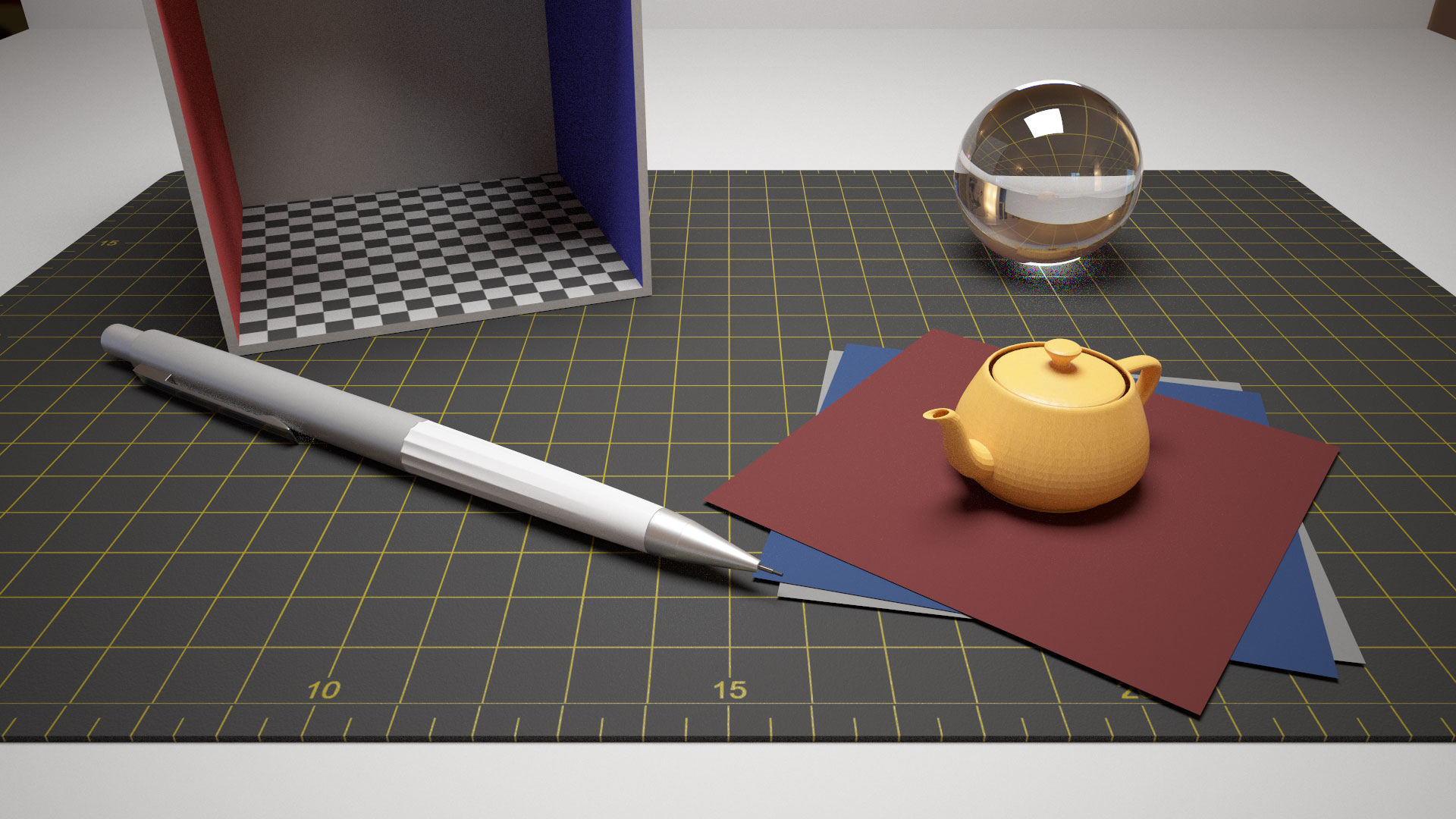
IBL image: sIBL Archive
VLRはNVIDIA OptiX 7を使用したGPUモンテカルロレイトレーシングレンダラーです。
VLR is a GPU Monte Carlo ray tracing renderer using NVIDIA OptiX 7.
- GPU Renderer using NVIDIA OptiX 7
- Full Spectral Rendering (Monte Carlo Spectral Sampling)
(For RGB resources, RGB->Spectrum conversion is performed using Meng-Simon's method [Meng2015]) - RGB Rendering (built by default)
- BSDFs
- Ideal Diffuse (Lambert) BRDF
- Ideal Specular BRDF/BSDF
- Microfacet (GGX) BRDF/BSDF
- Fresnel-blended Lambertian BSDF
- UE4- or Frostbite-like BRDF [Karis2013, Lagarde2014]
Parameters can be specified using UE4 style (base color, roughness/metallic) or old style (diffuse, specular, glossiness). - Mixed BSDF
- Shader Node System
- Bump Mapping (Normal Map / Height Map)
- Alpha Texture
- Light Source Types
- Area (Polygonal) Light
- Point Light
- Image Based Environmental Light
- Camera Types
- Perspective Camera with Depth of Field (thin-lens model)
- Environment (Equirectangular) Camera
- Geometry Instancing
- Light Transport Algorithms
- Path Tracing [Kajiya1986] with MIS
- Light Tracing
- Light Vertex Cache Bidirectional Path Tracing (LVC-BPT) [Davidovič2014]
- Correct handling of non-symmetric scattering due to shading normals [Veach1997]
- libVLR - Renderer Library based on OptiX
CのAPIを定義しています。
Exposes C API. - vlrcpp.h - Single file wrapper for C++
std::shared_ptrを用いてオブジェクトの寿命管理を自動化しています。
Automatically manages lifetime of objects via std::shared_ptr. - HostProgram - A program to demonstrate how to use VLR
Code Example using VLRCpp (C++ wrapper)
using namespace vlr;
ContextRef context = Context::create(cuContext, enableLogging, maxCallableDepth);
// Construct a scene by defining meshes and materials.
SceneRef scene = context->createScene();
TriangleMeshSurfaceNodeRef mesh = context->createTriangleMeshSurfaceNode("My Mesh 1");
{
Vertex vertices[] = {
Vertex{ Point3D(-1.5f, 0.0f, -1.5f), Normal3D(0, 1, 0), Vector3D(1, 0, 0), TexCoord2D(0.0f, 5.0f) },
// ...
};
// ...
mesh->setVertices(vertices, lengthof(vertices));
{
Image2DRef imgAlbedo = loadImage2D(context, "checkerboard.png", "Reflectance", "Rec709(D65) sRGB Gamma");
Image2DRef imgNormalAlpha = loadImage2D(context, "normal_alpha.png", "NA", "Rec709(D65)");
ShaderNodeRef nodeAlbedo = context->createShaderNode("Image2DTexture");
nodeAlbedo->set("image", imgAlbedo);
nodeAlbedo->set("min filter", "Nearest");
nodeAlbedo->set("mag filter", "Nearest");
ShaderNodeRef nodeNormalAlpha = context->createShaderNode("Image2DTexture");
nodeNormalAlpha->set("image", imgNormalAlpha);
// You can flexibly define a material by connecting shader nodes.
SurfaceMaterialRef mat = context->createSurfaceMaterial("Matte");
mat->set("albedo", nodeAlbedo->getPlug(VLRShaderNodePlugType_Spectrum, 0));
ShaderNodeRef nodeTangent = context->createShaderNode("Tangent");
nodeTangent->set("tangent type", "Radial Y");
uint32_t matGroup[] = { 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3 };
mesh->addMaterialGroup(matGroup, lengthof(matGroup), mat,
nodeNormalAlpha->getPlug(VLRShaderNodePlugType_Normal3D, 0), // normal map
nodeTangent->getPlug(VLRShaderNodePlugType_Vector3D, 0), // tangent
nodeNormalAlpha->getPlug(VLRShaderNodePlugType_Alpha, 0)); // alpha map
}
// ...
}
// You can construct a scene graph with transforms
InternalNodeRef transformNode = context->createInternalNode("trf A");
transformNode->setTransform(context->createStaticTransform(scale(2.0f)));
transformNode->addChild(mesh);
scene->addChild(transformNode);
// Setup a camera
CameraRef camera = context->createCamera("Perspective");
camera->set("position", Point3D(0, 1.5f, 6.0f));
camera->set("aspect", (float)renderTargetSizeX / renderTargetSizeY);
camera->set("sensitivity", 1.0f);
camera->set("fovy", 40 * M_PI / 180);
camera->set("lens radius", 0.0f);
// Setup the output buffer (OpenGL buffer can also be attached)
context->bindOutputBuffer(1024, 1024, 0);
// Let's render the scene!
context->setScene(scene);
context->render(cuStream, camera, enableDenoiser, 1, firstFrame, &numAccumFrames);- Make the rendering properly asynchronous.
- Python Binding
- Simple Scene Editor
- Compile shader node at runtime using NVRTC to remove overhead of callable programs.
現状以下の環境で動作を確認しています。
I've confirmed that the program runs correctly on the following environment.
- Windows 10 (21H2) & Visual Studio 2022 (17.2.4)
- Core i9-9900K, 32GB, RTX 3080 10GB
- NVIDIA Driver 516.40 (Note that versions around 510-512 had several OptiX issues.)
動作させるにあたっては以下のライブラリが必要です。
It requires the following libraries.
- libVLR
- CUDA 12.5
- OptiX 8.0.0 (requires Maxwell or later generation NVIDIA GPU)
- Host Program
- OpenEXR 3.1
- assimp 5.0
モデルデータやテクスチャーを読み込むシーンファイルがありますが、それらアセットはリポジトリには含まれていません。
There are some scene files loading model data and textures, but those assets are NOT included in this repository.
[Davidovič2014] "Progressive Light Transport Simulation on the GPU: Survey and Improvements"
[Kajiya1986] "THE RENDERING EQUATION"
[Karis2013] "Real Shading in Unreal Engine 4"
[Lagarde2014] "Moving Frostbite to Physically Based Rendering 3.0"
[Meng2015] "Physically Meaningful Rendering using Tristimulus Colours"
[Veach1997] "ROBUST MONTE CARLO METHODS FOR LIGHT TRANSPORT SIMULATION"
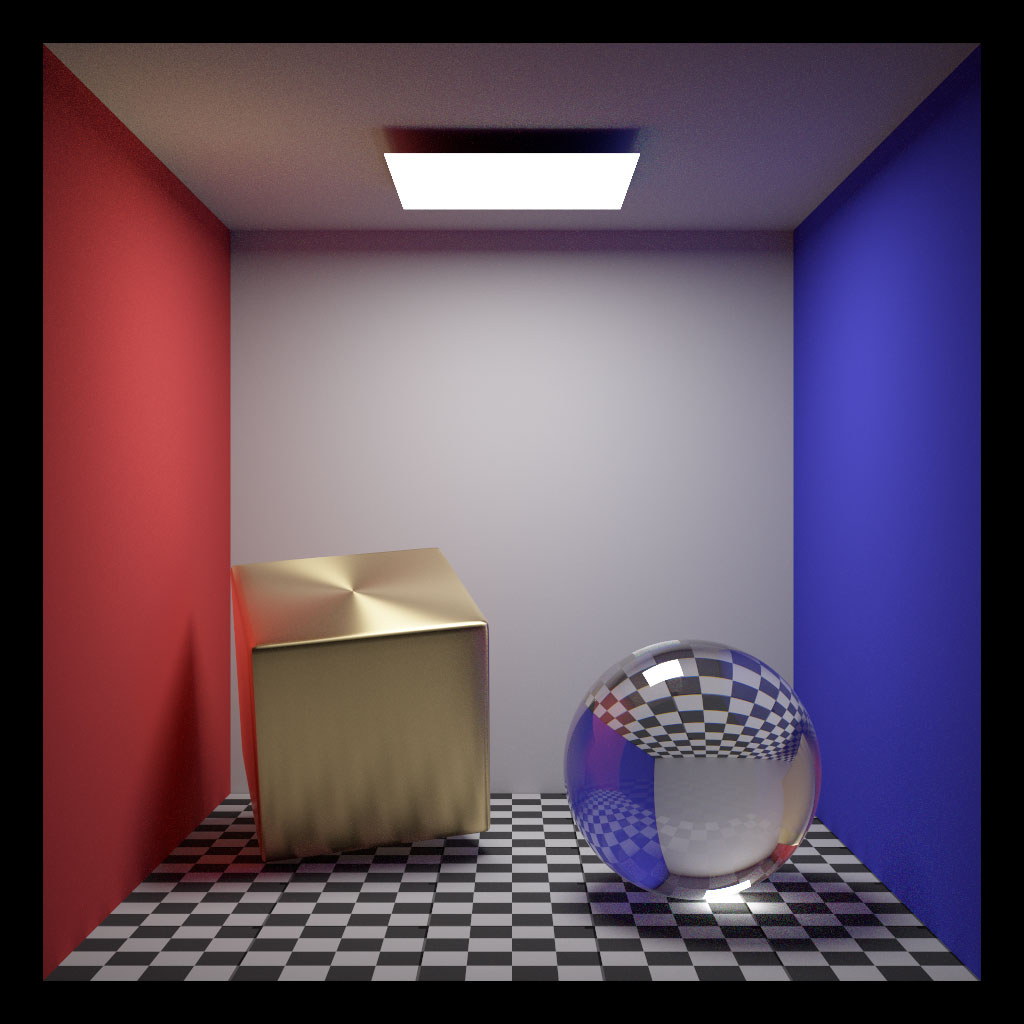
A variant of the famous Cornell box scene. The left box has anisotropic BRDF with circular tangents along its local Y axis (roughness is smoother along tangent, rougher along bitangent).
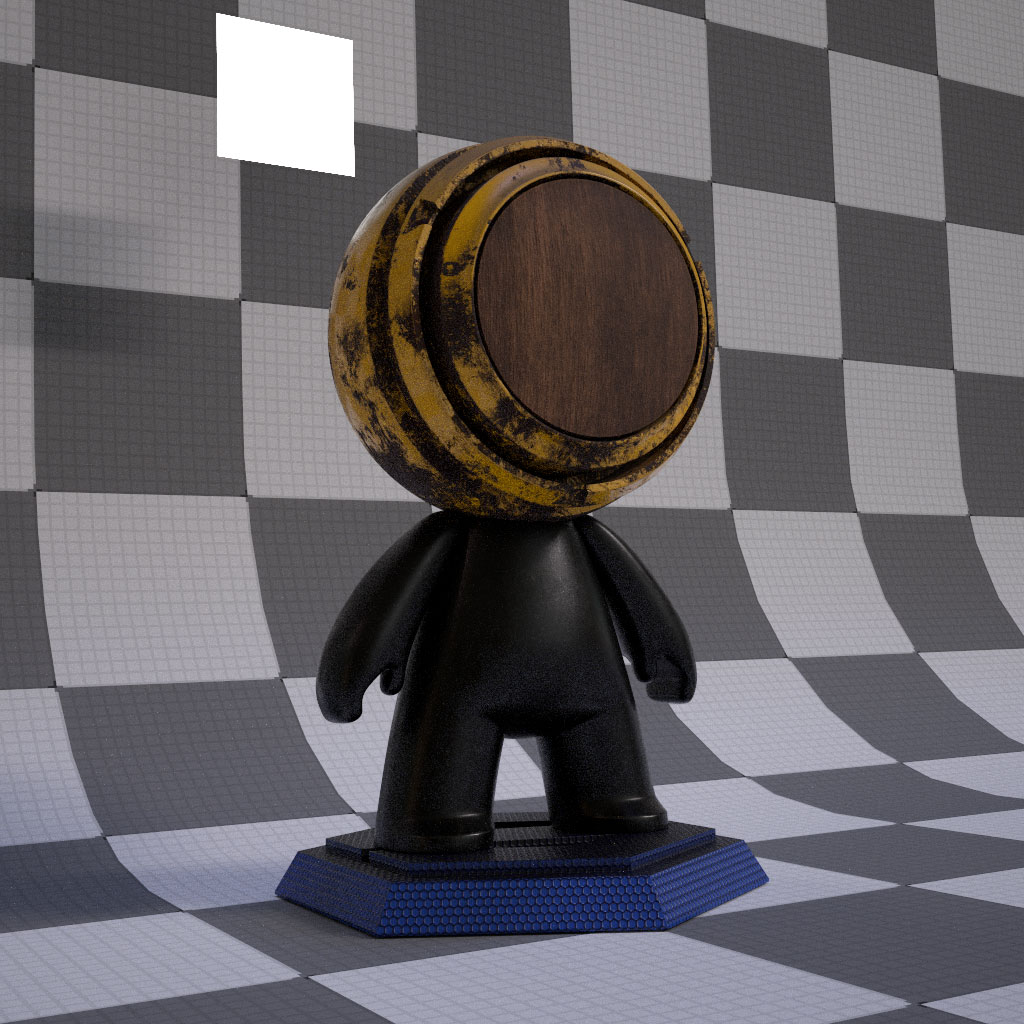

An object with UE4- or Frostbite 3.0-like BRDF (Textures are exported from Substance Painter) illuminated by an area light and an environmental light.
Model: Substance Painter
IBL image: sIBL Archive
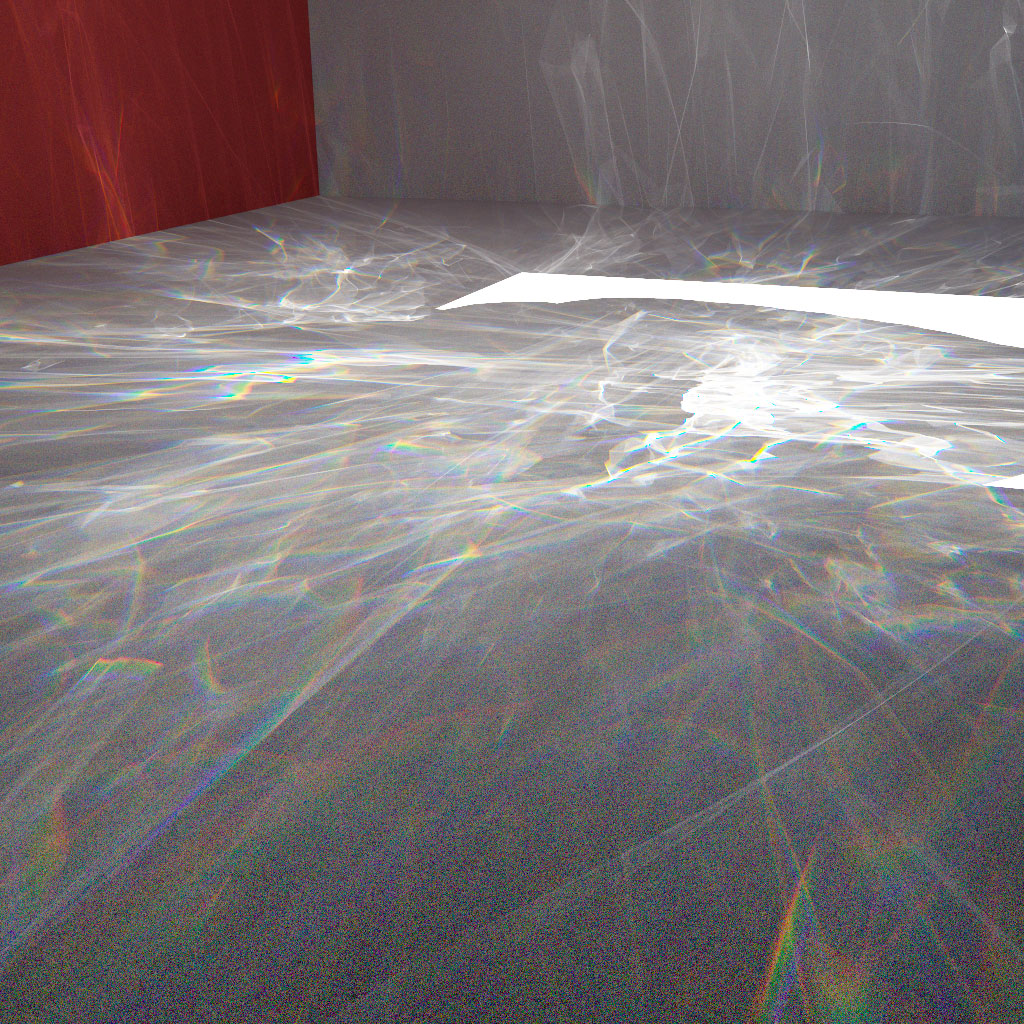
Caustics generated from Stanford bunny model illuminated by directional area light.
The renderer uses spectral rendering for this.
Model: Stanford Bunny
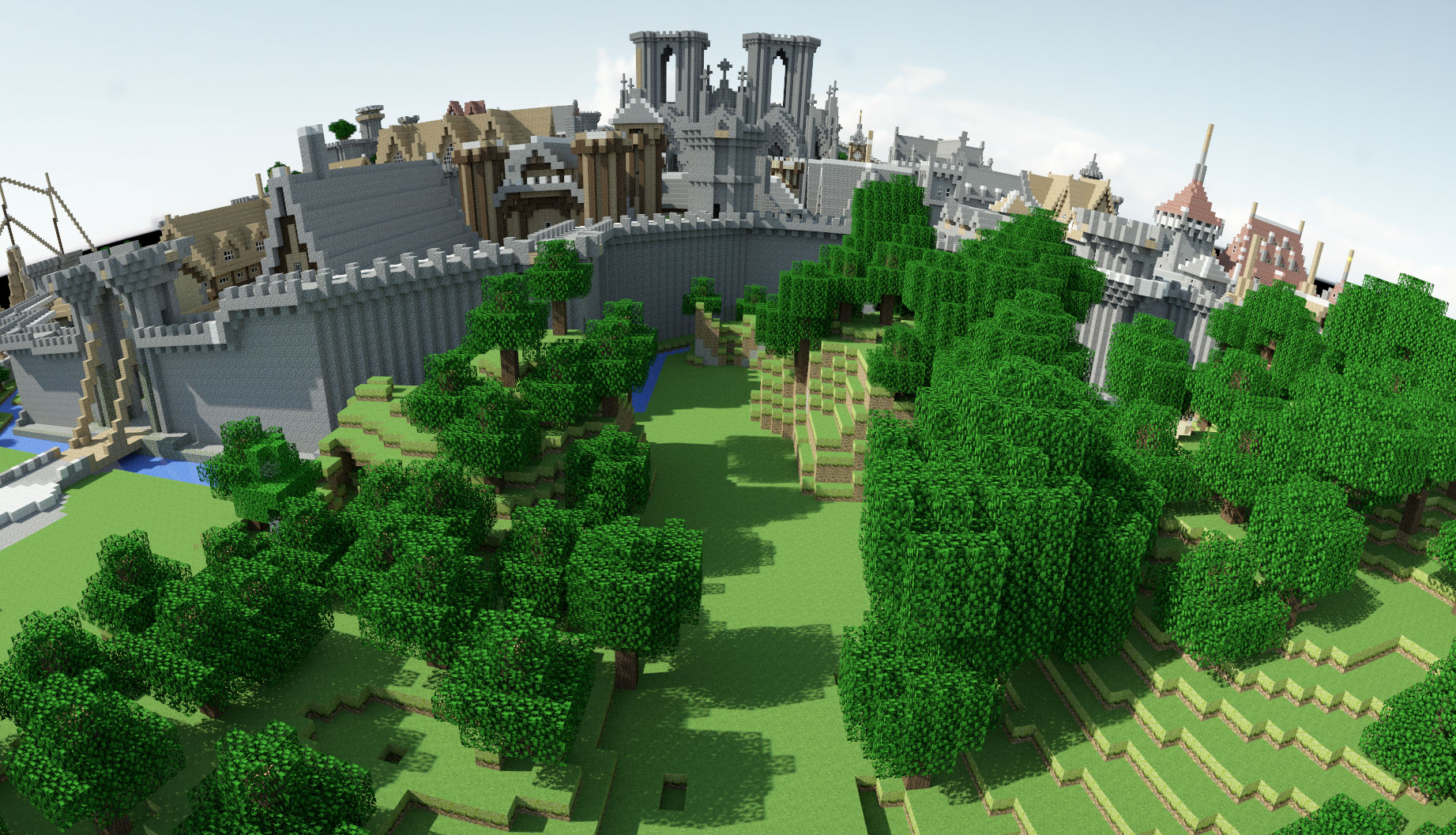
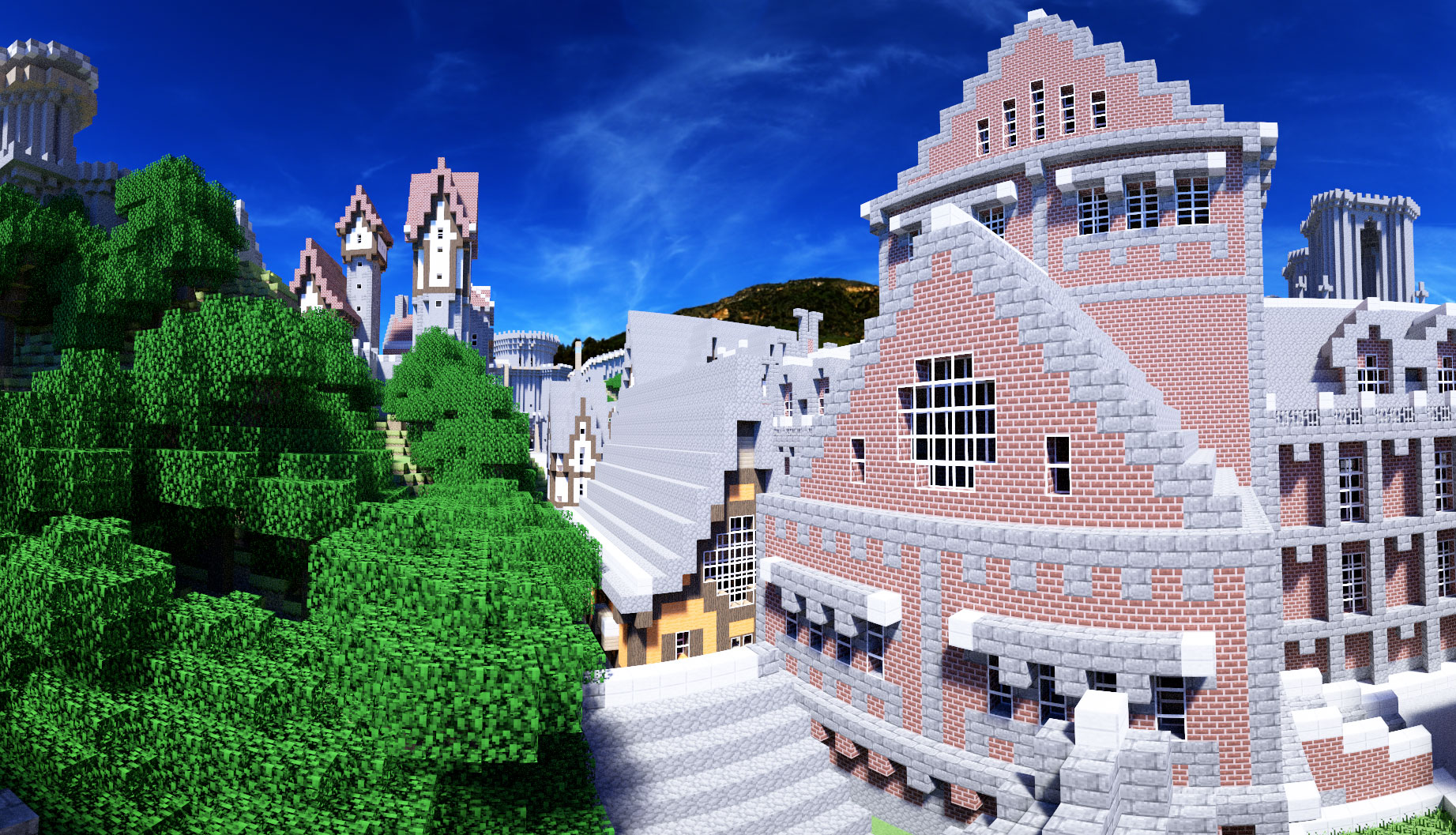


Rungholt model illuminated by outdoor environment light.
Model: Rungholt from Morgan McGuire's Computer Graphics Archive
IBL image 1: Direct HDR Capture of the Sun and Sky
IBL image 2: sIBL Archive
2022 @Shocker_0x15