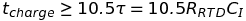MAX31865
This is a driver for the MAX31865 RTD-to-Digital converter (RTD: resistance temperature detectors).
Table of Content
- Getting Started
- Creating an Object
- Measuring Temperature
- Changig the Threshold values
- Faults
- Prospects
- Contributing
- Authors
- License
- Acknowledgments
1. Getting Started
These instructions will help you implement the driver step by step into your project.
The driver has an object-oriented approach which enbales a certain abstraction which helps to minimize complexety and improve readability.
1.1. Prerequisites
- Download and place the max31865.c/.h files into a desired folder inside your project.
- Knowledge about the functionality of the Device and it's hardware aspects (see Datasheet).
- fully configured hardware, this implies:
- hardware configured for 3-wire od 2/4-wire
- reference Resistor chosen according to Datasheet
- RTD (PT100 ot PT1000 etc.)
- low level software for GPIO and SPI must be provided
1.2. Advice
If you want to get familiar with the MAX31865 device I recomend you to buy a breakout board from adafruit which altready contains the whole hardware and documentation neccesary to enable fast prototyping.
2. Creating an Object
First we have to include the driver as follows...
#include "<your path>/max31865.h"Then we can create an instance...
max31865_t TempSensor;This instance has not yet been initialized and must be done with the init function to complete the process as following...
max31865_init(&TempSensor,...);The init function will update all the struct members of the TempSensor Object with your desired configurations. It will aslo automatically write the desired configurations and the upper and lower temperature fault thresholds directly to the device (MAX31865).
2.1. Init Function Parameters Description
max31865_init(max31865_t* device,...);device is a pointer to your Object. Your Oject must be passed by pointer to be able to initialized. For example...
max31865_init(&TempSensor,...);
max31865_readADC(&TempSensor);
//...max31865_init(...,fptr_b_t chipselect_cb,...);chipselect_cp is a function pointer to a chipselect function for SPI interface. This function shold contain the needed GPIO manipulations to select the device. The callback function must have a bool type as parameter and void type as return parameter as shown here...
void chipselect(boot enable) {
if(enable){ // device selected
// pull chip select pin low
} else { // device not selected
// pull chip select pin high
}
}max31865_init(...,u8_fptr_u8_t spi_trx_cb,,...);spi_trx_cb is a function pointer to a callback for a SPI transrecive (full duplex) function. This function should contain all the Master SPI transrecive manipulations.The callback function must have a uint8_t type as parameter and uint8_t type as return parameter as shown here...
uint8_t spi_trx(uint8_t data) {
// SPI manipulations
return RX_data;
}max31865_init(..., fptr_t charged_time_delay_cb,...);charged_time_delay_cb is a function pointer to a callback for the chargetime delay function. This function should contain a delay cycle of at least 10.5 times the charging constant given by the capacitance of the capacitor between RTDI+ and RTDIN- and resistance of the RTD. One possibility is to use a delay from a RTOS system.
The callback function must have a void type as parameter and void type as return parameter as shown here...
void charge_time_delay_cb(void) {
// 10.5*tau delay
}max31865_init(..., fptr_t conversion_timer_deay_cb,...);conversion_timer_deay_cb is a function pointer to a callback for the conversion time delay function. The delay time is dependent on the choice of the common mode filter. The callback function must have a void type as parameter and void type as return parameter as shown here...
void conversion_time_delay_cb(void) {
// 65.2 ms for 50Hz or 52 ms for 60Hz surpression
}max31865_init(..., fptr_t highFaultThreshold_callback,
fptr_t lowFaultThreshold_callback, ...);highFaultThreshold_callback and lowFaultThreshold_callback are both function pointers to callbacks to handle a high and low threshold fault. The callback function must have a void type as parameter and void type as return parameter as shown here...
void threshold_fault(void) {
// handle threshold fault
}max31865_init(..., uint16_t rtd_ohm,...);rtd_ohm is the value of the RTD in Ohms at 0°C. For example; a PT100 has a resistiv value of 100Ω at 0°C.
max31865_init(..., uint16_t rref_ohm,...);rref_ohm is the value of the Reference Resistor in Ω.
max31865_init(..., uint16_t lowerFaulThreshold,
uint16_t higherFaultThreshold, ...);lowerFaulThreshold and higherFaultThreshold are the threshold values. The ADC has a 15 bit ADC which implies a range from 0x0000 to 0x7FFF for the threshold values. Note that the upper threshold value must be greater than the lower one.
max31865_init(..., bool wire_3,...);wire_3 is a switch between 2/4-wire operation or 3-wire operation. To choose 2/4-wire operation write false and for 3-wire operation write true.
max31865_init(..., bool filter_50Hz, ...);filter_50Hz is a switch for the common mode filter. Either 50Hz or 60Hz supression can be choosen. Note that the conversion time differs between 50Hz and 60Hz. The following shows what delay times are needed...
| Frequency | delay time |
|---|---|
| 50Hz | 62.5 ms |
| 60Hz | 52 ms |
3. Measuring Temperature
There are four ways one can get the remperature.
- as raw ADC value with
uint16_t max31865_readADC(const max31865_t* device);
- as Resistance Value in Ω with
float max31865_readRTD_ohm(const max31865_t* device);
- as Celsius Value in °C
float max31865_readCelsius(const max31865_t* device);
- as Kelvin Value in °K
float max31865_readKelvin(const max31865_t* device);
For reading Celsius °C the Resistance of the RTD is measured and is then calculated with a polynomial approximation of the RTD curve. It is done with the Horners method to reduce the needed multiplication and addition numbers.
For reading Kelvin °K the measured Value in °C is added with the offset of 273.15 °K.
3.1. Automatic Threshold Fault Detection
Each time when a mesurement is done (raw ADC, Ω, °C or °K) the value is checked if it lies within the boundarys set by the upper and lower Threshold values. If the measured Value is over the upper threshold the highFaultThreshold_callback is called. If the value is below the lower threshold the lowFaultThreshold_callback is calles. After completion of the callbacks all Faults are cleared.
4. Changig the Threshold values
It is possible to change the upper and lower threshold at anny given time by calling the following functions...
void max31865_setHighFaultThreshold(max31865_t* device,
uint16_t threshold);
void max31865_setLowFaultThreshold(max31865_t* device,
uint16_t threshold);
5. Faults
5.1. Reading Faults
It is possible to read the faults as follows...
uint8_t max31865_readFault(const max31865_t* device);The return value can be checked with the typedef enum members of max31865_err_t. For example...
errors = max31865_readFault(&TempSensor);
if(error & max31865_err_VOLTAGE_FAULT) {
// handle voltage fault error
}
if(error & max31865_err_VRTDIN_TO_LOW){
// ...
}
//etc...
max31865_clearFault(&TempSensor);
5.2. Clearing Faults
It is possible to clear all faults as follows...
uint8_t max31865_clearFault(const max31865_t* device);6. Prospects
6.1. Feature Ideas
- handler for the faults which calls the associated callbacks to each error when using...
uint8_t max31865_readFault(const max31865_t* device);- system check which performs a fault detection cycle
7. Contributing
Please read CONTRIBUTING.md for details on my code of conduct, and the process for submitting pull requests to us.
8. Authors
- Edwin Koch - Initial work - polymurph
See also the list of contributors who participated in this project.
9. License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details