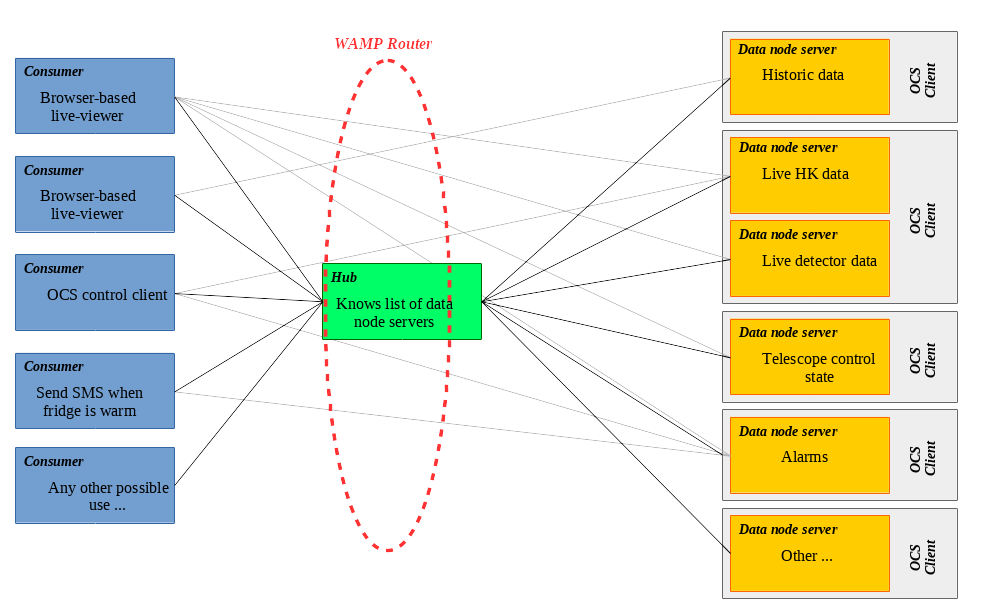
Sisock is a suite of software for serving Simons Observatory data over websockets.
The key components are:
- A WAMP server — This runs on just one computer; all data are routed through it.
- Data node servers — These can be spread across the internet, located on machines from which data are to be served (data nodes).
- A hub — The hub keeps track of which data node servers are online. Only one hub is run, by default on the computer running the WAMP server).
- Consumers — These are clients that request data from data node
servers. They connect to the hub in order to know which data node servers are
available and how to access them.
- The
components/grafana_serveris an example of a consumer. It reads data viasisockand then passes it to Grafana over HTTP.
- The
The following diagram illustrates the above:
First, we need to set up the crossbar configuration. For this, you need access to the ocs-site-configs repository.
Everything you need to do to run sisock can be done from the templates
directory of this ocs-site-configs repo; if you are modifying anything for
local development, you can make a copy of this directory elsewhere.
Important: if you make a copy of these files, for security reasons do not do it in the root directory of your sisock clone, since it will put the encryption certificates in your docker image. This is not necessarily a problem on your local machine, but would compromise security if the image gets pushed to the public DockerHub.
A default configuration can be found in the templates directory.
You will need first to run setup_tls.py to generate encryption certificates in
templates/.crossbar
Important: the ‘common name’ (CN) of the certificate should be
localhostif you are doing local development, or else the hostname of your server if you are in production mode and will be serving over the internet. The certificates will be rejected if their CN does not match the real-life hostname. You will have to modify the above script if you do not wantlocalhost. Seetemplates/.crossbar/README.mdfor instructions on manually generating the certificates.
The .crossbar/config.json file should work out of the box, but advanced users
can tweak settings as they see fit.
You will need to have docker and docker-compose installed on your system.
There are plenty of websites online that give instructions on how to do so, but
$ pip install docker docker-composeshould do the trick.
We will presume that you want to do local development in the following instructions.
If not, instead of using
templates/docker-compose_dev-mode.yamlfromocs-site-configs, you could usetemplates/docker-compose.yaml. In this case, you actually don't need any of thesisockcode locally, since it pulls all the docker images fromgrumpy.physics.yale.edu: see below for how to access images from this computer.
Sisock is normally run in docker containers using docker-compose. You will
need to create a YAML file for configuring this. Again, you can find an example
in the ocs-site-configs in
templates/docker-compose_dev-mode.yaml.
If you want to use this file ‘out of the box’, define the following environment variable:
SISOCK_DIRto point to the root of yoursisockclone.
You can also customise which ports are used for various services, though the default values are probably fine on most machines.
SISOCK_SQL_PORT(default = 3308; chosen in order not to conflict with 3306 if you are already running an SQL server).SISOCK_HTTP_PORT(default = 5000)SISOCK_GRAFANA_PORT(default = 3000)
Additionally, if you want to use certain data node servers that read data from your local disc, you should also define:
- For
g3-reader, define${SISOCK_HK_DIR}. - For
radiometer-server, define${SISOCK_RADIOMETER_DIR}. - For
apex-weather-server, define${SISOCK_APEX_DIR}.
The g3_reader data node server uses the so3g library, whose image is pulled
by components/g3_file_scanner/Dockerfile. By default, this image is pulled
from grumpy at Yale. You will need to do the following to enable this:
$ docker login grumpy.physics.yale.eduThe username/password is a SO standard: ask Brian Koopman if you don't know it.
Alternatively, you can create your own image locally and alter
components/g3file_scanner/Dockerfile as appropriate.
If it doesn't yet exist, create the overarching network for the system:
$ docker network create --driver bridge sisock-netTo run all the services, simply do:
$ docker-compose upNote that this and all subsequent
docker-composecommands assume your YAML file is nameddocker-compose.yaml. If you are using the out-of-the-box configuration fromocs-site-configs, use the-fflag to specify the filename.
Or, you can select which services listed in docker-compose.yaml you want to
run. For instance, the following is a nice, minimal check that things are
working:
$ docker-compose up grafana sisock-http sensors-serverThe commands above attach the
stdoutof all the containers to your terminal; you can terminate with good ol' ctrl-c. This mode is helpful for debugging. However, if you'd like to background this, throw the-dflag.
Grafana should now be running: access it at localhost:3000. You'll need to
configure the Grafana data source as the SimpleJson type with a URL of
http://sisock-http:5000. (The user defined bridge network, sisock-net,
enables DNS resolution by container name, in this case sisock-http, as is
defined in the docker-compose.yaml file.)
If you make modifications to the code, docker-compose up won't automatically
update the images. You will need to do this yourself with docker-compose build. For instance, if you were working on the code in
components/data_node_servers/sensors/, you would do:
$ docker-compose build sensors-serverTo rebuild all the images (normally not necessary), just do:
$ docker-compose buildTo shutdown and cleanup, run:
$ docker-compose downIf you'd like to remove the images as well run:
$ docker-compose down --rmi allThis will not remove sisock-net. To do so:
$ docker network rm sisock-netFurthermore, if you really don't want your saved grafana configuration, you can remove the grafana-storage container:
$ docker volume rm grafana-storageThis project is licensed under the BSD 2-Clause License - see the LICENSE.txt file for details.