 'select * from rpat.mtn_2g_targets_2020_quarter4_health_index' | tr '\t' ',' > mtn_2g_targets_2020_quarter4_health_index.csv
1- sudo apt-get purge mongodb-org*
2- sudo rm -r /var/log/mongodb
3- sudo rm -r /var/lib/mongodb
Then start installing with the following commands:
4- sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 0C49F3730359A14518585931BC711F9BA15703C6
5- echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu xenial/mongodb-org/3.4 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.4.list
6- sudo apt-get update
7- sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org
redis-cli
Go to db:
>> select 4
Show keys:
>> keys *
Set:
>> set name "mohamad"
Get:
>> get name
Cunt of keys:
>> dbsize
Info:
>> nfo keyspace
Check redis version:
>> info