Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is one of the fundamental capabilities for intelligent mobile robots to perform state estimation in unknown environments. However, most visual SLAM systems rely on the static scene assumption and consequently have severely reduced accuracy and robustness in dynamic scenes. Moreover, the metric maps constructed by many systems lack semantic information, so the robots cannot understand their surroundings at a human cognitive level.
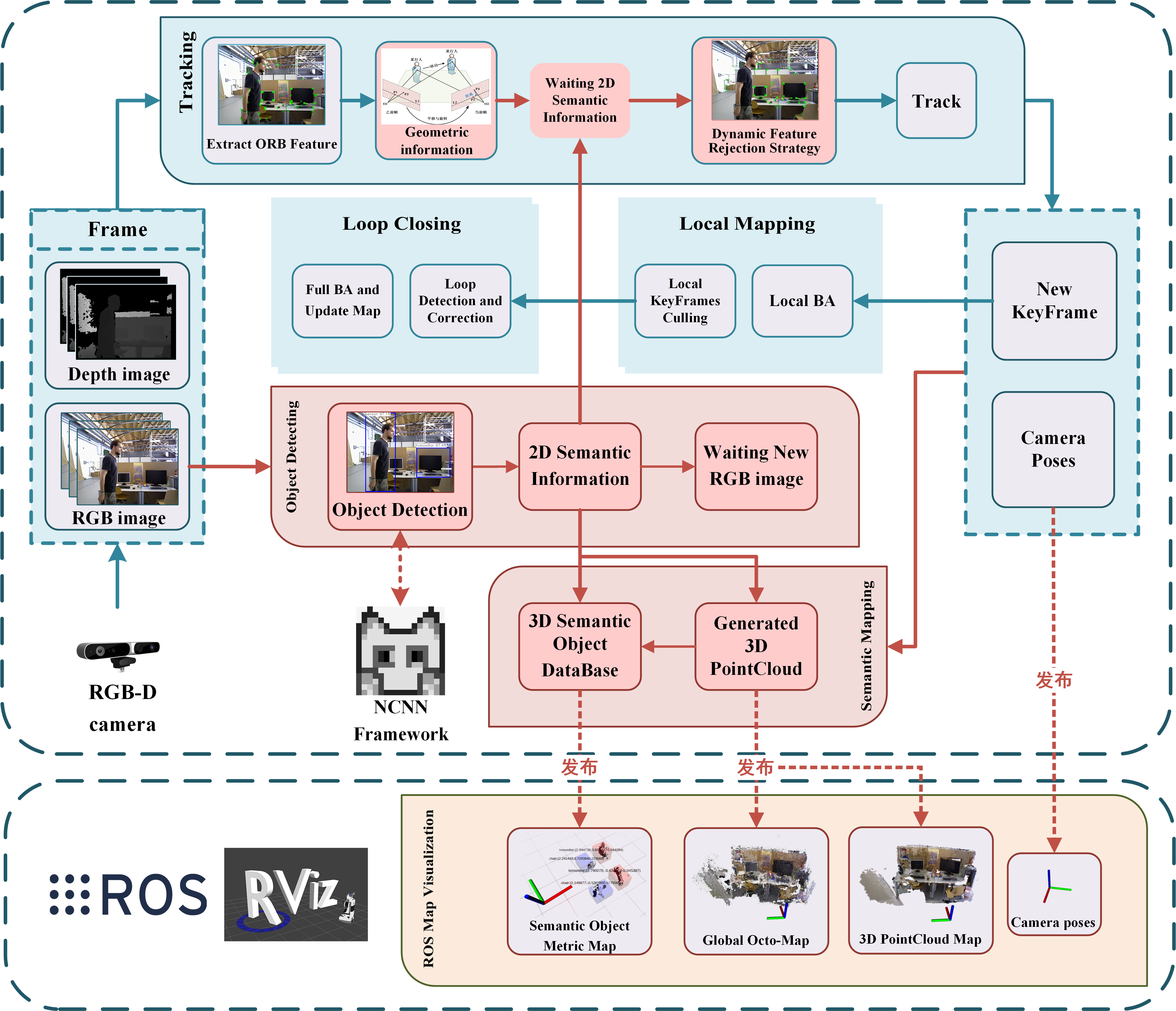
In this paper, we propose SG-SLAM, which is a real-time RGB-D semantic visual SLAM system based on the ORB-SLAM2 framework. First, SG-SLAM adds two new parallel threads: an object detecting thread to obtain 2D semantic information and a semantic mapping thread. Then, a fast dynamic feature rejection algorithm combining semantic and geometric information is added to the tracking thread. Finally, they are published to the ROS system for visualization after generating 3D point clouds and 3D semantic objects in the semantic mapping thread.
We performed an experimental evaluation on the TUM dataset, the Bonn dataset, and the OpenLORIS-Scene dataset. The results show that SG-SLAM is not only one of the most real-time, accurate, and robust systems in dynamic scenes, but also allows the creation of intuitive semantic metric maps.
【BiliBili】VIDEO
【Youtube】VIDEO
(For the Chinese version, see the README-zh.md file in the directory)
(中文版本见目录下README-zh.md文件)
Figure1. Overview of the framework of the SG-SLAM system. The original work of ORB-SLAM2 is presented on an aqua-green background, while our main new or modified work is presented on a red background.
Figure2. Semantic object metric map for tum rgbd dataset fr3/walking_xyz sequence
Figure3. octo map for tum rgbd dataset fr3/long office household sequence
Figure4. Actual effect
System Features :
- Based on ORB-SLAM2, NCNN, ROS, etc.
- Fast running (if NCNN is well configured)
- Easy to deploy
- ...
SG-SLAM is released under a GPLv3 license.
Paper is available on IEEE Xplore.
If you use SG-SLAM in an academic work, please cite:
S. Cheng, C. Sun, S. Zhang and D. Zhang, "SG-SLAM: A Real-Time RGB-D Visual SLAM toward Dynamic Scenes with Semantic and Geometric Information," in IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, doi: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3228006.
#Basic
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install git
sudo apt install cmake
sudo apt install build-essential
sudo apt vim
#test
git --version
gcc --version
g++ --version
cmake --version
#Pangolin
sudo apt install libglew-dev
sudo apt install libboost-dev libboost-thread-dev libboost-filesystem-dev
sudo apt install libpython2.7-dev
git clone https://github.com/stevenlovegrove/Pangolin.git
cd Pangolin/
git checkout v0.5
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make -j4
sudo make install
#OpenCV,refer https://docs.opencv.org/3.4.15/d7/d9f/tutorial_linux_install.html
sudo apt install libgtk2.0-dev pkg-config libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev
sudo apt install python-dev python-numpy libtbb2 libtbb-dev libjpeg-dev libpng-dev libtiff-dev libjasper-dev libdc1394-22-dev
git clone https://github.com/opencv/opencv.git
cd opencv/
git checkout 3.4.15
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -D CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -D CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local ..
sudo make install
#test
pkg-config opencv --modversion
#Eigen
git clone https://gitlab.com/libeigen/eigen.git
cd eigen/
git checkout 3.1.0
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
sudo make install
#test
cat /usr/local/include/eigen3/Eigen/src/Core/util/Macros.h
#Compile orb-slam2 with build.sh,and now orbslam2 can perform well
#ROS
#For china,first,replace our resource(http://wiki.ros.org/ROS/Installation/UbuntuMirrors)
sudo sh -c '. /etc/lsb-release && echo "deb http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ros/ubuntu/ `lsb_release -cs` main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
#Set up keys
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver 'hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80' --recv-key C1CF6E31E6BADE8868B172B4F42ED6FBAB17C654
sudo apt update
#this ros below is for ubuntu 18.04
sudo apt install ros-melodic-desktop-full
#Environment setup
echo "source /opt/ros/melodic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
#Dependencies for building packages
sudo apt install python-rosinstall python-rosinstall-generator python-wstool build-essential
#Initialize rosdep.If you encounter problems, refer to this article,https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/397966333
sudo apt install python-rosdep
sudo rosdep init
rosdep update
#test
roscore
#PCL,and pcl-tools(optional)
sudo apt install libpcl-dev pcl-tools
#Octomap,and octovis(optional)
sudo apt install liboctomap-dev octovis
sudo apt install ros-melodic-octomap ros-melodic-octomap-mapping ros-melodic-octomap-msgs ros-melodic-octomap-ros ros-melodic-octomap-rviz-plugins
#SG-SLAM
git clone https://github.com/silencht/SG-SLAM
#Build Thirdparty Liarbry
cd SG-SLAM/src/sg-slam/
./ThirdpartyBuild.sh
#How to build ncnn completely? Please refer HowTo in https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/README.md
#After installing the nvidia driver,vulkan and etc., compile ncnn and install
#-DNCNN_DISABLE_RTTI=OFF (https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/issues/2665)
cd SG-SLAM/src/sg-slam/Thirdparty/ncnn/
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=../toolchains/host.gcc.toolchain.cmake -DNCNN_DISABLE_RTTI=OFF ..
make -j4
sudo make install
#Modify the path in SG-SLAM/src/sg-slam/CMakeLists.txt
#set(ncnn_DIR "there,replace with your path/SG-SLAM/src/sg-slam/Thirdparty/ncnn/build/install/lib/cmake/ncnn" CACHE PATH "Directory that contains ncnnConfig.cmake")
#Init ROS workspace and compile package
cd SG-SLAM/src
catkin_init_workspace
cd ..
catkin_make --pkg cv_bridge
catkin_make --pkg image_geometry
catkin_make --pkg octomap_server
catkin_make --pkg sg-slamPut the TUM dataset into the Music Path according to the run_tum_walking_xyz.sh file (or adjust the script yourself)
#Runing SG-SLAM
#terminal 1
roscore
#terminal 2
cd your_sg-slam_path/src/octomap_server/launch
roslaunch octomap.launch
#terminal 3,you can use my rviz configuration file(like the command below), its path is located in your_sg-slam_path/src/sg-slam/Examples/rvizconfig.rviz, This will subscribe to some map-published topics directly in rviz.
#Of course, you can also open rviz directly, and then manually subscribe to the related topic.
rviz -d your_sg-slam_path/src/sg-slam/Examples/rvizconfig.rviz
#terminal 4
cd your_sg-slam_path/src/sg-slam/
./run_tum_walking_xyz.shIncluding but not limited to the following repositories (In no particular order)
- https://github.com/raulmur/ORB_SLAM2
- https://github.com/ivipsourcecode/DS-SLAM
- https://github.com/Ewenwan/ORB_SLAM2_SSD_Semantic
- https://github.com/MRwangmaomao/semantic_slam_nav_ros
- https://github.com/gaoxiang12/ORBSLAM2_with_pointcloud_map
- https://github.com/abhineet123/ORB_SLAM2
- https://github.com/floatlazer/semantic_slam
- https://github.com/bijustin/YOLO-DynaSLAM
- https://github.com/bijustin/Fast-Dynamic-ORB-SLAM
- https://github.com/halajun/VDO_SLAM
- https://github.com/Quitino/IndoorMapping
- https://github.com/ninedayhx/orb_slam2_ros_dense_map
- https://github.com/lturing/ORB_SLAM3_ROS
- https://github.com/IATBOMSW/ORB-SLAM2_DENSE
- https://github.com/xiaobainixi/ORB-SLAM2_RGBD_DENSE_MAP
- https://github.com/laavanyebahl/3D-Object-Detection-with-Point-Clouds
- ...
/SG-SLAM/src/octomap_server/launch/octomap.launch
This file is used to start the octomap_server node and configure some parameters. You can see what these parameters mean here(http://wiki.ros.org/octomap_server、https://octomap.github.io/)
Among them, the param name=resolution parameter indicates the voxel resolution of the octomap. The smaller the parameter, the finer the map voxel segmentation and the higher the resolution. But the processing time and computational complexity also increase.
The occupancy_min_z and occupancy_max_z parameters can selectively pass through the point cloud within the z-axis range. If your initial camera view is parallel to the ground, you can also use the occupancy_min_z parameter to do a trick to filter out the ground. Similarly, the occupancy_min_z parameter can be used to filter out the top voxels of the house.
filter_ground is the normal algorithm for filtering out the ground (not the trick of directly using occupancy_min_z to filter out the ground). Usage can refer to the above URL.
<!--
Example launch file for octomap_server mapping:
-->
<launch>
<node pkg="octomap_server" type="octomap_server_node" name="octomap_server">
<remap from="cloud_in" to="/SG_SLAM/Point_Clouds" />
<param name="frame_id" type="string" value="/map" />
<param name="resolution" value="0.05" />
<param name="sensor_model/hit" value="0.7" />
<param name="sensor_model/miss" value="0.4" />
<param name="sensor_model/max" value="0.99" />
<param name="sensor_model/min" value="0.12" />
<param name="sensor_model/max_range" value="-1.0" />
<param name="height_map" type="bool" value="false" />
<param name="colored_map" type="bool" value="true" />
<param name="latch" type="bool" value="false" />
<param name="occupancy_min_z" type="double" value="-1.5" />
<param name="occupancy_max_z" type="double" value="1.5" />
<param name="filter_ground" type="bool" value="false" />
<param name="base_frame_id" type="string" value="/map" />
<param name="filter_speckles" type="bool" value="true" />
<param name="ground_filter/distance" type="double" value="0.05" />
<param name="ground_filter/angle" type="double" value="0.15" />
<param name="ground_filter/plane_distance" type="double" value="0.05" />
<param name="pointcloud_min_z" type="double" value="-5.0" />
<param name="pointcloud_max_z" type="double" value="5.0" />
</node>
</launch>SG-SLAM/src/sg-slam/Examples/astra_pro_camera.yaml
SG-SLAM/src/sg-slam/Examples/TUM1.yaml
……
The following parameter items have been newly added to the imager configuration parameters file, and the roles of these parameters are described in turn later.
%YAML:1.0
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Camera Parameters. Adjust them!
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Camera calibration and distortion parameters (OpenCV)
Camera.fx: 575.520619
Camera.fy: 575.994771
…………omitted here
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Viewer Parameters
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Viewer.KeyFrameSize: 0.05
…………omitted above
PointCloudMapping.is_map_construction_consider_dynamic: 0
PointCloudMapping.camera_valid_depth_Min: 0.5
PointCloudMapping.camera_valid_depth_Max: 5.0
PointCloudMapping.is_octo_semantic_map_construction: 0
PointCloudMapping.Sor_Local_MeanK: 50
PointCloudMapping.Sor_Local_StddevMulThresh: 2.0
PointCloudMapping.Voxel_Local_LeafSize: 0.01
PointCloudMapping.is_global_pc_reconstruction: 1
PointCloudMapping.Sor_Global_MeanK: 50
PointCloudMapping.Sor_Global_StddevMulThresh: 2.0
PointCloudMapping.Voxel_Global_LeafSize: 0.01
Detector3D.Sor_MeanK: 50
Detector3D.Sor_StddevMulThresh: 1.0
Detector3D.Voxel_LeafSize: 0.01
Detector3D.EuclideanClusterTolerance: 0.02
Detector3D.EuclideanClusterMinSize: 1000
Detector3D.EuclideanClusterMaxSize: 30000
Detector3D.DetectSimilarCompareRatio: 0.1
Detector3D.global_pc_update_kf_threshold: 30
Detector2D.detection_confidence_threshold: 0.985
Detector2D.dynamic_detection_confidence_threshold: 0.1- PointCloudMapping.is_map_construction_consider_dynamic
When performing octomap or 3D point cloud map builds, dynamic objects in the map can affect the quality of the map build. When this parameter is set to 1, the map will be built with dynamic objects excluded as much as possible (the code implementation is to exclude pedestrians), i.e., no dynamic objects will be built in map. If there is no dynamic object class in scenes, this parameter can be set to 0.
- PointCloudMapping.camera_valid_depth_Min and PointCloudMapping.camera_valid_depth_Max
RGB-D depth cameras have effective observation range limits for depth image data due to hardware and principle limitations. These two parameters are used to limit the effective value range of the depth image. They can be adjusted according to the camera model, and the default effective range here is 0.5 m to 5 m.
- PointCloudMapping.is_octo_semantic_map_construction
Whether to build octomap and semantic object metric map, 1 is to build, 0 is not to build.
- PointCloudMapping.Sor_Local_MeanK,PointCloudMapping.Sor_Local_StddevMulThresh and PointCloudMapping.Voxel_Local_LeafSize
If is_octo_semantic_map_construction is set to 1, namely, octomap will be constructed. these three parameters function as filter setting parameters for filtering the 3D point cloud obtained from the camera depth image conversion.
Take Voxel_Local_LeafSize as an example :
It can be seen from the code when System.cc reads the yaml configuration file that this parameter is finally passed to the Voxel filter object constructor in the PointCloudMapping class.
This parameter is finally passed to the voxel filter object, which is the resolution used for voxel filtering on the point cloud after the depth map is transformed into a 3D point cloud. Because the number of 3D point clouds directly converted from the depth map is large (640*480), the calculation burden is heavy, so filtering is performed. The resolution of the voxel filter is similar to that of the octomap, that is, the centroid of the same position is replaced, so that the amount of calculation is reduced.
After my test, it is generally set to 0.01 on my device, and the calculation efficiency and effect have reached a good balance. Adjustable to individual hardware.
- PointCloudMapping.is_global_pc_reconstruction
Whether to perform 3D point cloud map reconstruction, 1 is to do it, 0 is not to do it. Since map construction requires a significant computational cost, it is generally recommended that this parameter and the PointCloudMapping.is_octo_semantic_map_construction parameter not be turned on at the same time.
- PointCloudMapping.Sor_Global_MeanK, PointCloudMapping.Sor_Global_StddevMulThresh and PointCloudMapping.Voxel_Global_LeafSize
these parameters work similarly to parameters like PointCloudMapping.Sor_Local_MeanK.
- Detector3D.Sor_MeanK, Detector3D.Sor_StddevMulThresh and Detector3D.Voxel_LeafSize
These parameters act similar to parameters like PointCloudMapping.Sor_Local_MeanK. They are the parameters for filtering the point cloud clusters in the detection frame when acquiring 3D semantic objects. The following parameters of the Euclidean clustering settings are also used to extract the point cloud clusters of the target objects as accurately as possible.
- Detector3D.EuclideanClusterTolerance, Detector3D.EuclideanClusterMinSize, Detector3D.EuclideanClusterMaxSize
The setting parameters for Euclidean clustering segmentation of the point clouds in the object detection boundingbox. The purpose is to segment the point cloud of the target object among the point clouds in the detection frame as accurately as possible.
- Detector3D.DetectSimilarCompareRatio
The ratio parameter for filtering when finding the similarity match between a point cloud cluster and its target object. The effect is similar to that of the mfNNratio variable when performing bag-of-words matching in ORB-SLAM2. The smaller this value is, the more stringent the screening is.
- Detector3D.global_pc_update_kf_threshold
Functions such as global 3D point cloud map filtering and publishing in real time are very computationally intensive, so normally only each frame of the point cloud is processed and added to the global map. Only when the system is idle (no new keyframes in the buffer queue) or when the number of processed keyframes exceeds the current threshold parameter will the global point cloud filtering and publishing operations be performed.
- Detector2D.detection_confidence_threshold
A confidence threshold for detecting common objects, and a detection result is considered credible only if it is higher than this threshold. A low setting of this threshold may cause the semantic object metric map to detect the wrong target. Setting it too high may result in difficulty in acquiring some targets that are not easily discernible. Therefore it needs to be set according to the environment. There is a strong relationship with the current detection model.
- Detector2D.dynamic_detection_confidence_threshold
Confidence threshold when detecting dynamic objects, and the detection result is considered credible only if it is higher than this threshold. The reason for this threshold being set low is that dynamic objects have a greater negative impact on system tracking and map building. Therefore the detection results of dynamic objects need to be trusted as much as possible.
The code is located in the RmDynamicPointWithSemanticAndGeometry function of Frame.cc
The problem that some octree maps would "disappear" when Octomap built a map in the last version has been solved (rewritten the code of topic publishing function for point cloud and tf information).
Specific problem descriptions can be found at,
https://answers.ros.org/question/51837/octomap_server-globally-referenced-pointcloud-and-transform/