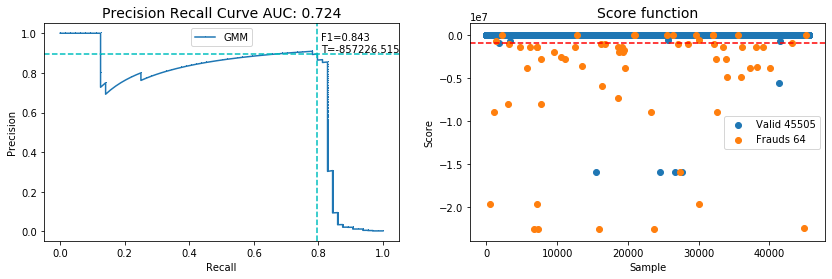
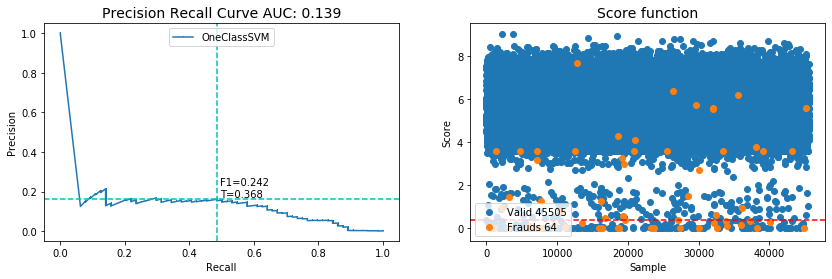
Supervised learning has been widely used to detect anomaly in credit card transaction records based on the assumption that the pattern of a fraud would depend on the past transaction. However, unsupervised learning does not ignore the fact that the fraudsters could change their approaches based on customers' behaviors and patterns. in this study we will present iterative method of using mixture of Gaussian's to detect anomaly in credit card transactions. We will compare it with iterative method using OneClassSVM. In each method our algorithm utilizes the model functions(likelihood and shifted from support vector) scores, evaluates samples with their scores and samples score under threshold T consider to be anomalies. the described method is iterative until model converges or max iteration exceeds. The data set used in this study is based on real-life data of credit card transaction. Due to the availability of the response(labels), after training the models we can evaluate the performance of each model. The performance of these two methods is discussed extensively in this paper.