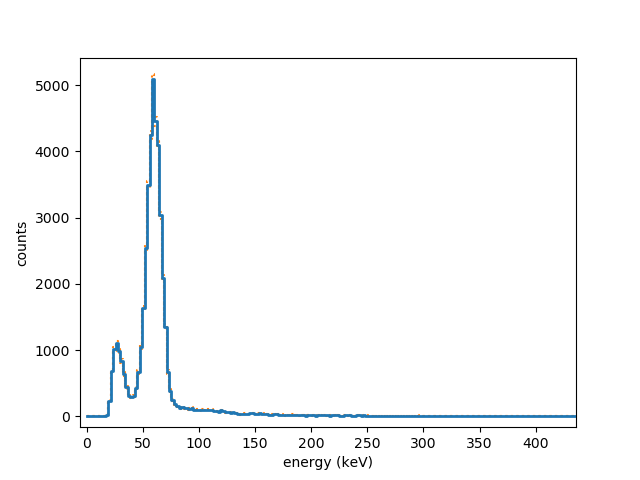
Python toolkit for soundcard gamma spectroscopy.
This package is a Python package for the acquisition and analysis of soundcard data, specifically for gamma spectroscopy kits that use a soundcard as their ADC interface. It consists of independent building blocks ("services") that can be connected and reconfigured to form different analysis pipelines. Examples of this are included in the repository in the examples directory.
You need at least:
- Python 2.7 or 3.6 or later,
- numpy
- pyaudio
and recommended is:
- matplotlib
Easiest is to use pip:
pip install GammaLab
An example application that acquires data and plots a gamma spectrum is included, you can get help:
./gammalab-histogram.py --help
This provides only a limited preview of the possibilities that the Gamma Lab offers. You can compose your own applications, examples of this are in the examples directory.
The applications consist of components "services" that are connected with "wires." For a component to be included it needs to be imported and instantiated, for example you almost always need:
from gammalab.acquisition import Soundcard soundcard=Soundcard()
After instantiating additional components, say:
from gammalab.backend import SaveRaw save=SaveRaw()
they need to be "wired":
soundcard.plugs_into(save)
At the moment, components can have one input and one output, but an output can be connected to multiple components. When all components are wired, you start the pipeline:
main(timout=100)
The time-out is optional. The application will run until <enter> is pressed or until the time-out reached.
The following services are available:
from gammalab.acquisition import SoundCard from gammalab.acquisition import Noise from gammalab.transform import Raw2Float from gammalab.transform import DownSampleMaxed from gammalab.transform import Identity from gammalab.analysis import PulseDetection from gammalab.analysis import Histogram from gammalab.analysis import Count from gammalab.backend import Playback from gammalab.backend import Monitor from gammalab.backend import SaveRaw
Note that most of these provide rudementary implementations and are open to improvement.
It is not difficult to program additional services.
A service is a class with at least the methods: `start `stop` and
`close`. A service which accepts input should instantiate a "wire"
class defining its input and have connect_input and receive_input methods
(normally taken care of by deriving from ReceivingService class). If it
generates output, the service should have an output_protocol method, which
checks the input wire format and propagates any additional information to
the wire. It also needs to have some methods normally implemented by
deriving from the SourceService class (notably the `plugs_into`
method).
Services start up a seperate thread to do their computations. This could also be using some other package's thread (e.g. for soundcard acquisition pyaudio's callback thread is used).
The simplest example of a service with input and output is the following:
class Identity(ThreadService, SourceService, ReceivingService):
def __init__(self):
super(Identity, self).__init__()
self.input_wire=RawWire()
def output_protocol(self, wire):
assert isinstance(wire, RawWire)
wire.CHANNELS=self.input_wire.CHANNELS
wire.RATE=self.input_wire.RATE
wire.FORMAT=self.input_wire.FORMAT
def process(self, data):
return data
This service just forwards the input data (a raw byte stream) to its output, retaining its sample rate, format and number of channels.