Ciro is a MVC PHP Framework to kickstart projects rapidly, it's designed to be simple, configurable, modular, decoupled, extensible and lightweight to make it easier to build better and easily maintained PHP code.
Out of the box Ciro comes with :
- Namespaced PSR-4 structure
- Single Entry Point PHP App
- Pretty Urls Support
- Default Routes
- Custom Routes
- Views Layouts
- Alerts & Flash Messages
- Custom Error Pages
- Exceptions & Errors Handler with logging
- Database helper classes for Mysqli, PDO, and MongoDB
- Composer's autoloading
- for Views, default template comes with
- Bootstrap 4
- Jquery 3.2.1
- Font Awesome 5
Ciro comes with a template project with a simple authentication system to kickstart developing for you project or prototype.
Online example of the framework template project: https://ciro-framework.herokuapp.com
- PHP 5.6 or greater.
- (PHP 7.0+ if you're using MongoDB helper class)
- Apache Web Server or equivalent with mod rewrite support.
- Download Ciro PHP Framework
- Download & install XAMPP with PHP 5.6+ (7.0+ Recommended) from Here.
- Copy Ciro PHP Framework folder contents to
C:\xampp\htdocsfor windows or/Applications/XAMPP/xamppfiles/htdocsfor mac. - OR Configure XAMPP's Apache's
httpd.confDirectory root to Ciro's Directory, see instructions: Here. - Open XAMPP and start both Apache and Mysql.
- Go to localhost and start developing!
-
To Use the pre-made Login/Register, and you're using SQL (not Mongo) you must create the database and tables in SQL.
- Go to
http://localhost/phpmyadminand execute the query insql_database_script.sqlthat exists in the root directory.
- Go to
-
To Use the pre-made Login/Register, and you want to be using MongoDB you must install
mongodb extensionandMongoDB PHP Libraryusing composer, instructions Here. also replaceModels/UserRepository.phpwithModels\.disabled.mongo.userrepository.class.phpto use the MongoDB version.
- The Framework comes with a blank template project contains a Homepage and a simple extensible User's Register/Login/View with 3 variants of 'User Repository' depending on your Database and extension of choice.
Mysqliversion for MySql.PDOVersion for PDO supported RDBMS(s).MongoDBversion (php 7.0+).
All configurable via the config files.
- Online preview of the framework template project: https://ciro-framework.herokuapp.com
The Project Structure follows namespaced PSR-4 specifications.
+---Config <- Contains Configurations Files.
+---Controllers <- Contains a Dir for each Route each contains this Route's Controllers.
+---Core <- Contains Core Classes for the framework
+---Logs <- Contains Logs created by the scripts (e.g Exception Handler logs)
+---Models <- Contains Models (can be sub-directoried using namespaces using PSR-4 specs.
+---Utilities <- Contains Utility Classes.
+---Vendor <- Composer's Vendor Dir, contains autoloader code and third-party packeges.
+---Views <- Contains Views, a Dir for each route, each contains a Dir for each Controller.
| +---_FullMessages <- Contains Full Messages HTML designs.
| +---_Layouts <- Contains Layouts
+---Webroot <- Public Dir contains the single point of entry of the program, and all public assets.
In Ciro a default URL route has the following structure:
http://example.io/{route}/{controller}/{action}/{param1?}/{param2?}/...
This url resolves to the method {action} of controller {controller} in namespace controllers/{route} so in PHP OOP notation corresponds to:
App\Controllers\{route}\{controller} -> {action}In configuration Config/config.php, you can specify A 'default_route' so if a url doesn't contain a route, the program will route according to default route. by default the 'default_route' is 'Web'.
So, a typical URL using default route will have the following structure:
http://example.io/{controller}/{action}/{param1?}/{param2?}/...
so in PHP OOP notation corresponds to:
App\Controllers\Web\{controller} -> {action}Another example:
for $id
http://example.io/{controller}/{action}/{param1}
http://example.io/ Product / View / 6800
-
if the Url doesn't specify
{action}, the program to route to the 'default_action' specified in 'Config/config.php'. -
if the Url doesn't specify
{controller}, the program to route to the 'default_controller' specified in 'Config/config.php'. -
to add a new route and access it using default routing, you must add it in
Config/config.phpRouting table.
Given this url for example:
for $id $color
http://example.io/{controller}/{action}/{param1}/{param2}
http://example.io/ Product / View / 6800 / red
-
Params are accessible inside the Controller's method via
$this -> params[0..*]array, for example$this->params[0]holds the value of{param1}in the url above. -
Another way to access params inside the Controller's method is by adding arguments to the controller's method itself. using the same example above, if
ProductController -> Viewis defined like this:class ProductController extends WebController { public function view($id, $color = 'white'){ /* controller's method code here */ } }
$id will have the value of {param1}, $color will have the value of {param2} and so on...
Notice that if {param2} wasn't in the URL, $color will use the default value specified, however if {param1} wasn't in the URL, the Program is going to render a 404: Not Found Message because $id has no default value specified in the controller's method.
-
Custom Routes give you the possibility to specify a URL with a specific pattern that if matched the URL is routed to the specified
{route}\{controller}::{action}with the proper specified params. -
Custom Routes can be Enabled/Disabled in
Config/config.php. -
You can specify a custom route for every REST HTTP Verb e.g(
GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc) or specify a custom route for All possible HTTP verbs using:// for GET requests Route::get($uri, $route, $controller, $action); // same for POST, PUT, DELETE, etc requests Route::post(), Route::put(), Route::delete(), Route::patch(), Route::options(); // for ALL requests Route::all();
-
Custom Routes are defined in /Config/routes.php.
Route::get('custom/route/{id}/{name}/{language?}','Web', 'Home', 'CustomRouteAction');
Any URL that matches
custom/route/{id}/{name}/{language?}will be routed to: Route:WebController:HomeAction:CustomRouteAction.
- Params should be surrounded by curly braces
{ name }, optional params should have a'?'at the end of their names{ optinoalParam? }. - Params are accessible inside the Controller's method via
$this -> params[0..*]array and are ordered respectively to the order of them in the URL.- in the above example,
$this -> param[0]corresponds to{id},$this -> param[1]corresponds to{name}, etc
- in the above example,
- If Controller's method has params defined, params are passed to this method ordered respectively to the order of them in the URL.
A Controller's Method of a custom route should be defined as follows:
class HomeController extends WebController {
public function CustomRouteAction($id, $name, $language = 'default'){
/* controller's method code here */
}
}Note in the above example: {language?} is an optional param, optional params should have a '?' at the end of their names, and should have a default value in the Controller's method, otherwise if the param is missing, the program will render a 404: Not Found Message because an optional param was not given and has no default value.
When setting a custom route, you can put a variable param in the target route, controller or action to create a more 'general' custom route.
Example:
Route::get('custom/{var_controller}/pattern/{action}/{param1}','Web', '{var_controller}', '{action}');Any URL that matches custom/{var_controller}/pattern/{action}/{param1}
will be routed to: Route: Web, Controller: {var_controller} , Action: {action} and params will not include neither {var_controller} nor {action} because they were used in the routing.
so if a request with URL = custom/Account/pattern/View/sherifabdlnaby came it
will be routed to: Route: Web, Controller: Account , Action: View and params[0] = 'sherifabdlnaby'
-
Controller are responsible for processing users requests and returning the output for the user either as a HTML for
WebControllers, or JsonResult forApiControllers, or redirect to another destination. -
Controllers Directory should match the controller's namespace and should be as follows
Controllers\{route}\{ControllerName}Controller.phpand using the namespaceApp\Controllers\{route}where{route}is the route where this controller belongs to.
+---Controllers
| +---Api <-- Api route dir.
| | HomeController.php <-- Home Controller for API route.
| |
| \---Web <-- Web (Default) route dir.
| AccountController.php
| HomeController.php <-- Home Controller for Web default route.
-
a controller has 4 protected variables that it utilizes:
$params; // array() that holds method's params $model; // controller's model $data; // the $data array() is what is passed to the controller's view. $meta; // the $meta array() is what is passed to $layout meta section (for WebControllers Only)
-
The output of a controller (and what the user sees) is what is returned via it.
-
Controllers in Ciro have various functions to use when returning output inside controllers to ease these tasks.
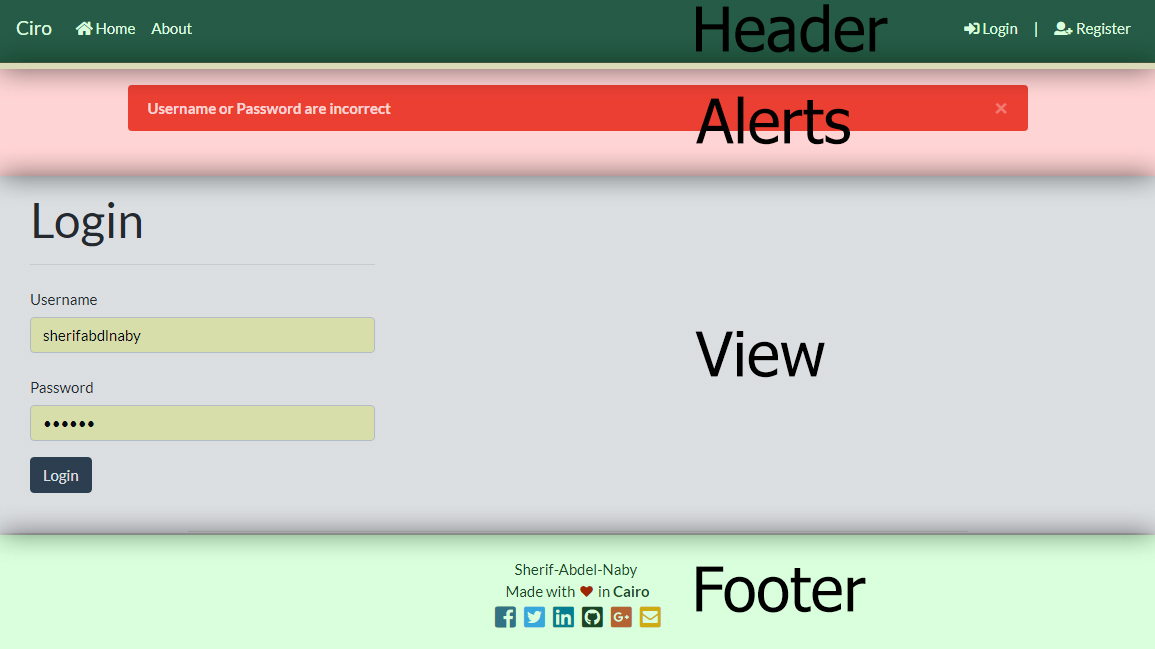
Render will render an HTML webpage using a layout, a layout contains header, metadata section, alerts, body, and footer. The body section of the layout is determined according the controller's method viewpath.
The controller's view uses the $data[] array to render its elements, and the metadata section uses the $meta[] array.
render($layout = null, $viewPath = null, &$data = null, &$meta = null);| Arg | Description | Default-value |
|---|---|---|
$layout |
Specifies the view layout used to render | Default layout specified in config.php |
$viewPath |
Specifies the path for the view to render | View determined according to Controller's method name |
$data |
the $data array() view will have access too |
The Controller's own $data array() |
$meta |
the $meta array() layout will have access too |
The Controller's own $meta array() |
return $this->render(); without any given arguments (using default values) will be sufficient in 90% of the cases.
Basic usage of $this -> render();
class AccountController extends WebController {
public function View($username){
$this -> data['name'] = $username;
return $this->render();
}
}renderFullError and renderFullMessage will render a custom message/error page. if a status code is given in 2nd parameter the controller send the corresponding HTTP status code header and renders this code's view.
function renderFullError($message, $statusCode = null, $layout = null);
function renderFullMessage($message, $statusCode = null, $layout = null);| Arg | Description | Default-value |
|---|---|---|
$message |
A message to be rendered in the view. | NONE (Required field) |
$statusCode |
HTTP Status Code | null |
$layout |
Specifies the view layout used to render | Default layout specified in config.php |
Basic usage of $this -> renderFullError() / renderFullMessage();
class AccountController extends WebController {
public function View($username){
if(/* User Found */)
return $this->render();
else
return $this->renderFullError('User not found!', 404);
}
}if any exception was raised during script execution the framework will render a 500 Internal Server Error custom error page.
When returning $this -> return() from a controller's no output is sent to the user but the user is redirected to the given URL.
function redirect($path);| Arg | Description | Default-value |
|---|---|---|
| $path | A Relative or Full Path to be redirected to |
NONE (Required field) |
Basic usage of $this -> redirect();
class AccountController extends WebController {
public function Login($username, $password){
if(/* Login Success */)
return $this->redirect('/'); // redirect to homepage.
else
return $this->renderFullMessage('Incorrect Username or Password', 401);
}
}Check if User is/n't logged in, redirect to homepage/login if not.
These functions are not used by return statement, however it stops script if they are redirecting the user, which means any code below this functions will not be executed if their validation is false;
function verifyLoggedIn();
function verifyNotLoggedIn();Basic usage of $this -> verifyLoggedIn() / verifyNotLoggedIn();
class AccountController extends WebController {
public function Login($username, $password){
$this -> verifyNotLoggedIn(); //Redirects to Homepage if user is already logged in.
if(/* Login Success */)
return $this->redirect('/');
else
return $this->renderFullMessage('Incorrect Username or Password', 401);
}
}The Session Class is an extensible class that will manage the usage of $_SESSION across the programs to enforce single responsibility principle.
/* Save Parameters to $_SESSION, use for Login */
public static function saveLoginSession($_id, $username);
/* Return TRUE if user is logged On */
public static function isLoggedIn();
/* Unset and Destroy current Session, use for logout */
public static function destroyLoginSession();
/* Add Error Alerts to be rendered to user when controller's $this -> render() is called */
public static function addErrorAlert($errorAlert);
/* Add Warning Alerts to be rendered to user when controller's $this -> render() is called */
public static function addWarningAlert($warningAlert);
/* Add info Alerts to be rendered to user when controller's $this -> render() is called */
public static function addInfoAlert($infoAlert);
/* Add success Alerts to be rendered to user when controller's $this -> render() is called */
public static function addSuccessAlert($successAlert);-
Alerts are flash messages saved in user's sessions, alerts can then be showed to user either by rendering as an HTML or encoding them in JSON in-case of an API.
-
Alerts can be used to show errors about form-validation, or a message if a process succeeded or failed.
-
Alerts have their own section in any layout, Controller -> render() function will render any alerts stored in User Session.
-
There are 4 types of Alerts:
- Error Alerts, used in displaying errors.
- Warning Alerts, used in displaying warnings.
- Info Alerts, used in displaying information, hint or a notice.
- SuccessAlert, used in displaying success operations.
A Layout is the structure of the HTML webpage, it consists of 5 sections
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| meta | This section renders HTML metadata tags for title, desc and SEO tags. metadata passed and filled by Controller and is accessible in the $meta array() |
| header | This section renders the page Header |
| alerts | This section renders alerts stored in user's session if any |
| content | This section renders Main part of the page, and has its data passed and filled by the controller |
| footer | This section renders the page footer |
+---Views
| \---_Layouts
| \---default <-- Layout root directory.
| | | footer.html
| | | header.html
| | | layout.html
| | | meta.html
| | \---alerts <-- alerts directory.
| | errors.html
| | infos.html
| | successes.html
| | warnings.html
| \---anotherLayout
layout.html is the final file rendered when rendering the layout, it is the structure of which goes over which, etc and any CSS/JS that are used in this layout must be included in layout.html such as Bootstrap CSS and JS
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<?= $data['meta'] ?>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<?= $data['header'] ?>
<?= $data['alerts'] ?>
<?= $data['content'] ?>
<?= $data['footer'] ?>
<script src="/bootstrap/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>A view is the output of a web controller's action, a view has a $data assoc array which is passed by the controller, It is used to pass data between controller and view. the view location must match the controller path/namespace structure.
- Example for action
ViewofAccount Controllerin theWebRoute
+---Controllers
| +---Api
| | HomeController.php
| |
| \---Web
| AccountController.php <-- Account Controller of Web route in Controllers\Web
| HomeController.php
|
+---Views
| +---Web
| | +---Account <-- Account Controller View Dir in Controller\Web\Account
| | | Index.html
| | | Login.html
| | | Register.html
| | | View.html <-- The View for action 'View', of 'Account Controller' in the 'Web' Route
| | |
| | \---Home
| | About.html
| | Index.html
- Exception & Error Handler can be Enabled/Disabled in
Config/config.php. - Exception & Error handler will convert any error to an ErrorException.
- If Enabled in configurations, Exception Handler will log any uncaught exceptions or errors.
- Logs file directory is specified in configurations too.
Database Helper classes are used to get a singleton instance for Database connections, where connection credentials are store in config files.
| Class | Extension | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DBPdo | PDO |
A Singleton Class for PDO DB Extension, PDO can be used to connect to various RDBMs like MySql, MariaDB, or PostgreSQL, connection credentials set at Config\pdo.php and enabled at Config/config.php |
| DBSql | Mysqli |
A Singleton Class for Mysqli Extension, connection credentials for mysql set at Config\mysqli.php and enabled at Config/config.php |
| DBMongo | mongodb using MongoDB PHP Library (Php 7.0+) |
A Singleton Class for a connection of MongoDB PHP Library that is built around low-level mongodb extension, credentials are stored at Config\mongo.php and enabled at Config/config.php |
- Note: DBMongo requires
mongodbextension andMongoDB PHP Library, which both requires PHP 7.0+
- to install mongodb extension : http://php.net/manual/en/mongodb.installation.php
- to install MongoDB PHP Library : https://docs.mongodb.com/php-library/current/tutorial/install-php-library/
- Composer:
composer require mongodb/mongodb
- Ciro is already using composer autoload, just run the command above and you're cool.
- Composer:
Ciro PHP Framework is under the MIT License, you can view the license Here.