Solving algorithm problems with C++ language
- 1. block
- [2. Big integer calculator]
- [3. 좌표압축]
- 1. Time Check
when you wanna check how much time the algorithm takes, use <time.h>( in C++)
#include <ctime>
clock_t start = clock();
clock_t endC = clock();
printf("걸린시간 : %0.9f\n", float(endC - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);- 1. freopen()
If you have a lot of inputs, you better use 'std::freopen() Sometimes freopen( ) cant be used. Must use freopen_s() due to a safety problem. If you dont like this, just use <fstream.h>
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);- 2. fstream
But!!!! i think freopen is much better than fstream expecially in algorithms solving. Because when i submit my source code, i dont need to change code in 'freopen' code (입력받는 코드가 동일하다. scanf나 cin으로 그냥 받을 수 있다!!!!) 따라서 freopen을 주로 쓰자
#include <fstream.h>
int main(){
int n;
ifstream myText("input.txt");
if(myText.fail()){
cout<< "File stream error" << endl;
return -1;
}
myText >> n ;
myText.close();
}- 1. '+=' instead of 'pushback'
same result
answer[k] += ('#');
answer[k].push_back('#');- 2. strcmp
if you use , then use str1.campare(str2)
int strcmp(char s[], char t[])
{
int i;
for (i = 0; s[i] == t[i]; i++)
{
if (s[i] == '\0')
return 0;
}
return s[i] - t[i];
}- 3. strcpy
if you use , just use str1 = str2 to assgin str2 to str1
void strcpy(char s[], char t[])
{
int i = 0;
while (s[i] != '\0')
{
t[i] = s[i];
i++;
}
t[i] = '\0';
}- 4. read several line strings
you can use 'ifstream' instead of 'cin'
while (cin >> str) // 더이상 입력이 안되면 조건문을 빠져나온다.
{
// 이걸 추가 안해주면 마지막 문자열이 계속 반복해서 들어와서 끝나질 않는다.
str = "";
}- 1. sstream >> INT
num = 183
if there are number characters like '1', '8', '3' in string, ss >> (int)num change number characters from char to int. So, you can get 183 integer in num variable;
string str = "183DF";
stringstream ss(str);
int num;
ss >> num; // num = 183;- 2. ss.get() & ss.unget()
ss.get() is same with ss >> c1
string str = "DF";
stringstream ss(str);
char c1;
char c2;
c1 = ss.get(); // c1 = D
c2 = ss.get(); // c2 = Fss.unget take cursor back
string str = "DFG";
stringstream ss(str);
char c1;
char c2;
char c3;
c1 = ss.get(); // c1 = D
c2 = ss.get(); // c2 = F
ss.unget();
c3 = ss.get(); // c3 = F not G-
3.1 jeongho
stringstream can be used like 'cin' or 'cout'
focus on ss >>nAct[i];
#include <sstream>
vector<string> solution(vector<string> record)
{
int size = record.size();
vector<string> nAct(size);
vector<string> nUid(size);
vector<string> nNickName(size);
for (int i = 0; i < record.size(); i++)
{
stringstream ss(record[i]);
ss >> nAct[i];
ss >> nUid[i];
ss >> nNickName[i];
}
}- 3.2 seongjun
focus on
while (ss >> buf)
#include <sstream>
for (int i = 0; i < record.size(); i++)
{
vector<string> solution(vector<string> record)
{
stringstream ss(record[i]);
string buf;
vector<string> tokens;
while (ss >> buf)
tokens.push_back(buf);
if (tokens[0] == "Enter")
}
}- [1. Initialization]
1번째 문장은 int 2차원 벡터를 3X3 사이즈로 크기를 규정하는 것이다. 2번째 문장은 1로 초기화 하는거다.
vector<vector<int>> v(3, vector<int>(3));
vector<vector<int>> v(3, vector<int>(3,1));row x col 크기의 벡터를 1로 초기화 하는거다.
vector<vector<int>> v
int row = 15;
int col = 10;
table.assign(row, vector<int>(col, 1));각 element의 값을 직접 지정할 수 있다. vector[0].size() = 1 vector[1].size() = 2 vector[2].size() = 3 이다
vector<vector<int>> v{{1},{2,3},{4,5,6}}- 1. Re-initialize
to initialize, use .clear()
vector<int> graph[MAXSIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < MAXSIZE; i++)
{
graph[i].clear();
}begin() 함수는 벡터의 데이터가 있는 리스트의 시작 주소를 리턴하는데, 첫 번째 값 주소를 반환한다. end() 함수는 리스트의 끝 주소를 리턴하는데, 마지막 값보다 한 칸 뒤 값의 주소를 반환한다.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sort(graph[i].begin(), graph[i].end());
}include<algorithm>
auto itr = find(v.begin(), v.end(), value);- 4. .erase()
cache.end() return the next itr of the end index of vector
but i think erase() allow erase(cache,end()) to erase last index
== cache.erase(cache.end()-1) == cache.pop_back() erase() return current iterator after erase the value and move all remain values to each 1 block left
v.erase(itr);
v.erase(v.end())
// == v.erase(v.end()-1)
// == v.pop_back()
// erase 0~5 idx and then return itr = 6
v.erase(v.begin(), v.begin()+5);- 3. insert()
insert(itr, value) makes vector insert a value on the itr index. itr 위치에 삽입을 하면 itr부터 end까지의 모든 값들은 한칸씩 뒤로 이동된다. O(n)의 시간복잡도가 들것이다. so if you would use insert frequently, use linked list
v.insert(v.begin(), value);- 1. Initialize by struct
When you can't use <string.h>, this method will works good. Because Array is reference type, it is impossible to assign. But struct is value type, so it is possible
typedef struct
{
bool arr[MAXSIZE];
} Arr;
Arr init_arr;
Arr check;
//initialize
check = init_arr;- 2. Initialize by memset()
When you can use <string.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
int main (){
int check[MAXSIZE];
// 4바이트마다 모두 0로 초기화
// 배열을 채울 때는 memset()함수를 사용하면 됩니다.
// sizeof 함수 - 배열의 전체 바이트 크기를 반환한다.
memset(check, 0, sizeof(check));
}- 1. Linked list class by 동적할당
pop(), push(), size()등의 구현도 아래 코드를 응용하면 충분히 가능하므로 생략.
typedef struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
} Node;
class linked_list
{
private:
Node *head, *tail;
public:
linked_list()
{
head = NULL;
tail = NULL;
}
void add_node(int key)
{
// 동적할당!
Node *tmp = new Node;
tmp->data = key;
tmp->next = NULL;
// 처음 데이터를 저장할 때
if (head == NULL)
{
head = tmp;
tail = tmp;
}
else
{
tail->next = tmp;
tail = tail->next;
}
}
bool isExist(int key) // 해당 데이터가 존재하는지 여부
{
Node *cur;
cur = head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->data == key)
return true;
else
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return false;
}
// Linked list 삭제하기
void clear()
{
Node *tmp;
while (head != NULL)
{
tmp = head;
head = head->next;
delete tmp;
}
tail = NULL;
}
};int recursion(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
return 0;
else if(n==2)
return 1;
else
return recursion(n - 1) + recursion(n-2);
}- 2. Tail recursion 기존에 recursive 함수를 짜거나 DP를 짠 경우 함수 호출이 너무 많이 일어나는 문제가 발생한다. 이를 해결하기 위해 Tail recursion 방식을 이용하거나 근본적으로는 loop를 사용하는게 제일 좋다.
Tail call이란 return후 원래 자리로 돌아와서 해야할 일이 남아 있지 않는 recursion 이다. 바꿔말하면 원래자리에서 해야할 일이 남아있지 않다면 돌아갈 원래 자리를 stack에 추가로 저장할 필요가 없다. 주의할 점은 어떤 함수를 호출하고 반환받은 후 아무일도 하지 않으려면 호출하려는 함수를 논리적으로 가장 마지막에 호출해야 한다.
요약하자면 Tail Call은 함수를 호출해서 값을 반환 받은 후 아무 일도 하지 않고 바로 반환하게 하기 위해 논리적으로 가장 마지막(꼬리) 위치에서 함수를 호출하는 방식을 말한다.
Tail recursion은 Tail Call로 호출하는 함수가 자기 자신인 경우입니다.
int fibonacciFunc(int n, int prev = 1, int prevPrev = 1)
{
if (n == 1)
return prevPrev;
if (n == 2)
reuturn prev;
else
return fibonacciFunc(n - 1, prev + prevPrev, prev);
}- 3. loop 아무리 tail recursion을 사용하더라도 Tail Call Optimization을 지원해주지 않는다면 똑같이 stack overflow가 발생할 수 있다. 이런 문제를 피하기 위해 반복을 사용하는 것이 좋다.
int fibonacciFunc(int n)
{
int prev, prevPrev, cur;
if (n == 1)
{
cout << 0 << ' ';
return 0;
}
if (n == 2)
{
cout << 1 << ' ';
return 1;
}
prev = 0;
prevPrev = 1;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
{
cur = prev + prevPrev;
prevPrev = prev;
prev = cur;
cout << cur << ' ';
}
return cur;
}재귀호출은 두겹 이상으로 사용하면 함수 호출 횟수가 상상하지 못할 정도로 증가하는 무제가 발생하고, 깊이가 깊어지면 stack을 많이 사용하는 문제가 발생한다. 이럴 때는 재귀 호출 대신 loop나 tail recursion방식으로 구현하면 문제 상황을 피해갈 수 있다. 하지만 javascript처럼 실행환경에서 tail call optimization을 지원해주지 않으면 사실 상 유일한 해결책은 반복문 뿐이다.
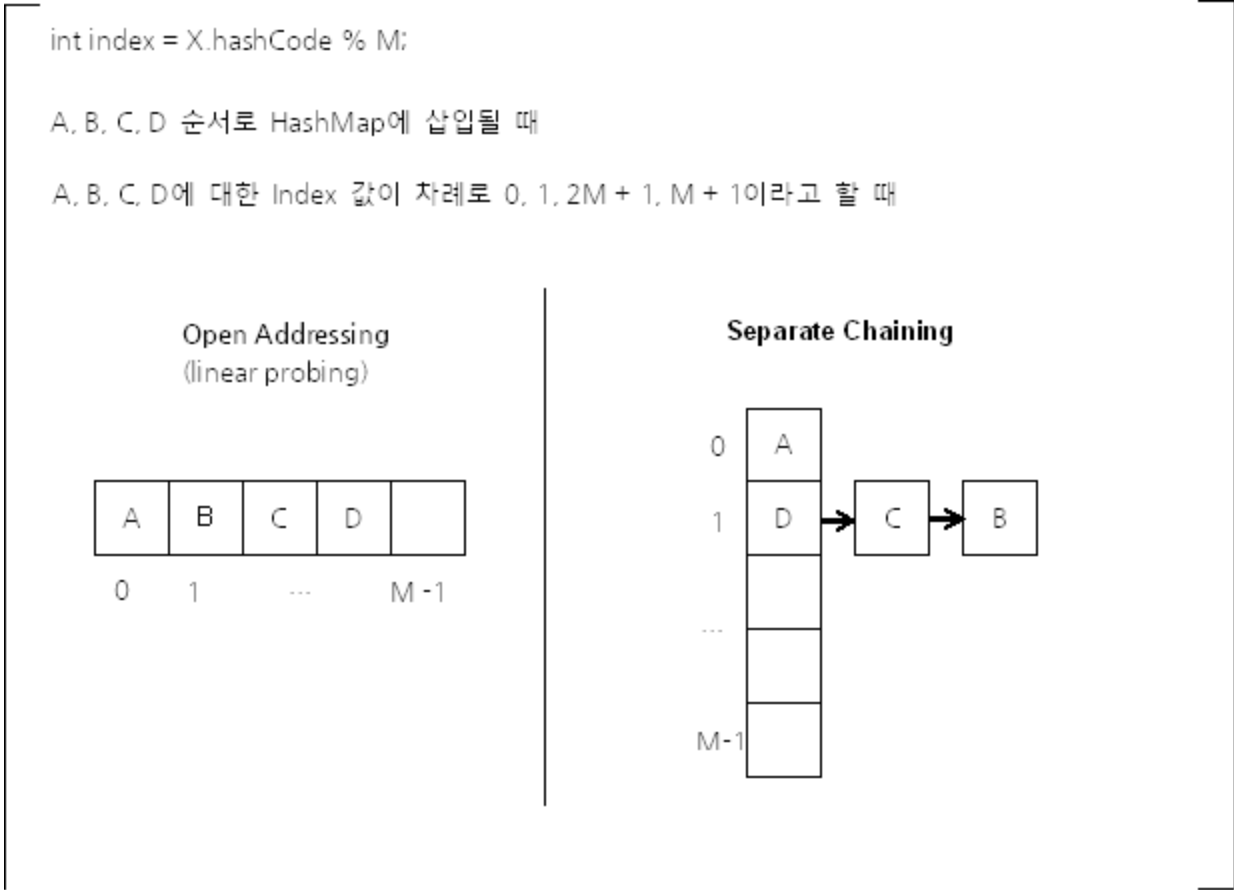
Open Addressing은 데이터를 삽입하려는 해시 버킷이 이미 사용 중인 경우 다른 해시 버킷에 해당 데이터를 삽입하는 방식이다. 데이터를 저장/조회할 해시 버킷을 찾을 때에는 Linear Probing, Quadratic Probing 등의 방법을 사용한다.
Separate Chaining에서 각 배열의 인자는 인덱스가 같은 해시 버킷을 연결한 링크드 리스트의 첫 부분(head)이다. Open Addressing은 연속된 공간에 데이터를 저장하기 때문에 Separate Chaining에 비하여 캐시 효율이 높다. 따라서 데이터 개수가 충분히 적다면 Open Addressing이 Separate Chaining보다 더 성능이 좋다. 하지만 배열의 크기가 커질수록(M 값이 커질수록) 캐시 효율이라는 Open Addressing의 장점은 사라진다
Java HashMap에서 사용하는 방식은 Separate Channing이다. Open Addressing은 데이터를 삭제할 때 처리가 효율적이기 어려운데, HashMap에서 remove() 메서드는 매우 빈번하게 호출될 수 있기 때문이다. 게다가 HashMap에 저장된 키-값 쌍 개수가 일정 개수 이상으로 많아지면, 일반적으로 Open Addressing은 Separate Chaining보다 느리다. Open Addressing의 경우 해시 버킷을 채운 밀도가 높아질수록 Worst Case 발생 빈도가 더 높아지기 때문이다. 반면 Separate Chaining 방식의 경우 해시 충돌이 잘 발생하지 않도록 '조정'할 수 있다면 Worst Case 또는 Worst Case에 가까운 일이 발생하는 것을 줄일 수 있다 출처: https://d2.naver.com/helloworld/831311
- 3. Easy code
해당 키는 이 문제에 특화된 해쉬키이므로 일반적인 hashtable 구현과는 상이할 수 있다. 또한 이 문제에서는 사실 key값은 존재하지 않고 value 만 존재하므로 hashtable이라 명할 수 있고, key값과 value값이 따로따로 있는 경우 hashmap이라 명하여 그에 상응한 코드를 작성해야한다. key 값을 주로 문자열로 되어 있으므로 문자열을 hash function으로 해쉬화 해줘야 한다.
int checkKey(int key)
{
int hash_key = key % HASHSIZE; // easy hash function
if (!hash_memory[hash_key].isExist(key))
{
hash_memory[hash_key].add_node(key);
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}- 4.Seperate chaining
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int T_S = 20;
class ListHead
{
public:
int k, v;
ListHead *n;
ListHead(int k, int v)
{
this->k = k;
this->v = v;
this->n = NULL;
}
};
class HashMapTable
{
private:
ListHead **ht;
public:
HashMapTable()
{
ht = new ListHead *[T_S];
for (int i = 0; i < T_S; i++)
{
ht[i] = NULL;
}
}
int HashFunc(int k)
{
return k % T_S;
}
void Insert(int k, int v)
{
int hash_v = HashFunc(k);
if (ht[hash_v] == NULL)
ht[hash_v] = new ListHead(k, v);
else
{
ListHead *en = ht[hash_v];
while (en->n != NULL && en->k != k)
en = en->n;
if (en->k == k)
en->v = v;
else
en->n = new ListHead(k, v);
}
}
int SearchKey(int k)
{
int hash_v = HashFunc(k);
if (ht[hash_v] == NULL)
return -1;
else
{
ListHead *en = ht[hash_v];
while (en != NULL && en->k != k)
en = en->n;
if (en == NULL)
return -1;
else
return en->v;
}
}
void Remove(int k)
{
int hash_v = HashFunc(k);
if (ht[hash_v] != NULL)
{
ListHead *en = ht[hash_v];
ListHead *p = NULL;
while (en->n != NULL && en->k != k)
{
p = en;
en = en->n;
}
if (en->k == k)
{
if (p == NULL)
{
ListHead *n = en->n;
delete en;
ht[hash_v] = n;
}
else
{
ListHead *n = en->n;
delete en;
p->n = n;
}
}
}
}
~HashMapTable()
{
delete[] ht;
}
};
int main()
{
HashMapTable hash;
int k, v;
int c;
hash.Insert(3, 100);
hash.Insert(103, 200);
hash.Insert(3, 300);
cout << hash.SearchKey(3) << endl;
while (1)
{
cout << "1.Insert element into the table" << endl;
cout << "2.Search element from the key" << endl;
cout << "3.Delete element at a key" << endl;
cout << "4.Exit" << endl;
cout << "Enter your choice: ";
cin >> c;
switch (c)
{
case 1:
cout << "Enter element to be inserted: ";
cin >> v;
cout << "Enter key at which element to be inserted: ";
cin >> k;
hash.Insert(k, v);
break;
case 2:
cout << "Enter key of the element to be searched: ";
cin >> k;
if (hash.SearchKey(k) == -1)
cout << "No element found at key " << k << endl;
else
{
cout << "Elements at key " << k << " : ";
cout << hash.SearchKey(k) << endl;
}
break;
case 3:
cout << "Enter key of the element to be deleted: ";
cin >> k;
if (hash.SearchKey(k) == -1)
cout << "Key " << k << " is empty" << endl;
else
{
hash.Remove(k);
cout << "Entry Removed" << endl;
}
break;
case 4:
exit(1);
default:
cout << "\nEnter correct option\n";
}
}
return 0;
}#include <map>
map<string, string> userMap;
userMap[key] = value;below two statements are same
userMap[key] </br>
userMap.find(key)->second </br>'itr == wordMap.end()' means the map doesn't have 'key' data
#include <map>
map<string, bool> wordMap;
auto itr = wordMap.find(key);
if (itr == wordMap.end())
wordMap[key] = true;-
- by Array
#include <iostream>
#define STACK_LEN 100
using namespace std;
class ArrayStack
{
private:
int stackArr[STACK_LEN];
int topIndex;
public:
ArrayStack()
{
topIndex = -1;
}
bool IsEmpty();
void Push(int data);
int Pop();
int Peek();
};
bool ArrayStack::IsEmpty()
{
if (topIndex == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void ArrayStack::Push(int data)
{
topIndex += 1;
stackArr[topIndex] = data;
}
int ArrayStack::Pop()
{
int rIdx;
if (IsEmpty())
{
cout << "Stack is empty!" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
rIdx = topIndex;
topIndex -= 1;
return stackArr[rIdx];
}
int ArrayStack::Peek()
{
if (IsEmpty())
{
cout << "Stack is empty!" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
return stackArr[topIndex];
}
int main()
{
ArrayStack stack;
stack.Push(1);
stack.Push(2);
stack.Push(3);
stack.Push(4);
stack.Push(5);
while (!stack.IsEmpty())
cout << stack.Pop() << " ";
stack.Pop();
return 0;
}-
- by Linked List
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class ListStack
{
private:
Node *head;
public:
ListStack()
{
head = nullptr;
}
bool IsEmpty();
void Push(int data);
int Pop();
int Peek();
};
bool ListStack::IsEmpty()
{
if (head == nullptr)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void ListStack::Push(int data)
{
Node *newNode = new Node;
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
}
int ListStack::Pop()
{
int rdata;
Node *rnode;
if (IsEmpty())
{
cout << "Stack is empty!" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
rdata = head->data;
rnode = head;
head = head->next;
delete rnode;
return rdata;
}
int ListStack::Peek()
{
if (IsEmpty())
{
cout << "Stack is empty!" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
return head->data;
}
int main()
{
ListStack stack;
stack.Push(1);
stack.Push(2);
stack.Push(3);
stack.Push(4);
stack.Push(5);
while (!stack.IsEmpty())
cout << stack.Pop() << " ";
stack.Pop();
return 0;
}-
If you can't use <queue.h> library, you can make yours (by array) Q. QUEUE_SIZE 정하는 합리적인 근거?! 이 경우는 queue가 꽉찼을 때 처리하는 코드가 없으므로queue size를 크게 잡아줘야한다. 배열로 Queue를 만들 때에는 circular Queue로 하는게 좀 더 효율적으로 배열을 사용할 수 있다.
#include <iostream>
#define QUEUE_LEN 100
using namespace std;
class ArrQueue
{
private:
int front;
int rear;
int queArr[QUEUE_LEN];
public:
ArrQueue()
{
front = 0;
rear = 0;
}
bool IsEmpty();
void Enqueue(int data);
int Dequeue();
int Peek();
};
bool ArrQueue::IsEmpty()
{
if (front == rear)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void ArrQueue::Enqueue(int data)
{
if ((rear + 1) % QUEUE_LEN == front)
{
cout << "Queue is full!" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
rear = (rear + 1) % QUEUE_LEN;
queArr[rear] = data;
}
int ArrQueue::Dequeue()
{
if (IsEmpty())
{
cout << "Queue is empty!" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
front = (front + 1) % QUEUE_LEN;
return queArr[front];
}
int ArrQueue::Peek()
{
if (IsEmpty())
{
cout << "Queue is empty!" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
return queArr[(front + 1) % QUEUE_LEN];
}
int main()
{
ArrQueue Queue;
Queue.Enqueue(1);
Queue.Enqueue(2);
Queue.Enqueue(3);
Queue.Enqueue(4);
Queue.Enqueue(5);
while (!Queue.IsEmpty())
cout << Queue.Dequeue() << " ";
Queue.Dequeue();
return 0;
}- 2. by Linked List
you can define queue struct or class (by 동적배열!!)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class ListQueue
{
private:
Node *front;
Node *rear;
public:
ListQueue()
{
front = nullptr;
rear = nullptr;
}
bool IsEmpty();
void Enqueue(int data);
int Dequeue();
int Peek();
};
bool ListQueue::IsEmpty()
{
if (front == nullptr)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void ListQueue::Enqueue(int data)
{
Node *newNode = new Node;
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = nullptr;
if (IsEmpty())
{
front = newNode;
rear = newNode;
}
else
{
rear->next = newNode;
rear = newNode;
}
}
int ListQueue::Dequeue()
{
int rdata;
Node *delNode;
if (IsEmpty())
{
cout << "Queue is empty!" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
delNode = front;
rdata = delNode->data;
front = front->next;
delete delNode;
return rdata;
}
int ListQueue::Peek()
{
if (IsEmpty())
{
cout << "Queue is empty!" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
return front->data;
}
int main()
{
ListQueue queue;
queue.Enqueue(1);
queue.Enqueue(2);
queue.Enqueue(3);
queue.Enqueue(4);
queue.Enqueue(5);
while (!queue.IsEmpty())
cout << queue.Dequeue() << " ";
queue.Dequeue();
return 0;
}-
우선순위 큐를 구현하는 세가지 방법은 Array, Linkedlist, Heap을 이용하는 것이다. 배열이나 연결 리스트를 이용하면 우선순위 큐를 매우 간단히 구현할 수 있다.
- 1.1 Array 먼저 배열을 보면 데이터의 우선순위가 높을수록 배열의 앞쪽에 데이터를 위치시킨다. 이 경우 데이터를 삽입 및 삭제하는 과정에서 데이터가 밀려지거나 당겨지는 연산이 추가되는 단점이 있다. worst big-O(n2). 또한 배열에 길이가 정해져있다는 점도 큰 단점이다.
- 1.2 Linked list 연결 리스트의 경우 삽입의 위치를 찾기 위해서 모든 노드에 저장된 데이터와 우선순위를 비교해야 할 수 있다.
- 1.3 Heap 우선순위큐와 가장 잘 맞는 자료구조는 Heap이다.
-
Heap is Complete binary tree
- 2.1 Max heap 루트 노드로 올라갈수록 저장된 값이 커진다.
- 2.2 Min heap 루트 노드로 올라갈수록 저장된 값이 작아진다.
- 2.3 구현하기 heap을 연결리스트를 기반으로 구현한다면 새로운 노드를 힙의 마지막 위치에 추가하는 것이 쉽지 않다. 따라서 힙은 배열을 기반으로 트리를 구현해야 한다.
배열과 연결리스트 중 하나를 선택해야하는데 연결 리스트를 기반으로 힙을 구현한다면, 새로운 노드를 힙의 '마지막 위치'에 추가하는 것이 쉽지 않다. 따라서 힙은 배열을 기반으로 트리를 구현해야 한다.
left child = parent 2 right child = parent 2 + 1 parent = chile / 2
class minHeap
{
private:
int heap[HEAP_SIZE] = {0};
int count;
public:
minHeap()
{
count = 0;
}
void push(int newValue)
{
// heap index start from 1. 연산 쉽게 해줄려고!
if (count + 1 == HEAP_SIZE)
{
cout << "FULL !!" << endl;
return;
}
else
{
heap[++count] = newValue;
int cur = count;
int parent = cur / 2;
// maxHeap이라면 부등호의 방향만 반대로 해주면 된다.
while (parent && heap[parent] > heap[cur])
{
int tmp = heap[parent];
heap[parent] = heap[cur];
heap[cur] = tmp;
cur = parent;
parent = cur / 2;
}
}
}
int pop()
{
if (count == 0)
{
cout << "EMPTY !!" << endl;
throw "error";
}
else
{
int ret = heap[1];
// 맨 뒤에 있는 heap data를 가져온다.
heap[1] = heap[count--];
int cur = 1;
// base로 left child를 선정한다.
int child = cur * 2;
// right child가 있는경우
if (child + 1 <= count)
{
// 더 작은 쪽의 child를 선택한다.
child = heap[child] < heap[child + 1] ? child : child + 1;
}
while (child <= count && heap[cur] > heap[child])
{
int tmp = heap[cur];
heap[cur] = heap[child];
heap[child] = tmp;
cur = child;
child = cur * 2;
if (child + 1 <= count)
{
child = heap[child] < heap[child + 1] ? child : child + 1;
}
}
return ret;
}
}
};
- 1. Consider all case
'num' is total num of cases
from 00000001 to 11111111 (when column is 8)
i start from 1 because 0 means 00000000, none of Attributes is included.
int num = 1 << col;
for (int i = 1; i < num; i++){
...
}- 2. Add attribute to tmp
when 'i' is 10011101 in bit, (i & (1 << k)) makes me add relation[j][k] to tmp only when bit is 1.
for (int i = 1; i < num; i++){
for (int k = 0; k < col; k++)
{
if (i & (1 << k))
{
tmp += relation[j][k];
}
}
}- 3. Bitmask Solving
완전탐색 문제를 해결하는 또다른 방법. Bitmasking
int solution(vector<int> numbers, int target) {
int answer = 0;
int size = 1 << numbers.size();
for(int i = 1 ; i < size ; i++){
int temp = 0;
for(int j = 0 ; j < numbers.size() ; j++)
{
if(i &(1 << j)){
temp -= numbers[j];
}
else temp += numbers[j];
}
if(temp == target) answer++;
}
return answer;
}- 4. Bitmask for Coordinate line
좌표점이 아니라 좌표 선분을 체크해야 할 때는 bitmask를 이용하면 수월하게 문제를 해결해 나갈 수 있다.
#define U 1 // 0001
#define R 2 // 0010
#define D 4 // 0100
#define L 8 // 1000
if (!(map[cur.x][cur.y] & U))
{
map[cur.x][cur.y] += U;
map[next.x][next.y] += D; // 처음 문제 풀 때 해당 라인을 추가 하지 않아서 틀렸다. 좌표점이 아니라 좌표 선분이기 때문에 지나온길을 체크 해주려면 next Pos 입장에서도 체크해줘야 한다.
count++;
}- 1. DFS by stack
push 'cur' to go back to 'cur' later
void dfs_stack(int start)
{
stack<int> s;
s.push(start);
check[start] = true;
printf("%d ", start);
while (!s.empty())
{
int cur = s.top();
s.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < graph[cur].size(); i++)
{
int next = graph[cur][i];
if (!check[next])
{
printf("%d ", next);
check[next] = true;
// remember this line!! must push 'cur' to go back to 'cur' later
s.push(cur);
s.push(next);
break;
}
}
}
}void dfs_recursive(int cur)
{
//check = init_arr(); // 재귀함수기 때문에 이곳에서 초기화를 하면 안된다!!!!
printf("%d ", cur);
check[cur] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[cur].size(); i++)
{
int next = graph[cur][i];
if (!check[next])
{
check[next] = true;
dfs_recursive(next);
}
}
}void bfs_queue(int start)
{
queue<int> q;
check[start] = true;
q.push(start);
while (!q.empty())
{
int cur = q.front();
q.pop();
printf("%d ", cur);
for (int i = 0; i < graph[cur].size(); i++)
{
int next = graph[cur][i];
if (!check[next])
{
check[next] = true;
q.push(next);
}
}
}
}- 1. Fibonacci problem(1)
my own way. I calculated about zeroNum and oneNum. But many people didnt like that. Because my way has same pattern.
caution: i abbereviated many code, so you should check real sourse code to fully understand!
>you dont need to use DP to solve fibonacci. because it take mememory, and recursion which makes too many call stack
void fibonacciFunc(){
if (!cache[x].visited)
{
fibonacciFunc(x - 1);
fibonacciFunc(x - 2);
cache[x].zeroNum = cache[x - 1].zeroNum + cache[x - 2].zeroNum;
cache[x].oneNum = cache[x - 1].oneNum + cache[x - 2].oneNum;
cache[x].visited = true;
return;
}
}
int main(){
fibonacciFunc(n);
cout << cache[n].zeroNum << " " << cache[n].oneNum << endl;
}- 2. Fibonacci problem(2)
others's way. they excluded redundancy. So code can became shorter and easier.
int fibonacciFunc(int x)
{
if (cache[x] != -1)
return cache[x];
return cache[x] = fibonacciFunc(x - 1) + fibonacciFunc(x - 2);
}
int main(){
fibonacciFunc(n + 1);
cout << cache[n] << " " << cache[n + 1] << endl;
}- 3. DP vs DFS(다시풀어봐도 좋을 문제)
cacheMap에 가능 여부에 대한 데이터를 저장해준다.
int dp(int x, int y)
{
// basecase : 게임판 범위를 벗어난 경우
if (x >= n || y >= n)
return 0;
// basecase : 마지막칸에 도착한 경우
if (x == n - 1 && y == n - 1)
return 1;
int jumpSize = map.arr[x][y];
// 배열을 계속 쓰면 인덱스 실수나 의미가 점점 애매해져서 reference 변수로 참조하는게 더 좋다.
int &ret = cacheMap.arr[x][y];
if (ret != -1)
return ret;
return ret = dp(x + jumpSize, y) || dp(x, y + jumpSize);
}memoization이 없기 때문에 매번 반복해서 계산을 해줘야 한다.
bool dfs(int x, int y)
{
// basecase : 게임판 범위를 벗어난 경우
if (x >= n || y >= n)
return false;
// basecase : 마지막칸에 도착한 경우
if (x == n - 1 && y == n - 1)
return true;
int jumpSize = map.arr[x][y];
return dfs(x + jumpSize, y) || dfs(x, y + jumpSize); // readme작성
}차이점 1 : dfs는 도달했는가 에 대한 정보만 true or false로 전달하면 되지만 dp는 최종적으로 도달할 수 있는지에 대한 정보(true or false)와 memoization에 도달 정보가 저장 되었는지(-1)를 표시 해줘야 하므로 int 형으로 선언해야 한다.
int dp(int x, int y);
bool dfs(int x, int y);차이점 2 : memoization 에 저장되어 있다면(ret != -1) 저장된 값을 반환하고, 저장되어 있지 않다면 recursive하게 값을 구하고 ret 에 저장한 후 반환한다. Tip: // 배열을 계속 써야 하는 경우, 인덱스 실수를 저지를 수 있고 뒤로갈수록 해당 배열의 의미를 한눈에 볼 수 없기 때문에 reference 변수로 참조하는게 더 좋다.
int &ret = cacheMap.arr[x][y];
if (ret != -1)
return ret;
// || 를 이용하여 손쉽게 반환하는 것을 잘 익히면 많이 편해질 것같다.
return ret = dp(x + jumpSize, y) || dp(x, y + jumpSize);int bSearchRec(int low, int high, int target)
{
if (low > high)
return 0;
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (arrN[mid] == target)
return 1;
else if (arrN[mid] > target)
return bSearchRec(low, mid - 1, target);
else
return bSearchRec(mid + 1, high, target);
}int bSearchLoop(int n, int target)
{
int start = 0;
int end = n;
int mid;
while (end >= start)
{
mid = (end + start) / 2;
if (arrN[mid] == target)
return 1;
else if (arrN[mid] > target)
end = mid - 1;
else
start = mid + 1;
}
return 0;
}- 1. segmentation fault
segmentation fault란 허용되지 않은 방법으로 메모리에 접근할 때, 허용되지 않은 메모리 영역에 접근할 때 발생해서 사용자가 메모리를 오염시키는 걸 막아주고, 디버깅 하기 힘든 메모리 버그를 알려주는 역할을 합니다. 참조 : https://hashcode.co.kr/questions/403/segmentation-fault%EB%8A%94-%EB%AD%94%EA%B0%80%EC%9A%94 just modified r range from 100 to 99 i took HASH_SIZE to 100. so if r is more than 100, it makes segmentation fault. because the return value of hashCode() would be used as idx value of hashmap[HASH_SIZE]
#define HASH_SIZE 100
int hashCode(string s)
{
int i;
int r = 0;
// Special Prime Number
int a = 13;
for (i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
{
r += r * a + s[i];
// just modified r range from 100 to 99
r %= 99;
// r %= (HASH_SIZE-1) would be better
}
return r;
}