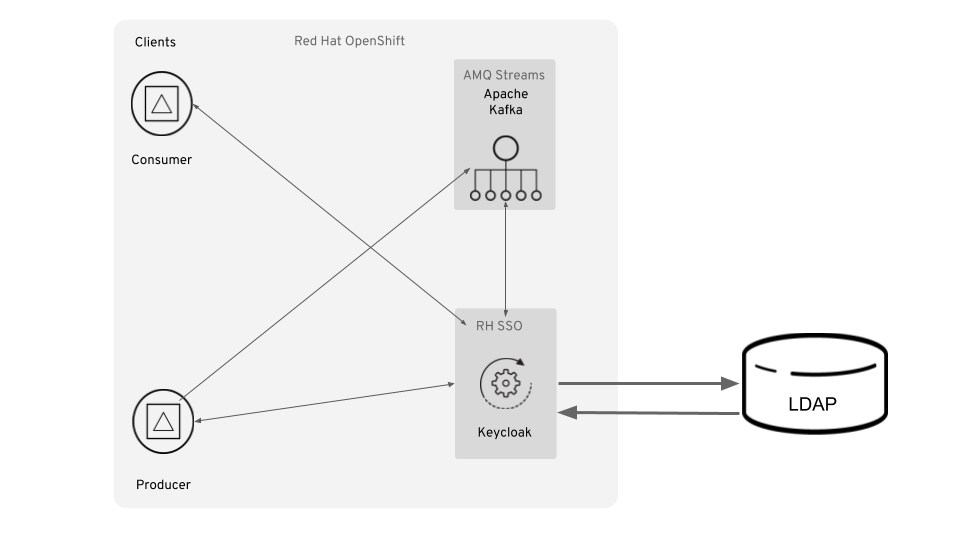
This project demonstrates how to setup and configure an AMQ Streams cluster on OpenShift with client RBAC enforcement (authentication only) using RH-SSO (Keycloak).
The Authorization portion using LDAP to manage groups in available in community Strimzi, and will be updated here in the future.
The following product / OS prerequisities exist:
- OpenJDK 1.8+
- OpenShift 3.11.x
- An LDAP server. If you don't have an LDAP server, follow this procedure to install a Docker image with a pre-built LDAP server. Additionally, follow this tutorial to configure sample users / groups for your test.
To get things started, we need to install on RH-SSO on OCP. For the purposes of this demo, I'm using the stateless option (ethemeral) and am creating my own keystore and truststore.
-
Via the CLI, create a new OCP project:
oc new-project streams-oauth. -
Via the CLI, enter the following to generate a CA certificate (using
passwordas the PEM passphrase):
openssl req -new -newkey rsa:4096 -x509 -keyout xpaas.key -out xpaas.crt -days 365 -subj "/CN=secure-sso.streams-oauth.svc"
- Via the CLI, generate a CA certificate for the HTTPS keystore (using
passwordas the keystore password):
keytool -genkeypair -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -dname "CN=secure-sso.streams-oauth.svc.cluster.local" -alias jboss -keystore keystore.jks -ext SAN=dns:secure-sso.streams-oauth.svc,dns:secure-sso.streams-oauth.svc.cluster.local
- Generate a CSR for the HTTPS keystore (using
passwordas the keystore password):
keytool -certreq -keyalg rsa -alias jboss -keystore keystore.jks -file sso.csr
- Sign the CSR using
password:
openssl x509 -req -CA xpaas.crt -CAkey xpaas.key -in sso.csr -out sso.crt -days 365 -CAcreateserial
- Import the the CA certificate into the HTTPS keystore:
keytool -import -file xpaas.crt -alias xpaas.ca -keystore keystore.jks
- Import the signed CSR into the HTTPS keystore (using
passwordas the keystore password):
keytool -import -file sso.crt -alias jboss -keystore keystore.jks
- Generate a secure key for the JGroups keystore:
keytool -genseckey -alias secret-key -storetype JCEKS -keystore jgroups.jceks
- Import the CA cert into a new SSO truststore (using
passwordas the keystore password):
keytool -import -file xpaas.crt -alias xpaas.ca -keystore truststore.jks
- Create the secrets for the HTTPS and JGroups keystores:
oc secret new sso-app-secret keystore.jks jgroups.jceks truststore.jks
- Link the secrets to the default service account:
oc secrets link default sso-app-secret
- You can verify the keystores using the following commands:
keytool -v -list -keystore keystore.jks | grep Alias
keytool -v -list -keystore jgroups.jceks -storetype jceks | grep Alias
- Lastly, deploy RH-SSO:
oc new-app --template=sso73-https \
-p HTTPS_SECRET="sso-app-secret" \
-p HTTPS_KEYSTORE="keystore.jks" \
-p HTTPS_NAME="jboss" \
-p HTTPS_PASSWORD="password" \
-p JGROUPS_ENCRYPT_SECRET="sso-app-secret" \
-p JGROUPS_ENCRYPT_KEYSTORE="jgroups.jceks" \
-p JGROUPS_ENCRYPT_NAME="secret-key" \
-p JGROUPS_ENCRYPT_PASSWORD="password" \
-p SSO_ADMIN_USERNAME="admin" \
-p SSO_ADMIN_PASSWORD="password" \
-p SSO_TRUSTSTORE="truststore.jks" \
-p SSO_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD="password" \
-p SSO_TRUSTSTORE_SECRET="sso-app-secret"
- You should receive the following output via the CLI:
--> Deploying template "openshift/sso73-https" to project streams-oauth
Red Hat Single Sign-On 7.3 (Ephemeral with passthrough TLS)
---------
An example application based on RH-SSO 7.3 image. For more information about using this template, see https://github.com/jboss-container-images/redhat-sso-7-openshift-image/docs.
A new RH-SSO service has been created in your project. The admin username/password for accessing the master realm via the RH-SSO console is admin/password. Please be sure to create the following secrets: "sso-app-secret" containing the keystore.jks file used for serving secure content; "sso-app-secret" containing the jgroups.jceks file used for securing JGroups communications; "sso-app-secret" containing the truststore.jks file used for securing RH-SSO requests.
* With parameters:
* Application Name=sso
* Custom http Route Hostname=
* Custom https Route Hostname=
* Custom RH-SSO Server Hostname=
* Server Keystore Secret Name=sso-app-secret
* Server Keystore Filename=keystore.jks
* Server Keystore Type=
* Server Certificate Name=jboss
* Server Keystore Password=password
* Datasource Minimum Pool Size=
* Datasource Maximum Pool Size=
* Datasource Transaction Isolation=
* JGroups Secret Name=sso-app-secret
* JGroups Keystore Filename=jgroups.jceks
* JGroups Certificate Name=secret-key
* JGroups Keystore Password=password
* JGroups Cluster Password=I4kq7RL8 # generated
* ImageStream Namespace=openshift
* RH-SSO Administrator Username=admin
* RH-SSO Administrator Password=password
* RH-SSO Realm=
* RH-SSO Service Username=
* RH-SSO Service Password=
* RH-SSO Trust Store=truststore.jks
* RH-SSO Trust Store Password=password
* RH-SSO Trust Store Secret=sso-app-secret
* Container Memory Limit=1Gi
--> Creating resources ...
service "sso" created
service "secure-sso" created
service "sso-ping" created
route.route.openshift.io "sso" created
route.route.openshift.io "secure-sso" created
deploymentconfig.apps.openshift.io "sso" created
--> Success
Access your application via route 'sso-streams-oauth.apps.tiaa-ad83.open.redhat.com'
Access your application via route 'secure-sso-streams-oauth.apps.tiaa-ad83.open.redhat.com'
Run 'oc status' to view your app.
-
Once the RH-SSO pod starts up, you can access the Admin console via:
https://secure-sso-streams-oauth.apps.tiaa-ad83.open.redhat.com/auth/adminand credentials u:admin p:password. -
Import the kafka clients + broker configuration by clicking on
Manage > Importand selecting theconf/sso/realm-export.jsonfile. Be sure to regenerate the secret forkafka-broker,kafka-consumerandkafka-producer.
Now that RH-SSO is installed and we have the OAUTH2 clients setup, we need to install and configure AMQ Streams.
-
Via the CLI, change to the
/conf/streamsdirectory. -
Run the following command to update the namespace in each definition file:
sed -i '' 's/namespace: .*/namespace: streams-oauth/' install/cluster-operator/*RoleBinding*.yaml
- Install the AMQ Streams cluster operator on OCP:
oc apply -f install/cluster-operator -n streams-oauth
- Replace the
<broker secret>with the client secret forkafka-brokerin RH-SSO (on the Credentials tab), then execute the command via the CLI:
oc create secret generic broker-oauth-secret -n streams-oauth --from-literal=secret=<broker-secret>
- From the
conf/ssodirectory, create the TLS (HTTPS) trusted cert used by RH-SSO via the CLI:
oc create secret generic ca-truststore --from-file=./xpaas.crt -n streams-oauth
- Deploy the AMQ Streams Zookeeper and Kafka brokers (but update the
validIssuerUriandjwksEndpointUrito match your hostname):
cat << EOF | oc create -f -
apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1alpha1
kind: Kafka
metadata:
name: my-cluster
spec:
kafka:
replicas: 3
listeners:
external:
type: route
plain: {}
tls:
authentication:
type: oauth
clientId: kafka-broker
clientSecret:
key: secret
secretName: broker-oauth-secret
validIssuerUri: https://secure-sso.streams-oauth.svc.cluster.local:8443/auth/realms/master
jwksEndpointUri: https://secure-sso.streams-oauth.svc.cluster.local:8443/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/certs
userNameClaim: preferred_username
tlsTrustedCertificates:
- secretName: ca-truststore
certificate: xpaas.crt
storage:
type: ephemeral
zookeeper:
replicas: 3
storage:
type: ephemeral
entityOperator:
topicOperator: {}
userOperator: {}
EOF
- Once both Kafka and Zookeeper pods have started, we can create a Kafka client shell pod to test the OAUTH2 connectivity and produce / consume messages. First we need to export the CA cert for the kafka client:
oc get secret my-cluster-cluster-ca-cert -n streams-oauth -o yaml | grep ca.crt | awk '{print $2}' | base64 --decode > kafka.crt
- Create a kafka client truststore and import both the CA and client certs :
keytool -keystore kafka-client-truststore.p12 -storetype PKCS12 -alias ca -storepass password -keypass password -import -file xpaas.crt -noprompt
keytool -keystore kafka-client-truststore.p12 -storetype PKCS12 -alias kafka -storepass password -keypass password -import -file kafka.crt -noprompt
- Create a new secret,
kafka-client-truststore, that contains the necessary client certs:
oc create secret generic kafka-client-truststore -n streams-oauth --from-file=./kafka-client-truststore.p12
- Create the kafka client shell pod:
cat << EOF | oc create -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: kafka-client-shell
spec:
containers:
- name: kafka-client-shell
image: strimzi/kafka:0.14.0-kafka-2.3.0
command: ["/bin/bash"]
args: [ "-c", 'for((i=0;;i+=1)); do echo "Up time: \$i min" && sleep 60; done' ]
env:
- name: CLASSPATH
value: /opt/kafka/libs/kafka-oauth-client-*:/opt/kafka/libs/kafka-oauth-common-*
- name: OAUTH_TOKEN_ENDPOINT_URI
value: https://secure-sso.streams-oauth.svc.cluster.local:8443/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token
volumeMounts:
- name: truststore
mountPath: "/opt/kafka/certificates"
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: truststore
secret:
secretName: kafka-client-truststore
EOF
- Open the shell via the CLI:
oc exec -n streams-oauth -ti kafka-client-shell /bin/bash
- Via the CLI, start the kafka-producer (but be sure to update OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET with the value from kafka-producer in RH-SSO):
export OAUTH_CLIENT_ID=kafka-producer
export OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET=<SECRET_FOR_KAFKA_PRODUCER_FROM_KEYCLOAK_CONSOLE>
export PASSWORD=password
export KAFKA_OPTS=" \
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/opt/kafka/certificates/kafka-client-truststore.p12 \
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=$PASSWORD \
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStoreType=PKCS12"
bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list \
my-cluster-kafka-bootstrap.streams-oauth.svc.cluster.local:9093 --topic simon-topic \
--producer-property 'security.protocol=SASL_SSL' \
--producer-property 'sasl.mechanism=OAUTHBEARER' \
--producer-property 'sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginModule required;' \
--producer-property 'sasl.login.callback.handler.class=io.strimzi.kafka.oauth.client.JaasClientOauthLoginCallbackHandler'
- Via a separate CLI window, start the kafka-consumers (but be sure to update OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET with the value from kafka-consumer in RH-SSO):
export OAUTH_CLIENT_ID=kafka-consumer
export OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET=<SECRET_FOR_KAFKA_CONSUMER_FROM_KEYCLOAK_CONSOLE>
export PASSWORD=password
export KAFKA_OPTS=" \
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/opt/kafka/certificates/kafka-client-truststore.p12 \
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=$PASSWORD \
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStoreType=PKCS12"
bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server \
my-cluster-kafka-bootstrap.streams-oauth.svc.cluster.local:9093 --topic simon-topic --from-beginning \
--consumer-property 'security.protocol=SASL_SSL' \
--consumer-property 'sasl.mechanism=OAUTHBEARER' \
--consumer-property 'sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginModule required;' \
--consumer-property 'sasl.login.callback.handler.class=io.strimzi.kafka.oauth.client.JaasClientOauthLoginCallbackHandler'
If all goes well, there should be no SSL handshake errors and you should be able to send and receive messages.