Zense is a mental health support platform designed to provide a safe and private environment for users to express their thoughts and feelings. Users can confide in an AI chatbot, participate in forums, and engage with a supportive community. The platform emphasizes privacy, empathy, and accessibility for anyone seeking mental health support.
- Project Goals
- How It Works
- Tech Stack
- Database Structure (ERD)
- Getting Started
- Api Documentation
- License
Zense aims to create a platform where users can confide in an AI chatbot and engage in meaningful, empathetic conversations that foster mental well-being.
Privacy is paramount in Zense. The AI confiding feature ensures that no conversation history is stored, providing users with a safe and private experience.
Zense is designed to be simple and intuitive, making it easy for users to interact with the AI, browse forums, and access the tools they need for mental health support.
- AI Chat: Users can chat with an AI that provides short, empathetic responses. No chat history is saved, ensuring complete privacy.
- Forum: Users can post questions, experiences, or support others in the community through the forum system.
- Journal: Zense includes a journaling feature to help users record their thoughts and feelings, allowing them to monitor their mental health more reflectively over time.
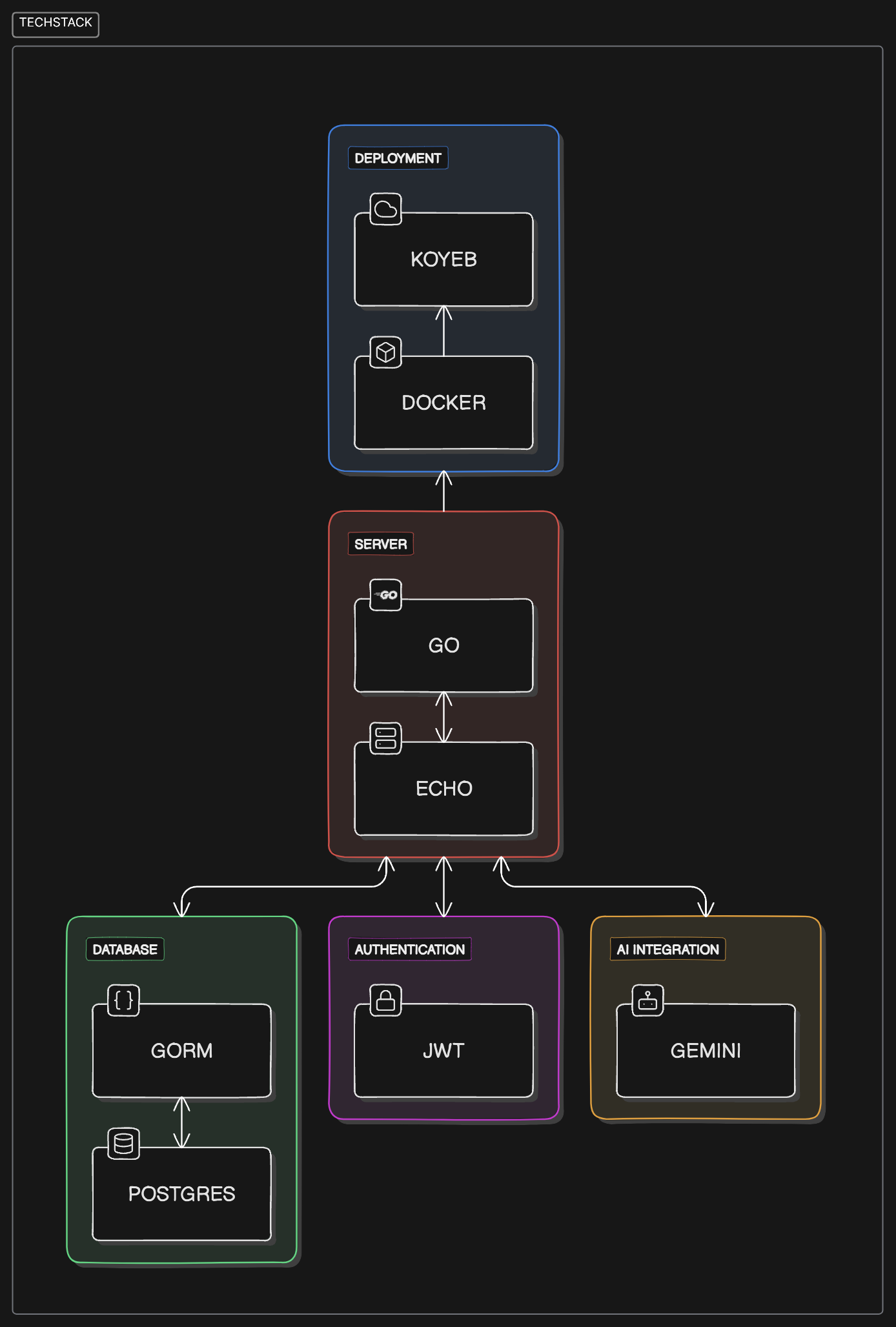
Zense is built with the following technologies:
- Go: The core programming language for the backend.
- Echo: A high-performance web framework for Go, used to handle routing and middleware.
- PostgreSQL: The relational database used to store user data, forum posts, and other platform data.
- GORM: The ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) library used to interact with the PostgreSQL database.
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens): For secure user authentication and authorization.
- Next.js: A React framework for building the frontend of the platform (planned).
- Google Gemini AI: For handling AI-driven responses in user conversations.
- Docker: Containerization of the application to ensure consistent deployment across different environments.
- Koyeb: Cloud hosting platform used for deploying the API and handling server infrastructure.
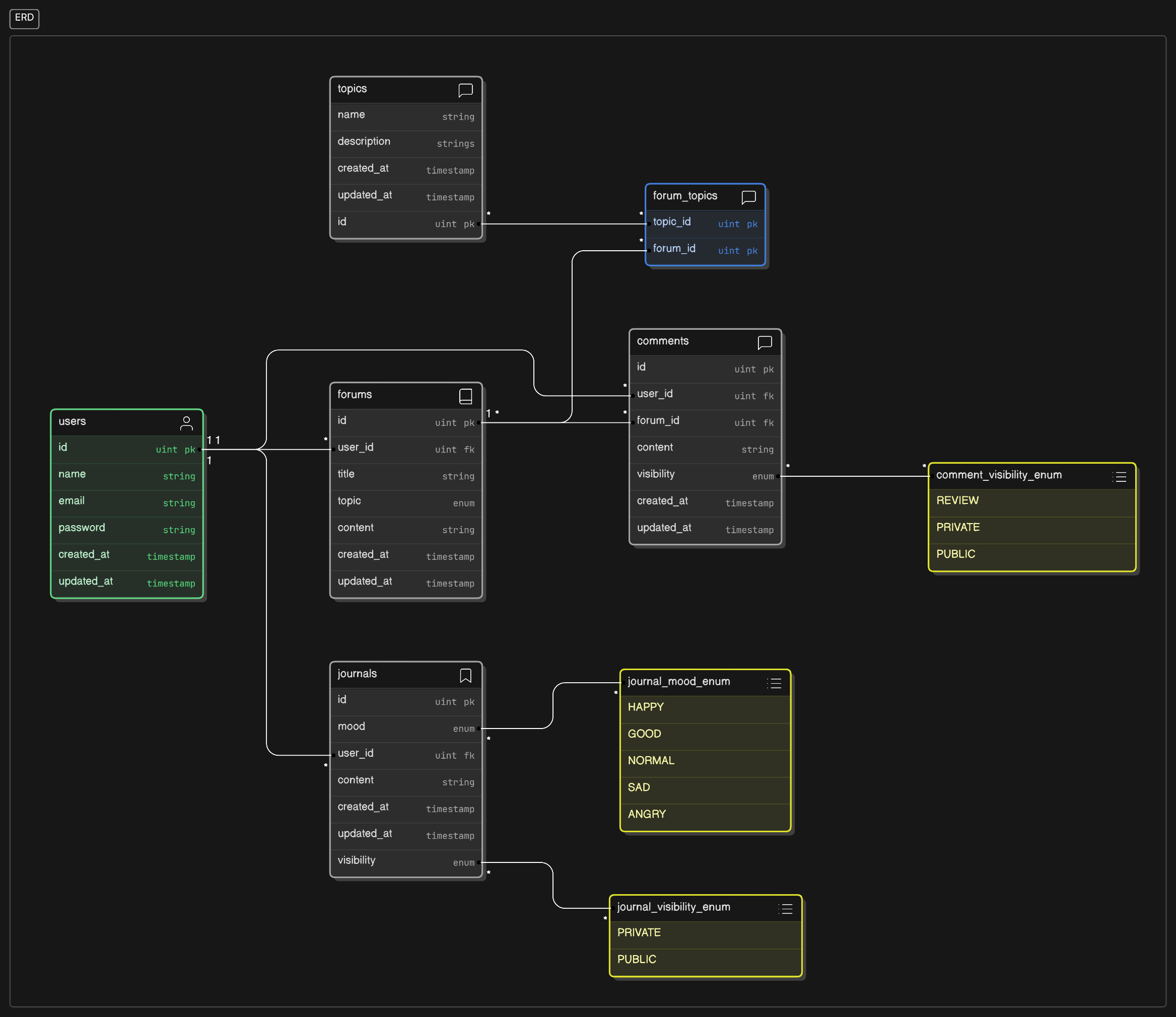
Zense's database structure is built with scalability and efficiency in mind, using PostgreSQL as the primary database. Below is the Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) outlining the main entities and relationships in the system:
- Users: Store user data, authentication details, and roles.
- Forums: Allow users to create posts and interact with the community.
- Comments: Users can leave comments on forum posts.
- Vent: Handles AI chat sessions.
- Go (version 1.23 or later)
- PostgreSQL (version 12 or later)
- Docker (for containerization)
- Git (for version control)
- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/shironxn/zense
cd zense
- Setup environment variables
cp .env.example .env
- Check available make commands
make help - With Docker
make docker-up
- Without Docker
make run
The API documentation is available via Swagger at: /api/v1/docs
Before using api docs, you must update the Swagger configuration in /cmd/main.go to reflect your deployment environment. Specifically, modify the schemes and host to match the deployment.
Example:
In /cmd/main.go:
// @host localhost:8080
// @schemes http