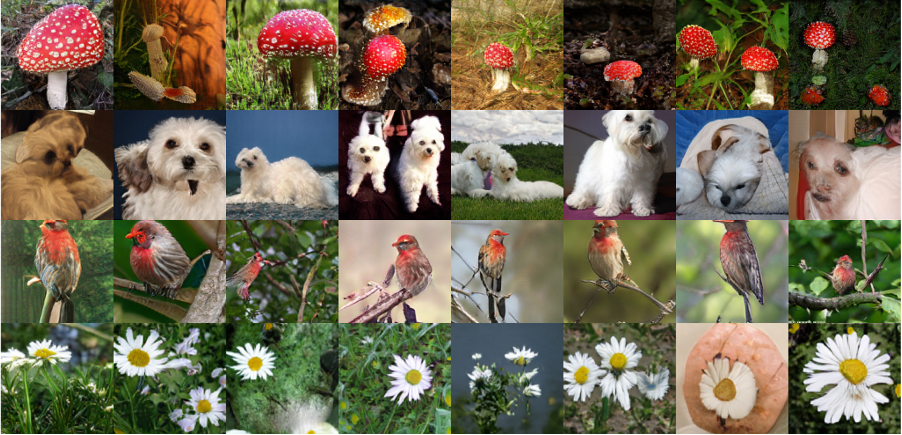
StudioGAN is a Pytorch library providing implementations of representative Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for conditional/unconditional image generation. StudioGAN aims to offer an identical playground for modern GANs so that machine learning researchers can readily compare and analyze the new idea.
- Extensive GAN implementations for Pytorch
- Comprehensive benchmark of GANs using CIFAR10, Tiny ImageNet, and ImageNet datasets (being updated)
- Better performance and lower memory consumption than original implementations
- Providing pre-trained models that are fully compatible with up-to-date PyTorch environment
- Support Multi-GPU(both DP and DDP), Mixed precision, Synchronized Batch Normalization, and Tensorboard Visualization
| Name | Venue | Architecture | G_type* | D_type* | Loss | EMA** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCGAN | arXiv' 15 | CNN/ResNet*** | N/A | N/A | Vanilla | False |
| LSGAN | ICCV' 17 | CNN/ResNet*** | N/A | N/A | Least Sqaure | False |
| GGAN | arXiv' 17 | CNN/ResNet*** | N/A | N/A | Hinge | False |
| WGAN-WC | ICLR' 17 | ResNet | N/A | N/A | Wasserstein | False |
| WGAN-GP | NIPS' 17 | ResNet | N/A | N/A | Wasserstein | False |
| WGAN-DRA | arXiv' 17 | ResNet | N/A | N/A | Wasserstein | False |
| ACGAN | ICML' 17 | ResNet | cBN | AC | Hinge | False |
| ProjGAN | ICLR' 18 | ResNet | cBN | PD | Hinge | False |
| SNGAN | ICLR' 18 | ResNet | cBN | PD | Hinge | False |
| SAGAN | ICML' 19 | ResNet | cBN | PD | Hinge | False |
| BigGAN | ICLR' 18 | Big ResNet | cBN | PD | Hinge | True |
| BigGAN-Deep | ICLR' 18 | Big ResNet Deep | cBN | PD | Hinge | True |
| CRGAN | ICLR' 20 | Big ResNet | cBN | PD/CL | Hinge | True |
| ICRGAN | arXiv' 20 | Big ResNet | cBN | PD/CL | Hinge | True |
| LOGAN | arXiv' 19 | Big ResNet | cBN | PD | Hinge | True |
| DiffAugGAN | arXiv' 20 | Big ResNet | cBN | PD/CL | Hinge | True |
| ADAGAN | arXiv' 20 | Big ResNet | cBN | PD/CL | Hinge | True |
| ContraGAN | arXiv' 20 | Big ResNet | cBN | CL | Hinge | True |
| FreezeD | CVPRW' 20 | - | - | - | - | - |
*G/D_type indicates the way how we inject label information to the Generator or Discriminator. **EMA means applying an exponential moving average update to the generator. ***Experiments on Tiny ImageNet are conducted using the ResNet architecture instead of CNN.
cBN : Conditional batch normalization. AC : Auxiliary classifier. PD : Projection discriminator. CL : Contrastive learning.
| Name | Venue | Architecture | G_type* | D_type* | Loss | EMA** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WCGAN | ICLR' 18 | Big ResNet | cWC | PD | Hinge | True |
| StyleGAN2 | CVPR' 20 | StyleNet | AdaIN | - | - | - |
cWC : conditional Whitening and Coloring batch transform. AdaIN : Adaptive Instance Normalization.
- Anaconda
- Python >= 3.6
- 6.0.0 <= Pillow <= 7.0.0
- scipy == 1.1.0 (Recommended for fast loading of Inception Network)
- sklearn
- seaborn
- h5py
- tqdm
- torch >= 1.6.0 (Recommended for mixed precision training and knn analysis)
- torchvision >= 0.7.0
- tensorboard
- 5.4.0 <= gcc <= 7.4.0 (Recommended for proper use of adaptive discriminator augmentation module)
You can install the recommended environment as follows:
conda env create -f environment.yml -n studiogan
With docker, you can use:
docker pull mgkang/studiogan:0.1
- Train (
-t) and evaluate (-e) the model defined inCONFIG_PATHusing GPU0
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 src/main.py -t -e -c CONFIG_PATH
- Train (
-t) and evaluate (-e) the model defined inCONFIG_PATHusing GPUs(0, 1, 2, 3)andDataParallel
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3 python3 src/main.py -t -e -c CONFIG_PATH
- Train (
-t) and evaluate (-e) the model defined inCONFIG_PATHusing GPUs(0, 1, 2, 3)andDistributedDataParallel
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3 python3 src/main.py -t -e -DDP -c CONFIG_PATH
Try python3 src/main.py to see available options.
Via Tensorboard, you can monitor trends of IS, FID, F_beta, Authenticity Accuracies, and the largest singular values:
~ PyTorch-StudioGAN/logs/RUN_NAME>>> tensorboard --logdir=./ --port PORT
-
CIFAR10: StudioGAN will automatically download the dataset once you execute
main.py. -
Tiny Imagenet, Imagenet, or a custom dataset:
- download Tiny Imagenet and Imagenet. Prepare your own dataset.
- make the folder structure of the dataset as follows:
┌── docs
├── src
└── data
└── ILSVRC2012 or TINY_ILSVRC2012 or CUSTOM
├── train
│ ├── cls0
│ │ ├── train0.png
│ │ ├── train1.png
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── cls1
│ └── ...
└── valid
├── cls0
│ ├── valid0.png
│ ├── valid1.png
│ └── ...
├── cls1
└── ...
- DistributedDataParallel
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,... python3 src/main.py -t -DDP -c CONFIG_PATH - Mixed Precision Training (Narang et al.)
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,... python3 src/main.py -t -mpc -c CONFIG_PATH - Standing Statistics (Brock et al.)
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,... python3 src/main.py -e -std_stat --standing_step STANDING_STEP -c CONFIG_PATH - Synchronized BatchNorm
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,... python3 src/main.py -t -sync_bn -c CONFIG_PATH - Load All Data in Main Memory
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,... python3 src/main.py -t -l -c CONFIG_PATH
The StudioGAN supports Image visualization, K-nearest neighbor analysis, Linear interpolation, and Frequency analysis. All results will be saved in ./figures/RUN_NAME/*.png.
- Image Visualization
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,... python3 src/main.py -iv -std_stat --standing_step STANDING_STEP -c CONFIG_PATH --checkpoint_folder CHECKPOINT_FOLDER --log_output_path LOG_OUTPUT_PATH
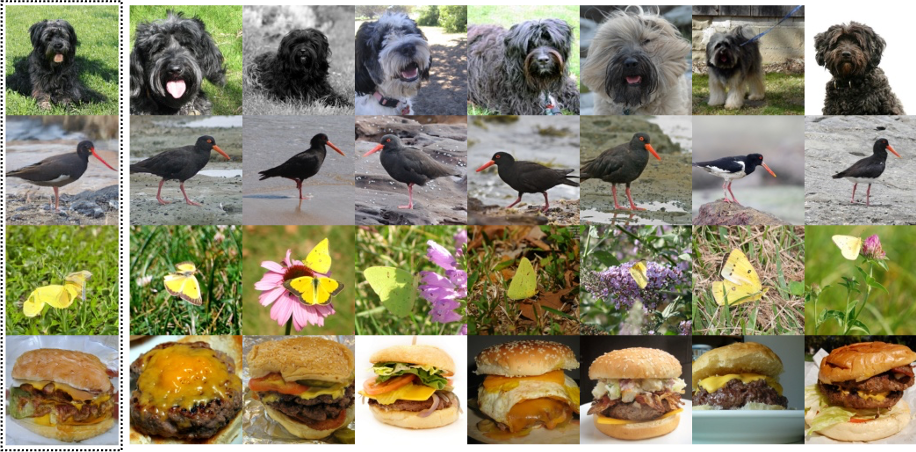
- K-Nearest Neighbor Analysis (we have fixed K=7, the images in the first column are generated images.)
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,... python3 src/main.py -knn -std_stat --standing_step STANDING_STEP -c CONFIG_PATH --checkpoint_folder CHECKPOINT_FOLDER --log_output_path LOG_OUTPUT_PATH
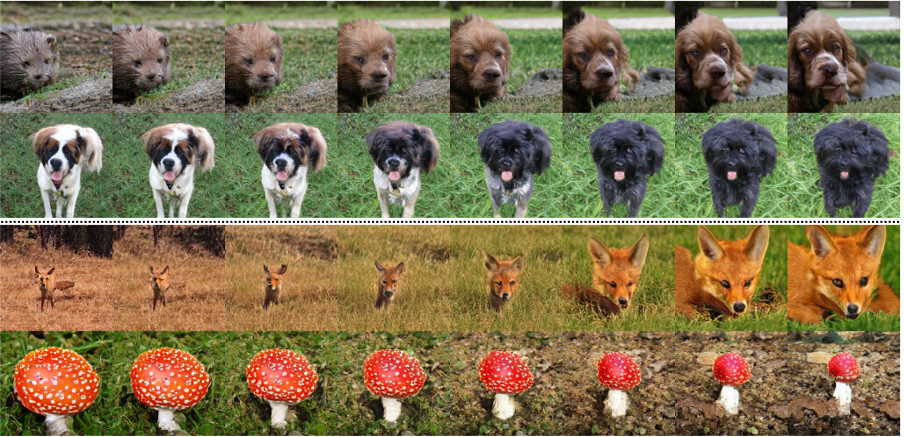
- Linear Interpolation (applicable only to conditional Big ResNet models)
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,... python3 src/main.py -itp -std_stat --standing_step STANDING_STEP -c CONFIG_PATH --checkpoint_folder CHECKPOINT_FOLDER --log_output_path LOG_OUTPUT_PATH
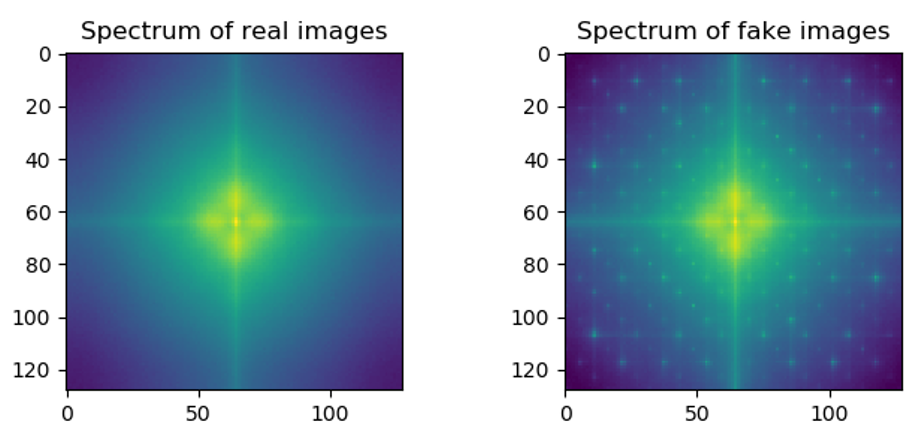
- Frequency Analysis
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,... python3 src/main.py -fa -std_stat --standing_step STANDING_STEP -c CONFIG_PATH --checkpoint_folder CHECKPOINT_FOLDER --log_output_path LOG_OUTPUT_PATH
Inception Score (IS) is a metric to measure how much GAN generates high-fidelity and diverse images. Calculating IS requires the pre-trained Inception-V3 network, and recent approaches utilize OpenAI's TensorFlow implementation.
To compute official IS, you have to make a "samples.npz" file using the command below:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,... python3 src/main.py -s -std_stat --standing_step STANDING_STEP -c CONFIG_PATH --checkpoint_folder CHECKPOINT_FOLDER --log_output_path LOG_OUTPUT_PATH
It will automatically create the samples.npz file in the path ./samples/RUN_NAME/fake/npz/samples.npz.
After that, execute TensorFlow official IS implementation. Note that we do not split a dataset into ten folds to calculate IS ten times. We use the entire dataset to compute IS only once, which is the evaluation strategy used in the CompareGAN repository.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,... python3 src/inception_tf13.py --run_name RUN_NAME --type "fake"
Keep in mind that you need to have TensorFlow 1.3 or earlier version installed!
Note that StudioGAN logs Pytorch-based IS during the training.
FID is a widely used metric to evaluate the performance of a GAN model. Calculating FID requires the pre-trained Inception-V3 network, and modern approaches use Tensorflow-based FID. StudioGAN utilizes the PyTorch-based FID to test GAN models in the same PyTorch environment. We show that the PyTorch based FID implementation provides almost the same results with the TensorFlow implementation (See Appendix F of our paper).
Precision measures how accurately the generator can learn the target distribution. Recall measures how completely the generator covers the target distribution. Like IS and FID, calculating Precision and Recall requires the pre-trained Inception-V3 model. StudioGAN uses the same hyperparameter settings with the original Precision and Recall implementation, and StudioGAN calculates the F-beta score suggested by Sajjadi et al.
※ We always welcome your contribution if you find any wrong implementation, bug, and misreported score.
We report the best IS, FID, and F_beta values of various GANs. (P) and (C) refer to GANs using PD (Projection Discriminator) and CL (Contrastive Learning) as conditional models, respectively.
| Name | Res. | Batch size | IS(⭡) | FID(⭣) | F_1/8(⭡) | F_8(⭡) | Config | Log | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCGAN | 32 | 64 | 6.697 | 50.281 | 0.851 | 0.788 | Config | Log | - |
| LSGAN | 32 | 64 | 5.537 | 67.229 | 0.790 | 0.702 | Config | Log | - |
| GGAN | 32 | 64 | 6.175 | 43.008 | 0.907 | 0.835 | Config | Log | - |
| WGAN-WC | 32 | 64 | 2.525 | 160.856 | 0.181 | 0.170 | Config | Log | - |
| WGAN-GP | 32 | 64 | 7.281 | 25.883 | 0.959 | 0.927 | Config | Log | - |
| WGAN-DRA | 32 | 64 | 6.452 | 41.633 | 0.925 | 0.861 | Config | Log | - |
| ACGAN | 32 | 64 | 6.696 | 46.081 | 0.886 | 0.820 | Config | Log | - |
| ProjGAN | 32 | 64 | 7.398 | 34.037 | 0.945 | 0.871 | Config | Log | - |
| SNGAN | 32 | 64 | 8.810 | 13.161 | 0.980 | 0.978 | Config | Log | - |
| SAGAN | 32 | 64 | 8.297 | 14.702 | 0.981 | 0.976 | Config | Log | - |
| BigGAN | 32 | 64 | 9.562 | 7.911 | 0.994 | 0.991 | Config | Log | - |
| ContraGAN | 32 | 64 | 9.729 | 8.065 | 0.993 | 0.992 | Config | Log | - |
| CRGAN(P) | 32 | 64 | 9.911 | 7.199 | 0.994 | 0.994 | Config | Log | - |
| CRGAN(C) | 32 | 64 | 9.812 | 7.685 | 0.995 | 0.993 | Config | Log | - |
| ICRGAN(P) | 32 | 64 | 9.781 | 7.550 | 0.994 | 0.992 | Config | Log | - |
| ICRGAN(C) | 32 | 64 | 10.117 | 7.547 | 0.996 | 0.993 | Config | Log | - |
| DiffAugGAN(P) | 32 | 64 | 9.649 | 7.369 | 0.995 | 0.994 | Config | Log | - |
| DiffAugGAN(C) | 32 | 64 | 9.896 | 7.285 | 0.995 | 0.988 | Config | Log | - |
| LOGAN | 32 | 64 | 9.576 | 8.465 | 0.993 | 0.990 | Config | Log | - |
※ IS, FID, and F_beta values are computed using 10K test and 10K generated Images.
| Name | Res. | Batch size | IS(⭡) | FID(⭣) | F_1/8(⭡) | F_8(⭡) | Config | Log | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCGAN | 64 | 256 | 5.640 | 91.625 | 0.606 | 0.391 | Config | Log | - |
| LSGAN | 64 | 256 | 5.381 | 90.008 | 0.638 | 0.390 | Config | Log | - |
| GGAN | 64 | 256 | 5.146 | 102.094 | 0.503 | 0.307 | Config | Log | - |
| WGAN-WC | 64 | 256 | 9.556 | 40.003 | 0.945 | 0.750 | Config | Log | - |
| WGAN-GP | 64 | 256 | 1.580 | 304.667 | 0.0 | 0.0 | Config | Log | - |
| WGAN-DRA | 64 | 256 | 9.323 | 40.822 | 0.926 | 0.732 | Config | Log | - |
| ACGAN | 64 | 256 | 6.603 | 72.239 | 0.675 | 0.521 | Config | Log | - |
| ProjGAN | 64 | 256 | 5.881 | 84.636 | 0.645 | 0.432 | Config | Log | - |
| SNGAN | 64 | 256 | 9.071 | 49.021 | 0.923 | 0.731 | Config | Log | - |
| SAGAN | 64 | 256 | 8.484 | 50.784 | 0.887 | 0.720 | Config | Log | - |
| BigGAN | 64 | 1024 | 12.057 | 32.079 | 0.951 | 0.868 | Config | Log | - |
| ContraGAN | 64 | 1024 | 13.494 | 27.027 | 0.975 | 0.902 | Config | Log | - |
| CRGAN(P) | 64 | 1024 | 14.887 | 21.488 | 0.969 | 0.936 | Config | Log | - |
| CRGAN(C) | 64 | 1024 | 15.623 | 19.716 | 0.983 | 0.941 | Config | Log | - |
| ICRGAN(P) | 64 | 1024 | 5.605 | 91.326 | 0.525 | 0.399 | Config | - | - |
| ICRGAN(C) | 64 | 1024 | 15.830 | 21.940 | 0.980 | 0.944 | Config | - | - |
| DiffAugGAN(P) | 64 | 1024 | 18.375 | 16.012 | 0.979 | 0.970 | Config | - | - |
| DiffAugGAN(C) | 64 | 1024 | 17.901 | 15.607 | 0.985 | 0.959 | Config | - | - |
| LOGAN | 64 | 256 | 9.909 | 41.781 | 0.897 | 0.806 | Config | - | - |
※ IS, FID, and F_beta values are computed using 50K validation and 50K generated Images.
- Note: We plan to conduct ImageNet generation experiments in the order of SNGAN -> SAGAN -> ContraGAN.
| Name | Res. | Batch size | IS(⭡) | FID(⭣) | F_1/8(⭡) | F_8(⭡) | Config | Log | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNGAN | 128 | 256 | - | - | - | - | Config | - | - |
| SAGAN | 128 | 256 | - | - | - | - | Config | - | - |
| BigGAN | 128 | 256 | - | - | - | - | Config | - | - |
| ContraGAN | 128 | 256 | - | - | - | - | Config | - | - |
| BigGAN | 128 | 2048 | 99.705 | 7.893 | 0.985 | 0.989 | Config | Log | - |
| ContraGAN | 128 | 2048 | - | - | - | - | Config | - | - |
※ IS, FID, and F_beta values are computed using 50K validation and 50K generated Images.
[1] Exponential Moving Average: https://github.com/ajbrock/BigGAN-PyTorch
[2] Synchronized BatchNorm: https://github.com/vacancy/Synchronized-BatchNorm-PyTorch
[3] Self-Attention module: https://github.com/voletiv/self-attention-GAN-pytorch
[4] Implementation Details: https://github.com/ajbrock/BigGAN-PyTorch
[5] Architecture Details: https://github.com/google/compare_gan
[6] DiffAugment: https://github.com/mit-han-lab/data-efficient-gans
[7] Adaptive Discriminator Augmentation: https://github.com/rosinality/stylegan2-pytorch
[8] Tensorflow IS: https://github.com/openai/improved-gan
[9] Tensorflow FID: https://github.com/bioinf-jku/TTUR
[10] Pytorch FID: https://github.com/mseitzer/pytorch-fid
[11] Tensorflow Precision and Recall: https://github.com/msmsajjadi/precision-recall-distributions
StudioGAN is established for the following research project. Please cite our work if you use StudioGAN.
@article{kang2020ContraGAN,
title = {{ContraGAN: Contrastive Learning for Conditional Image Generation}},
author = {Minguk Kang and Jaesik Park},
journal = {Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS)},
year = {2020}
}