The aim of the project is to ease out the often-caused troubles of marking a location in real life scenario by making a location pointer k/as ZIPPER. This project would analyses the situation and provide the solutions for the same. It will explain the purpose and used features in the zipper, what will the zipper do in various cases and the constraints under which will the zipper shall work and what shall be its behavior to the external stimuli. The document is to be submitted as a part of the course of Object Oriented Programming.
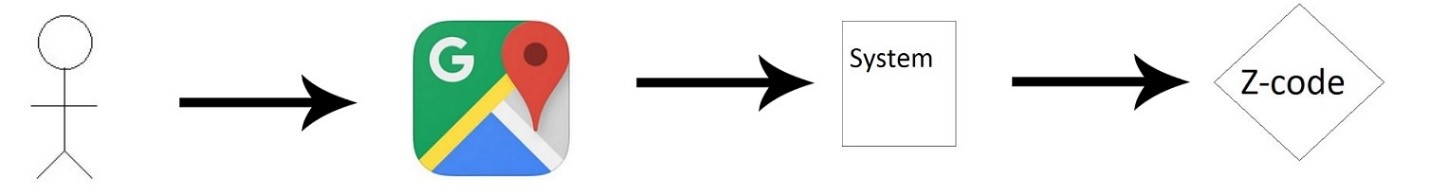
The software will counter the problem of difficulties faced in hunting a location/place in maps, for instance, any street no or any house number deep down some lane of old city. Many maps don’t even show the nearby arenas of the specified location. This would be a very productive way for all the users e any type, to search for his/her given location once the location has been registered in our zipper, that would be provided a unique identification, k/as zipper code with the help of its longitude and latitude, which will act as the tag for that particular location. The software would also be useful for all the companies/or services, which operate on any kind of maps or navigation system such as cab services or delivery hunters by catalysing their process of the location hunting which otherwise manually done could be treacherous and cumbersome. So, for example, the location with “X, Y” longitude might not be shown in the Google maps, but if assigned an alphabetical name to the given location, then it could be easily accessed on any map. To further, increase the utility of the project, we would be providing the custom choices to the given location and then audit it for selling purpose and hence thereby maintaining the competitive environment to survive in the real world economy. Also, the system will also lay scope of generating and maintaining the scope of various custom names, and z-code which has been provided to avoid any collision/overlapping. The location pointer system has 2 main user classes, first user, given the Z-code and gets the precise location. The second type of user given the location and takes Z-code. Herein, there is diversification in the type of Z-code a user gets depending on his preferences and system.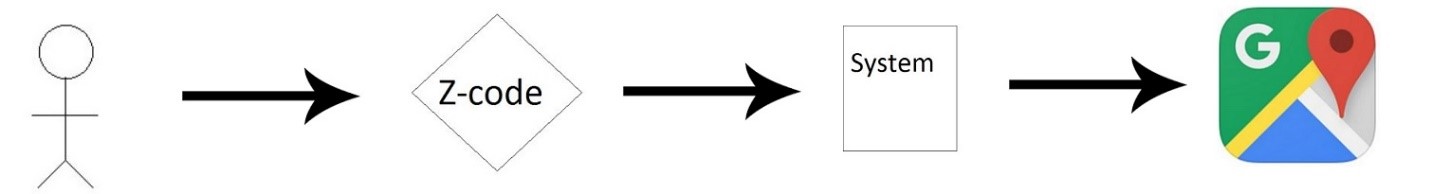 Use case: Search Location3
Brief description
The general end case user accesses the program by giving the Z-code through the web interface. Then he/she is directed to the relevant location which will be marked on Google maps.
Initial step-by-step description:
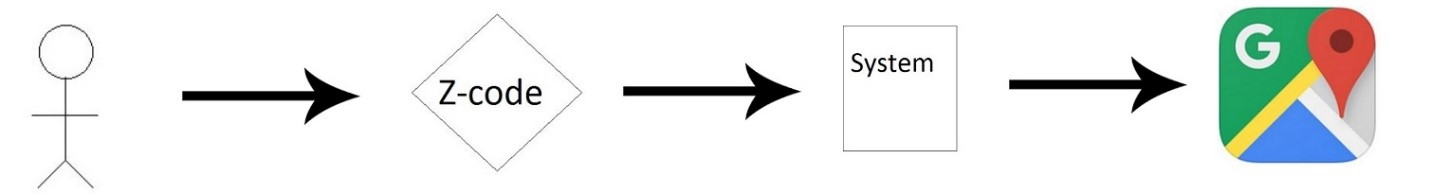
When the user uses this case he/she already has the Z-code for the location.
Use case: Search Location3
Brief description
The general end case user accesses the program by giving the Z-code through the web interface. Then he/she is directed to the relevant location which will be marked on Google maps.
Initial step-by-step description:
When the user uses this case he/she already has the Z-code for the location.
- Reader enters the Z-code in the interface.
- The system takes the Z-code and then it is validated against a set of rules.
- The code is then converted through an algorithm to the co-ordinates.
- The co-ordinates are passed to Google Maps.
- The relevant location is then marked on the map.
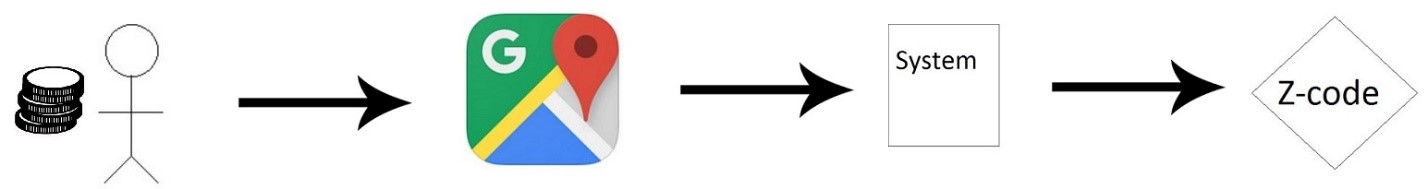
Use case: Make location pointer Brief description This use case will involve the stakeholder to generate the Z-code for a particular location relevant to her/him. The Z-code will be a generalized one which will be unique to the particular co-ordinate. Further, the stakeholder may use a custom name for the Z-code, provided the availability against a particular amount of monetary/barter exchange. As the case is pertained for a public/government body, the rates shall be subsidized. Initial step-by-step description: The stakeholder for this case knows the place on the maps.
- The address yields a rough location of the place.
- The stakeholder then manually finds the exact place.
- The system then imports the exact co-ordinates of the location.
- The co-ordinates are then filtered for the system.
- The co-ordinates are then converted to Z-code(custom) using the algorithms. The Z-code (custom) is then displayed to stakeholder which he/she can use for his commercial purpose.