This course aims to put together everything you need to know to become a Junior Developer. The internet is an invaluable, exhaustive - but sometimes exhausting resource for learning how to code. I will try to make this journey less daunting for you by stringing together excellent and relevant teaching resources from the internet, as well as explanations for their relevance.
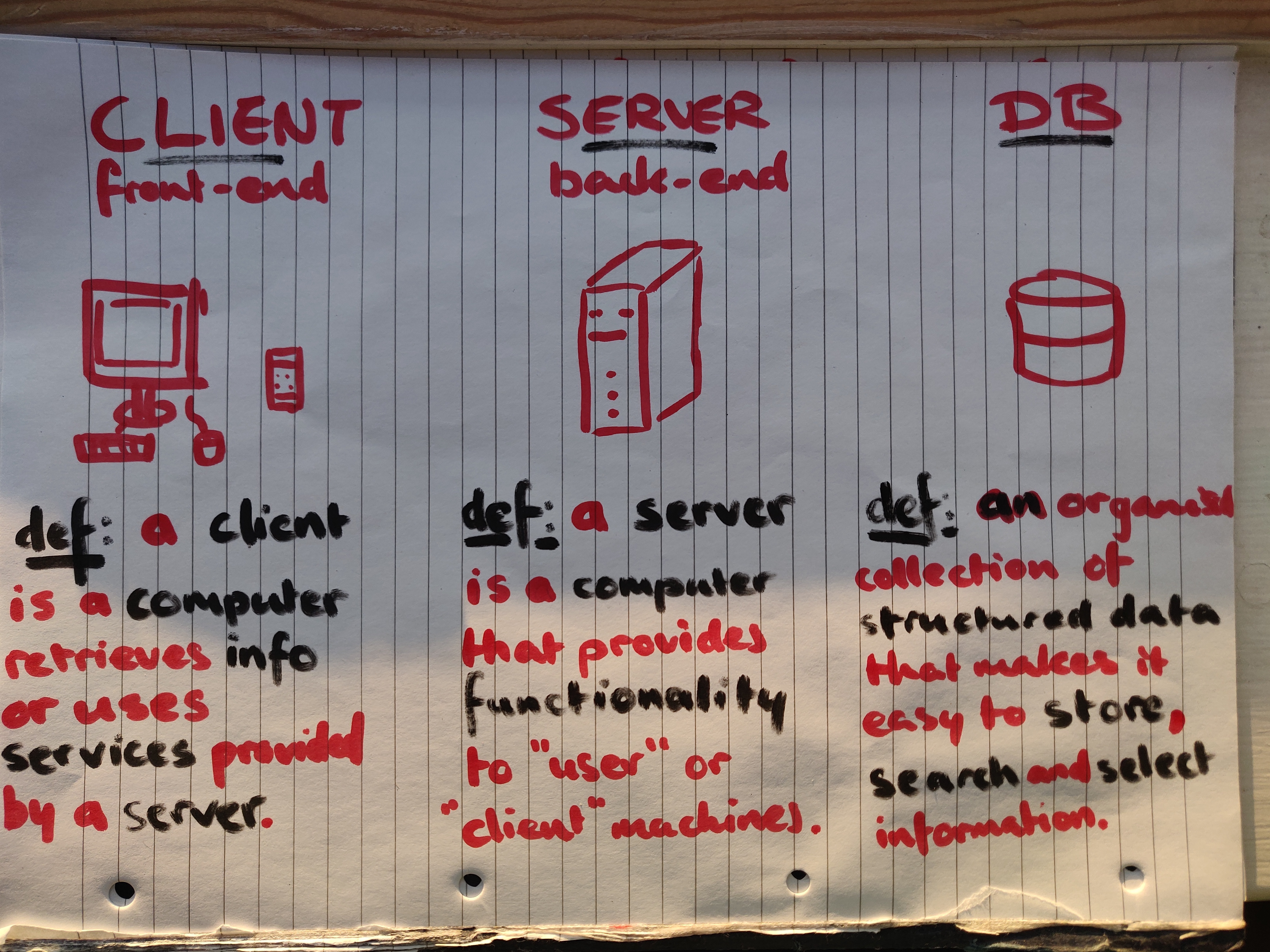
At a very simple level, programming can be separated into three basic areas. Databases, the BackEnd, and the FrontEnd.
Databases store organised information, and can be imagined a bit like a table or an excel spreadsheet. It runs on a server remote from the User's device.
The BackEnd handles this data, and the user's input. It also runs on a server remote from the User's device.
The FrontEnd part of an app is what displays the information to the viewer, and runs on the client (browser or mobile device).
Even if your have a preference for a certain area of coding, and intend to specialise in one area exclusively, at this stage learning the foundation of each area still has value. Seeing how they work together will give you an end to end understanding of how websites and apps work, and will help you write code that coordinates better with the rest of the website/app.
-
- Terminal
- Git
- Testing
-
- Flask (Python)
- Express/Node.js (javascript)
-
- SQL
- Firebase
-
- HTML/CSS
- React.js (javascript)
This site will help you install Git on your machine and get you on your way to creating, cloning, and updating repositories: https://help.github.com/en/articles/set-up-git.
Git is an example of 'Version Control', which is used to make and track changes to source code in software development. Using Git is a bit like saving your progress in a video game. It also allows for many developers to make and review changes to the same source code, which is invaluable in industry.
git clone- Clones a repository into the current directory.git status- See what files have been changed since the last commit, and have been added to the current one. Changed files are listed in red, files added to the current commit will be in green.git diff- See a side-by-side list of all the code changes made since the last commit.git add <filename>orgit add .- either add a specific edited file, or all edited files to the current commit.git commit -m "your message"- add a message to your current commit.git push- push up your most recent commit to GitHub.git pull- pull down all the most recent changes made to the repo.git log- see a list of all your commits, in chronological order.
Terminals, also known as command lines or consoles, allow us to accomplish and automate tasks on a computer without the use of a graphical user interface.
The Terminal is a way to control your computer using just text. It lets you run commands that are far more powerful than anything a GUI can do for you.
Essentially, a text editor is a program on you computer that allows you to create and edit a range of programming language files. This is the place where you write your code! Examples include Atom, VSCode, PyCharm, and many, many more. For the time being Atom is a great one to get started with.
We're using Python because as a language it's easier to pick up. Compared to languages like Javascript, Java and C, it is easier to read and write and has a lower barrier to entry. Another advantage in learning Python here is that it's the more industry ready language. I've seen a lot of companies rely on Python, and it's a great language for Data Science, so learning it now sets you up to learn more about both software development now, and Data Science in future.
- CodeCademy: https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-python: At the moment the Python 2 course is free. Although there are some pay-walled 'Pro' sections, ignore these. This is just to get started with some of the starting principles of programming, so whizz through the exercises and don't worry about remembering everything - you'll repeat these concepts over and over again and they will get hammered into your brain. If you're stuck for longer than an hour look up the solution or reach out. Why CodeCademy? You want to programme! CodeCademy lets you write, run, and debug code in the browser. It's a great way to get started with minimal effort.
- Learn Python The Hard Way: https://learnpythonthehardway.org/python3/ This resource is fantastic - it will give you a thorough breakdown of how to use the Terminal, as well as a solid grounding in the basics of Python.
- Python Koans: https://github.com/gregmalcolm/python_koans This is another run-through of some Python fundamentals, as well a gentle introduction to using tests.
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets with an emphasis placed on “Style.” While HTML is used to structure a web document (defining things like headlines and paragraphs, and allowing you to embed images, video, and other media), CSS comes through and specifies your document’s style—page layouts, colors, and fonts are all determined with CSS. Think of HTML as the foundation (every house has one), and CSS as the aesthetic choices (there’s a big difference between a Victorian mansion and a mid-century modern home).
- w3schools HTML: https://www.w3schools.com/html/default.asp
- w3schools CSS: https://www.w3schools.com/css/default.asp
- CodeCademy HTML & CSS:
- https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-html
- https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-css
- https://www.codecademy.com/learn/make-a-website
When the web was invented people were unsure of it was was going to do exactly. They new it needed to hold information and could send information but they weren't sure what kind of information it would send. The first major thing for the web was HTML of Hyper Text Markup Language. This HTML let people make text and link to it. Then people though... you know what would make this better. Pictures! So they added pictures and it was better. But then people wanted the pages to do other things... for example have a page automatically go to another page (Like redirect the page.) or to allow the user to type number in a box and get their sum like a calculator. So they made JavaScript.
However, it's been many years since the birth of JavaScript, and the language has grown. Nowadays it is the core language behind a lot of front-end design frameworks, like React and Angular. It can also be used in back-end and server development, through frameworks like Node and Express. Because of its versatility, it's almost everywhere in industry, and learning the language now not only adds a powerful tool to your kit, but it also prepares you to be able to start building apps and websites.